About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 16 results exploitation clear search
Using Agent-Based Modelling and Reinforcement Learning to Study Hybrid Threats
kpadur | Published Friday, September 20, 2024Hybrid attacks coordinate the exploitation of vulnerabilities across domains to undermine trust in authorities and cause social unrest. Whilst such attacks have primarily been seen in active conflict zones, there is growing concern about the potential harm that can be caused by hybrid attacks more generally and a desire to discover how better to identify and react to them. In addressing such threats, it is important to be able to identify and understand an adversary’s behaviour. Game theory is the approach predominantly used in security and defence literature for this purpose. However, the underlying rationality assumption, the equilibrium concept of game theory, as well as the need to make simplifying assumptions can limit its use in the study of emerging threats. To study hybrid threats, we present a novel agent-based model in which, for the first time, agents use reinforcement learning to inform their decisions. This model allows us to investigate the behavioural strategies of threat agents with hybrid attack capabilities as well as their broader impact on the behaviours and opinions of other agents.
Peer reviewed An IBM of a fishing fleet exploiting a pelagic resource and with a fisher management system. A preliminary version.
Paul Hart | Published Tuesday, March 19, 2024A fisher directed management system was describeded by Hart (2021). It was proposed that fishers should only be allowed to exploit a resource if they collaborated in a resource management system for which they would own and be collectively responsible for. As part of the system fishers would need to follow the rules of exploitation set by the group and provide a central unit with data with which to monitor the fishery. Any fisher not following the rules would at first be fined but eventually expelled from the fishery if he/she continued to act selfishly. This version of the model establishes the dynamics of a fleet of vessels and controls overfishing by imposing fines on fishers whose income is low and who are tempted to keep fishing beyond the set quota which is established each year depending on the abundance of the fish stock. This version will later be elaborated to have interactions between the fishers including pressure to comply with the norms set by the group and which could lead to a stable management system.
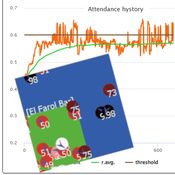
Peer reviewed Flibs’NFarol: Self-Organized Efficiency and Fairness Emergence in an Evolutive Game
Cosimo Leuci | Published Thursday, October 12, 2023According to the philosopher of science K. Popper “All life is problem solving”. Genetic algorithms aim to leverage Darwinian selection, a fundamental mechanism of biological evolution, so as to tackle various engineering challenges.
Flibs’NFarol is an Agent Based Model that embodies a genetic algorithm applied to the inherently ill-defined “El Farol Bar” problem. Within this context, a group of agents operates under bounded rationality conditions, giving rise to processes of self-organization involving, in the first place, efficiency in the exploitation of available resources. Over time, the attention of scholars has shifted to equity in resource distribution, as well. Nowadays, the problem is recognized as paradigmatic within studies of complex evolutionary systems.
Flibs’NFarol provides a platform to explore and evaluate factors influencing self-organized efficiency and fairness. The model represents agents as finite automata, known as “flibs,” and offers flexibility in modifying the number of internal flibs states, which directly affects their behaviour patterns and, ultimately, the diversity within populations and the complexity of the system.
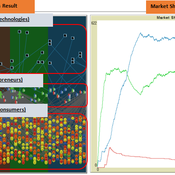
The simulation on the study of the optimal business strategy with the interaction between technologies and consumers.
sej-yoo | Published Monday, June 27, 2022 | Last modified Monday, July 04, 2022HOW IT WORKS
This model consists of three agents, and each agent type operates per business theories as below.
a. New technologies(Tech): It evolves per sustaining or disruptive technology trajectory with the constraint of project management triangle (Scope, Time, Quality, and Cost).
b. Entrepreneurs(Entre): It builds up the solution by combining Tech components per its own strategy (Exploration, Exploitation, or Ambidex).
c. Consumer(Consumer): It selects the solution per its own preference due to Diffusion of innovation theory (Innovators, Early Adopters, Early Majority, Late Majority, Laggards)
…
The conditional defector strategy can violate the most crucial supporting mechanisms of cooperation.
Ahmed Ibrahim | Published Tuesday, June 07, 2022 | Last modified Sunday, September 28, 2025Cooperation is essential for all domains of life. Yet, ironically, it is intrinsically vulnerable to exploitation by cheats. Hence, an explanatory necessity spurs many evolutionary biologists to search for mechanisms that could support cooperation. In general, cooperation can emerge and be maintained when cooperators are sufficiently interacting with themselves. This communication provides a kind of assortment and reciprocity. The most crucial and common mechanisms to achieve that task are kin selection, spatial structure, and enforcement (punishment). Here, we used agent-based simulation models to investigate these pivotal mechanisms against conditional defector strategies. We concluded that the latter could easily violate the former and take over the population. This surprising outcome may urge us to rethink the evolution of cooperation, as it illustrates that maintaining cooperation may be more difficult than previously thought. Moreover, empirical applications may support these theoretical findings, such as invading the cooperator population of pathogens by genetically engineered conditional defectors, which could be a potential therapy for many incurable diseases.
The Effect of Individual and Collective Characteristics on Team Performance: A Model of Networked Agents Engaged in Collective Problem Solving
Amin Boroomand | Published Tuesday, March 16, 2021 | Last modified Monday, July 26, 2021This code is for an agent-based model of collective problem solving in which agents with different behavior strategies, explore the NK landscape while they communicate with their peers agents. This model is based on the famous work of Lazer, D., & Friedman, A. (2007), The network structure of exploration and exploitation.
Peer reviewed FishMob: Interactions between fisher mobility and spatial resource heterogeneity
Emilie Lindkvist | Published Wednesday, October 16, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, June 23, 2020Migration or other long-distance movement into other regions is a common strategy of fishers and fishworkers living and working on the coast to adapt to environmental change. This model attempts to understand the general dynamics of fisher mobility for over larger spatial scales. The model can be used for investigating the complex interplay that exists between mobility and fish stock heterogeneity across regions, and the associated outcomes of mobility at the system level.
The model design informed by the example of small-scale fisheries in the Gulf of California, Mexico but implements theoretical and stylized facts and can as such be used for different archetypical cases. Our methodological approach for designing the model aims to account for the complex causation, emergence and interdependencies in small-scale fisheries to explain the phenomenon of sequential overexploitation, i.e., overexploiting one resource after another. The model is intended to be used as a virtual laboratory to investigate when and how different levels of mobile fishers affect exploitation patterns of fisheries resources.
Exploration and Exploitation: Persistence with local exploration under varying resource distribution, resource availability over time and cost of relocation
Arpan Jani | Published Monday, September 30, 2019Organisms, Individuals and Organizations face the dilemma of exploration vs. exploitation
Identifying the optimal trade-off between the two is a challenge
Too much exploration (e.g. gaining new knowledge) can be detrimental to day-to-day survival and too much exploitation (applying existing knowledge) could be detrimental to long term survival esp. if conditions change over time
The purpose of the model is to investigate how the amount of resources acquired (wealth/success) is related to persistence with the strategy of local exploration under different resource distributions, availability of resources over time and cost of relocation
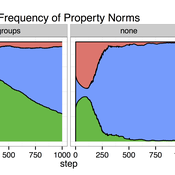
Cultural Group Selection of Sustainable Institutions
Timothy Waring Paul Smaldino Sandra H Goff | Published Wednesday, June 10, 2015 | Last modified Tuesday, August 04, 2015We develop a spatial, evolutionary model of the endogenous formation and dissolution of groups using a renewable common pool resource. We use this foundation to measure the evolutionary pressures at different organizational levels.
Peer reviewed Simple Coastal Exploitation in the American Samoa
Chloe Atwater | Published Wednesday, November 05, 2014This model employs optimal foraging theory principles to generate predictions of which coastal habitats are exploited in climatically stable versus variable environments, using the American Samoa as a study area.
Displaying 10 of 16 results exploitation clear search