About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 12 results genetic algorithm clear search
Social Construction of Reality Agent-Based Model
Manuel Castañón-Puga E. Dante Suarez Loren Demerath | Published Saturday, June 29, 2024This model illustrates the processes underlying the social construction of reality through an agent-based genetic algorithm. By simulating the interactions of agents within a structured environment, we have demonstrated how shared information and popularity contribute to the formation of emergent social structures with diverse cultures. The model illustrates how agents balance environmentally valid information with socially reliable information. It also highlights how social interaction leads to the formation of stable, yet diverse, social groups.
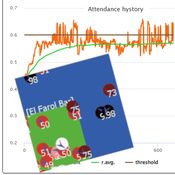
Peer reviewed Flibs’NFarol: Self-Organized Efficiency and Fairness Emergence in an Evolutive Game
Cosimo Leuci | Published Thursday, October 12, 2023According to the philosopher of science K. Popper “All life is problem solving”. Genetic algorithms aim to leverage Darwinian selection, a fundamental mechanism of biological evolution, so as to tackle various engineering challenges.
Flibs’NFarol is an Agent Based Model that embodies a genetic algorithm applied to the inherently ill-defined “El Farol Bar” problem. Within this context, a group of agents operates under bounded rationality conditions, giving rise to processes of self-organization involving, in the first place, efficiency in the exploitation of available resources. Over time, the attention of scholars has shifted to equity in resource distribution, as well. Nowadays, the problem is recognized as paradigmatic within studies of complex evolutionary systems.
Flibs’NFarol provides a platform to explore and evaluate factors influencing self-organized efficiency and fairness. The model represents agents as finite automata, known as “flibs,” and offers flexibility in modifying the number of internal flibs states, which directly affects their behaviour patterns and, ultimately, the diversity within populations and the complexity of the system.
NeoCOOP: The Neolithic Cooperation Model
Brandon Gower-Winter | Published Saturday, February 11, 2023NeoCOOP is an iteration-based ABM that uses Reinforcement Learning and Artificial Evolution as adaptive-mechanisms to simulate the emergence of resource trading beliefs among Neolithic-inspired households.
Peer reviewed Evolutionary Economic Learning Simulation: A Genetic Algorithm for Dynamic 2x2 Strategic-Form Games in Python
Vinicius Ferraz Thomas Pitz | Published Friday, April 08, 2022This project combines game theory and genetic algorithms in a simulation model for evolutionary learning and strategic behavior. It is often observed in the real world that strategic scenarios change over time, and deciding agents need to adapt to new information and environmental structures. Yet, game theory models often focus on static games, even for dynamic and temporal analyses. This simulation model introduces a heuristic procedure that enables these changes in strategic scenarios with Genetic Algorithms. Using normalized 2x2 strategic-form games as input, computational agents can interact and make decisions using three pre-defined decision rules: Nash Equilibrium, Hurwicz Rule, and Random. The games then are allowed to change over time as a function of the agent’s behavior through crossover and mutation. As a result, strategic behavior can be modeled in several simulated scenarios, and their impacts and outcomes can be analyzed, potentially transforming conflictual situations into harmony.
Large-scale land acqusitions and smallholder food security
Tim Williams | Published Thursday, September 16, 2021Large-scale land acquisitions (LSLAs) threaten smallholder livelihoods globally. Despite more than a decade of research on the LSLA phenomenon, it remains a challenge to identify governance conditions that may foster beneficial outcomes for both smallholders and investors. One potentially promising strategy toward this end is contract farming (CF), which more directly involves smallholder households in commodity production than conditions of acquisition and displacement.
To improve understanding of how CF may mediate the outcomes of LSLAs, we developed an agent-based model of smallholder livelihoods, which we used as a virtual laboratory to experiment on a range of hypothetical LSLA and CF implementation scenarios.
The model represents a community of smallholder households in a mixed crop-livestock system. Each agent farms their own land and manages a herd of livestock. Agents can also engage in off-farm employment, for which they earn a fixed wage and compete for a limited number of jobs. The principal model outputs include measures of household food security (representing access to a single, staple food crop) and agricultural production (of a single, staple food crop).
…
HyperMu’NmGA - Effect of Hypermutation Cycles in a NetLogo Minimal Genetic Algorithm
Cosimo Leuci | Published Tuesday, October 27, 2020 | Last modified Sunday, July 31, 2022A minimal genetic algorithm was previously developed in order to solve an elementary arithmetic problem. It has been modified to explore the effect of a mutator gene and the consequent entrance into a hypermutation state. The phenomenon seems relevant in some types of tumorigenesis and in a more general way, in cells and tissues submitted to chronic sublethal environmental or genomic stress.
For a long time, some scholars suppose that organisms speed up their own evolution by varying mutation rate, but evolutionary biologists are not convinced that evolution can select a mechanism promoting more (often harmful) mutations looking forward to an environmental challenge.
The model aims to shed light on these controversial points of view and it provides also the features required to check the role of sex and genetic recombination in the mutator genes diffusion.
Peer reviewed Flibs'NLogo - An elementary form of evolutionary cognition
Cosimo Leuci | Published Thursday, January 30, 2020Flibs’NLogo implements in NetLogo modelling environment, a genetic algorithm whose purpose is evolving a perfect predictor from a pool of digital creatures constituted by finite automata or flibs (finite living blobs) that are the agents of the model. The project is based on the structure described by Alexander K. Dewdney in “Exploring the field of genetic algorithms in a primordial computer sea full of flibs” from the vintage Scientific American column “Computer Recreations”
As Dewdney summarized: “Flibs […] attempt to predict changes in their environment. In the primordial computer soup, during each generation, the best predictor crosses chromosomes with a randomly selected flib. Increasingly accurate predictors evolve until a perfect one emerges. A flib […] has a finite number of states, and for each signal it receives (a 0 or a 1) it sends a signal and enters a new state. The signal sent by a flib during each cycle of operation is its prediction of the next signal to be received from the environment”
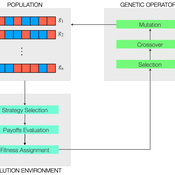
Peer reviewed MGA - Minimal Genetic Algorithm
Cosimo Leuci | Published Tuesday, September 03, 2019 | Last modified Thursday, January 30, 2020Genetic algorithms try to solve a computational problem following some principles of organic evolution. This model has educational purposes; it can give us an answer to the simple arithmetic problem on how to find the highest natural number composed by a given number of digits. We approach the task using a genetic algorithm, where the candidate solutions to the problem are represented by agents, that in logo programming environment are usually known as “turtles”.
Agent-Based Computational Modeling of Cryptocurrency Design
Felix Ude | Published Friday, June 28, 2019Agent-Based Computational Model of the cryptocurrency Bitcoin with a realistic market and transaction system. Bitcoin’s transaction limit (i.e. block size) and Bitcoin generation can be calibrated and optimized for wealth and network’s hashing power by the Non-Dominated Sorted Genetic Algorithm - II.
An adaptive model of homing pigeons: A genetic algorithm approach
Gudrun Wallentin Francis Oloo | Published Friday, January 27, 2017In this model, we simulate the navigation behavior of homing pigeons. Specifically we use genetic algorithms to optimize the navigation and flocking parameters of pigeon agents.
Displaying 10 of 12 results genetic algorithm clear search