About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 131 results for "Crooks Andrew" clear search
Benchmark for DMASON
Andreu Moreno Vendrell Josep Jorba Eduardo César Anna Sikora Cristina Peralta Quesada | Published Friday, November 22, 2024Agent-based modeling and simulation (ABMS) is a class of computational models for simulating the actions and interactions of autonomous agents with the goal of assessing their effects on a system as a whole. Several frameworks for generating parallel ABMS applications have been developed taking advantage of their common characteristics, but there is a lack of a general benchmark for comparing the performance of generated applications. We propose and design a benchmark that takes into consideration the most common characteristics of this type of applications and includes parameters for influencing their relevant performance aspects. We provide an initial implementation of the benchmark for DMASON parallel ABMS platform, and we use it for comparing the applications generated by these platforms.
AMBAWA, an Agent-based Model of Biomass flows in Agropastoral areas of West Africa
Christophe Le Page Tidiane Diarisso Nadine Andrieu Marc Corbeels François Bousquet Pablo Tittonell David Berre | Published Monday, November 23, 2015 | Last modified Sunday, April 12, 2020AMBAWA simulates the flows of biomass between crop and livestock systems at the field, farm, and village scales in order to showcase innovating management practices of soil fertility in West Africa.
Simulating Knowledge Dynamics in Innovation Networks
Nigel Gilbert | Published Wednesday, March 03, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 20133.8 with Unis
Peer reviewed Gregarious Behavior, Human Colonization and Social Differentiation Agent-Based Model
Gert Jan Hofstede Mark R Kramer Sebastian Fajardo Andrés Bernal Martijn de Vries | Published Thursday, August 20, 2020 | Last modified Thursday, October 29, 2020Studies of colonization processes in past human societies often use a standard population model in which population is represented as a single quantity. Real populations in these processes, however, are structured with internal classes or stages, and classes are sometimes created based on social differentiation. In this present work, information about the colonization of old Providence Island was used to create an agent-based model of the colonization process in a heterogeneous environment for a population with social differentiation. Agents were socially divided into two classes and modeled with dissimilar spatial clustering preferences. The model and simulations assessed the importance of gregarious behavior for colonization processes conducted in heterogeneous environments by socially-differentiated populations. Results suggest that in these conditions, the colonization process starts with an agent cluster in the largest and most suitable area. The spatial distribution of agents maintained a tendency toward randomness as simulation time increased, even when gregariousness values increased. The most conspicuous effects in agent clustering were produced by the initial conditions and behavioral adaptations that increased the agent capacity to access more resources and the likelihood of gregariousness. The approach presented here could be used to analyze past human colonization events or support long-term conceptual design of future human colonization processes with small social formations into unfamiliar and uninhabited environments.
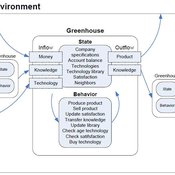
Universal Darwinism in Dutch Greenhouses
Julia Kasmire | Published Wednesday, May 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An ABM, derived from a case study and a series of surveys with greenhouse growers in the Westland, Netherlands. Experiments using this model showshow that the greenhouse horticulture industry displays diversity, adaptive complexity and an uneven distribution, which all suggest that the industry is an evolving system.
Socio-hydrologicalModel_version_SESMO
Marco Janssen Andres Baeza-Castro Paola Gomez Luis Bojorquez Fidel Serrano-Candela Hallie Eakin Yosune Miquelajauregui Rodrigo Garcia-Herrera | Published Tuesday, February 05, 2019We present here MEGADAPT_SESMO model. A hybrid, dynamic, spatially explicit, integrated model to simulate the vulnerability of urban coupled socio-ecological systems – in our case, the vulnerability of Mexico City to socio-hydrological risk.
Peer reviewed Descriptive Norm and Fraud Dynamics
Alexandra Eckert Matthias Meyer Christian Stindt | Published Tuesday, January 07, 2025The “Descriptive Norm and Fraud Dynamics” model demonstrates how fraudulent behavior can either proliferate or be contained within non-hierarchical organizations, such as peer networks, through social influence taking the form of a descriptive norm. This model expands on the fraud triangle theory, which posits that an individual must concurrently possess a financial motive, perceive an opportunity, and hold a pro-fraud attitude to engage in fraudulent activities (red agent). In the absence of any of these elements, the individual will act honestly (green agent).
The model explores variations in a descriptive norm mechanism, ranging from local distorted knowledge to global perfect knowledge. In the case of local distorted knowledge, agents primarily rely on information from their first-degree colleagues. This knowledge is often distorted because agents are slow to update their empirical expectations, which are only partially revised after one-to-one interactions. On the other end of the spectrum, local perfect knowledge is achieved by incorporating a secondary source of information into the agents’ decision-making process. Here, accurate information provided by an observer is used to update empirical expectations.
The model shows that the same variation of the descriptive norm mechanism could lead to varying aggregate fraud levels across different fraud categories. Two empirically measured norm sensitivity distributions associated with different fraud categories can be selected into the model to see the different aggregate outcomes.
Myside Bias and Group Discussion
Edoardo Baccini | Published Monday, November 14, 2022 | Last modified Tuesday, September 05, 2023The my-side bias is a well-documented cognitive bias in the evaluation of arguments, in which reasoners in a discussion tend to overvalue arguments that confirm their prior beliefs, while undervaluing arguments that attack their prior beliefs. This agent-based model in Netlogo simulates a group discussion among myside-biased agents, within a Bayesian setting. This model is designed to investigate the effects of the myside bias on the ability of groups to reach a consensus or collectively track the correct answer to a given binary issue.
Peer reviewed Neighbor Influenced Energy Retrofit (NIER) agent-based model
Eric Boria | Published Friday, April 03, 2020The NIER model is intended to add qualitative variables of building owner types and peer group scales to existing energy efficiency retrofit adoption models. The model was developed through a combined methodology with qualitative research, which included interviews with key stakeholders in Cleveland, Ohio and Detroit and Grand Rapids, Michigan. The concepts that the NIER model adds to traditional economic feasibility studies of energy retrofit decision-making are differences in building owner types (reflecting strategies for managing buildings) and peer group scale (neighborhoods of various sizes and large-scale Districts). Insights from the NIER model include: large peer group comparisons can quickly raise the average energy efficiency values of Leader and Conformist building owner types, but leave Stigma-avoider owner types as unmotivated to retrofit; policy interventions such as upgrading buildings to energy-related codes at the point of sale can motivate retrofits among the lowest efficient buildings, which are predominantly represented by the Stigma-avoider type of owner; small neighborhood peer groups can successfully amplify normal retrofit incentives.
Peer reviewed FishMob: Interactions between fisher mobility and spatial resource heterogeneity
Emilie Lindkvist | Published Wednesday, October 16, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, June 23, 2020Migration or other long-distance movement into other regions is a common strategy of fishers and fishworkers living and working on the coast to adapt to environmental change. This model attempts to understand the general dynamics of fisher mobility for over larger spatial scales. The model can be used for investigating the complex interplay that exists between mobility and fish stock heterogeneity across regions, and the associated outcomes of mobility at the system level.
The model design informed by the example of small-scale fisheries in the Gulf of California, Mexico but implements theoretical and stylized facts and can as such be used for different archetypical cases. Our methodological approach for designing the model aims to account for the complex causation, emergence and interdependencies in small-scale fisheries to explain the phenomenon of sequential overexploitation, i.e., overexploiting one resource after another. The model is intended to be used as a virtual laboratory to investigate when and how different levels of mobile fishers affect exploitation patterns of fisheries resources.
Displaying 10 of 131 results for "Crooks Andrew" clear search