About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 24 results livestock clear search
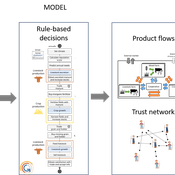
The SAFIRe model : Simulation of Agents for Fertility, Integrated Energy, Food security, and Reforestation
Etienne DELAY Lucas Broutin | Published Thursday, June 12, 2025The SAFIRe model (Simulation of Agents for Fertility, Integrated Energy, Food Security, and Reforestation) is an agent-based model co-developed with rural communities in Senegal’s Groundnut Basin. Its purpose is to explore how local farming and pastoral practices affect the regeneration of Faidherbia albida trees, which are essential for maintaining soil fertility and supporting food security through improved millet production. The model supports collective reflection on how different social and ecological factors interact, particularly around firewood demand, livestock pressure, and agricultural intensification.
The model simulates a 100-hectare agricultural landscape where agents (farmers, shepherds, woodcutters, and supervisors) interact with trees, land parcels, and each other. It incorporates seasonality, crop rotation, tree growth and cutting, livestock feeding behaviors, and farmers’ engagement in sapling protection through Assisted Natural Regeneration (ANR). Two types of surveillance strategies are compared: community-led monitoring and delegated surveillance by forestry authorities. Farmer engagement evolves over time based on peer influence, meeting participation, and the success of visible tree regeneration efforts.
SAFIRe integrates participatory modeling (ComMod and ComExp) and a backcasting approach (ACARDI) to co-produce scenarios rooted in local aspirations. It was explored using the OpenMole platform, allowing stakeholders to test a wide range of future trajectories and analyze the sensitivity of key parameters (e.g., discussion frequency, time in fields). The model’s outcomes not only revealed unexpected insights—such as the hidden role of farmers in tree loss—but also led to real-world actions, including community nursery creation and behavioral shifts toward tree care. SAFIRe illustrates how agent-based modeling can become a tool for social learning and collective action in socio-ecological systems.
Peer reviewed soslivestock model
Marco Janssen Irene Perez Ibarra Diego J. Soler-Navarro Alicia Tenza Peral | Published Wednesday, May 28, 2025 | Last modified Tuesday, June 10, 2025The purpose of this model is to analyze how different management strategies affect the wellbeing, sustainability and resilience of an extensive livestock system under scenarios of climate change and landscape configurations. For this purpose, it simulates one cattle farming system, in which agents (cattle) move through the space using resources (grass). Three farmer profiles are considered: 1) a subsistence farmer that emphasizes self-sufficiency and low costs with limited attention to herd management practices, 2) a commercial farmer focused on profit maximization through efficient production methods, and 3) an environmental farmer that prioritizes conservation of natural resources and animal welfare over profit maximization. These three farmer profiles share the same management strategies to adapt to climate and resource conditions, but differ in their goals and decision-making criteria for when, how, and whether to implement those strategies. This model is based on the SequiaBasalto model (Dieguez Cameroni et al. 2012, 2014, Bommel et al. 2014 and Morales et al. 2015), replicated in NetLogo by Soler-Navarro et al. (2023).
One year is 368 days. Seasons change every 92 days. Each step begins with the growth of grass as a function of climate and season. This is followed by updating the live weight of animals according to the grass height of their patch, and grass consumption, which is determined based on the updated live weight. Animals can be supplemented by the farmer in case of severe drought. After consumption, cows grow and reproduce, and a new grass height is calculated. This updated grass height value becomes the starting grass height for the next day. Cows then move to the next area with the highest grass height. After that, cattle prices are updated and cattle sales are held on the first day of fall. In the event of a severe drought, special sales are held. Finally, at the end of the day, the farm balance and the farmer’s effort are calculated.
MIXTRUST - crop-livestock interactions at regional level
Myriam Grillot Aurélien Peter | Published Tuesday, February 25, 2025 | Last modified Monday, September 01, 2025The basic idea behind developing MIXTRUST was to represent a network of agricultural stakeholders composed of farmers and a cooperative in a mixed landscape to test its performances in response to risks. A mixed landscape here is a landscape where crop and livestock systems interact by the intermediary of material flows of agricultural products. It can be within mixed farms, or between farms, often specialized, (e.g. straw-manure).
Peer reviewed Deforestation
MohammadAli Aghajani | Published Saturday, January 20, 2024 | Last modified Thursday, August 14, 2025Deforestation Simulation Model in NetLogo with GIS Layers
This model has developed in Netlogo software and utilizes
the GIS extension.
This NetLogo-based agent-based model (ABM) simulates deforestation dynamics using the GIS extension. It incorporates parameters like wood extraction, forest regeneration, agricultural expansion, and livestock impact. The model integrates spatial layers, including forest areas, agriculture zones, rural settlements, elevation, slope, and livestock distribution. Outputs include real-time graphical representations of forest loss, regeneration, and land-use changes. This model helps analyze deforestation patterns and conservation strategies using ABM and GIS.
Learning Extension - RAGE RAngeland Grazing Model
Nikita Strelkovskii Cristina I. Apetrei Nikolay Khabarov Valeria Javalera Rincón | Published Saturday, July 22, 2023This is an extension of the original RAGE model (Dressler et al. 2018), where we add learning capabilities to agents, specifically learning-by-doing and social learning (two processes central to adaptive (co-)management).
The extension module is applied to smallholder farmers’ decision-making - here, a pasture (patch) is the private property of the household (agent) placed on it and there is no movement of the households. Households observe the state of the pasture and their neighrbours to make decisions on how many livestock to place on their pasture every year. Three new behavioural types are created (which cannot be combined with the original ones): E-RO (baseline behaviour), E-LBD (learning-by-doing) and E-RO-SL1 (social learning). Similarly to the original model, these three types can be compared regarding long-term social-ecological performance. In addition, a global strategy switching option (corresponding to double-loop learning) allows users to study how behavioural strategies diffuse in a heterogeneous population of learning and non-learning agents.
An important modification of the original model is that extension agents are heterogeneous in how they deal with uncertainty. This is represented by an agent property, called the r-parameter (household-risk-att in the code). The r-parameter is catch-all for various factors that form an agent’s disposition to act in a certain way, such as: uncertainty in the sensing (partial observability of the resource system), noise in the information received, or an inherent characteristic of the agent, for instance, their risk attitude.
Peer reviewed SequiaBasalto model
Marco Janssen Irene Perez Ibarra Pierre Bommel Diego J. Soler-Navarro Alicia Tenza Peral Francisco Dieguez Cameroni | Published Friday, May 26, 2023This is a replication of the SequiaBasalto model, originally built in Cormas by Dieguez Cameroni et al. (2012, 2014, Bommel et al. 2014 and Morales et al. 2015). The model aimed to test various adaptations of livestock producers to the drought phenomenon provoked by climate change. For that purpose, it simulates the behavior of one livestock farm in the Basaltic Region of Uruguay. The model incorporates the price of livestock, fodder and paddocks, as well as the growth of grass as a function of climate and seasons (environmental submodel), the life cycle of animals feeding on the pasture (livestock submodel), and the different strategies used by farmers to manage their livestock (management submodel). The purpose of the model is to analyze to what degree the common management practices used by farmers (i.e., proactive and reactive) to cope with seasonal and interannual climate variations allow to maintain a sustainable livestock production without depleting the natural resources (i.e., pasture). Here, we replicate the environmental and livestock submodel using NetLogo.
One year is 368 days. Seasons change every 92 days. Each day begins with the growth of grass as a function of climate and season. This is followed by updating the live weight of cows according to the grass height of their patch, and grass consumption, which is determined based on the updated live weight. After consumption, cows grow and reproduce, and a new grass height is calculated. Cows then move to the patch with less cows and with the highest grass height. This updated grass height value will be the initial grass height for the next day.
Peer reviewed LUCID: Land Use Competition In Drylands
Birgit Müller Gunnar Dressler Lance Robinson | Published Wednesday, April 12, 2023The Land Use Competition in Drylands (LUCID) model is a stylized agent-based model of a smallholder farming system. Its main purpose is to illustrate how competition between pastoralism and crop cultivation can affect livelihoods of households, specifically their food security. In particular, the model analyzes whether the expansion of crop cultivation may contribute to a vicious circle where an increase in cultivated area leads to higher grazing pressure on the remaining pastureland, which in turn may cause forage shortages and livestock loss for households which are then forced to further expand their cultivated area in order to increase their food security. The model does not attempt to replicate a particular case study but to generate a general understanding of mechanisms and drivers of such vicious circles and to identify possible scenarios under which such circles may be prevented.
The model is inspired by observations of the Borana land use system in Southern Ethiopia. The climatic and ecological conditions of the Borana zone favor pastoralism, and traditionally livelihoods have been based mainly on livestock keeping. Recent years, however, have seen an advancement of crop cultivation as a coping strategy, e.g., to compensate the loss of livestock, even though crop yields are low on average and successful harvests are infrequent.
In the model, it is possible to evaluate patterns of individual (single household) as well as overall (across all households) consumption and food security, depending on a range of ecological, climatic and management parameters.
Peer reviewed Coupled demographic dynamics of herd and household in pastoral systems
Mark Moritz Ian M Hamilton Andrew Yoak Abigail Buffington Chelsea E Hunter Daniel C Peart | Published Saturday, April 08, 2023This purpose of this model is to understand how the coupled demographic dynamics of herds and households constrain the growth of livestock populations in pastoral systems.
Pastoralscape
Matthew Sottile | Published Tuesday, October 12, 2021Pastoralscape is a model of human agents, lifestock health and contageous disease for studying the impact of human decision making in pastoral communities within East Africa on livestock populations. It implements an event-driven agent based model in Python 3.
Large-scale land acqusitions and smallholder food security
Tim Williams | Published Thursday, September 16, 2021Large-scale land acquisitions (LSLAs) threaten smallholder livelihoods globally. Despite more than a decade of research on the LSLA phenomenon, it remains a challenge to identify governance conditions that may foster beneficial outcomes for both smallholders and investors. One potentially promising strategy toward this end is contract farming (CF), which more directly involves smallholder households in commodity production than conditions of acquisition and displacement.
To improve understanding of how CF may mediate the outcomes of LSLAs, we developed an agent-based model of smallholder livelihoods, which we used as a virtual laboratory to experiment on a range of hypothetical LSLA and CF implementation scenarios.
The model represents a community of smallholder households in a mixed crop-livestock system. Each agent farms their own land and manages a herd of livestock. Agents can also engage in off-farm employment, for which they earn a fixed wage and compete for a limited number of jobs. The principal model outputs include measures of household food security (representing access to a single, staple food crop) and agricultural production (of a single, staple food crop).
…
Displaying 10 of 24 results livestock clear search