About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 104 results for "Martijn de Vries" clear search
Peer reviewed Gregarious Behavior, Human Colonization and Social Differentiation Agent-Based Model
Gert Jan Hofstede Mark R Kramer Sebastian Fajardo Andrés Bernal Martijn de Vries | Published Thursday, August 20, 2020 | Last modified Thursday, October 29, 2020Studies of colonization processes in past human societies often use a standard population model in which population is represented as a single quantity. Real populations in these processes, however, are structured with internal classes or stages, and classes are sometimes created based on social differentiation. In this present work, information about the colonization of old Providence Island was used to create an agent-based model of the colonization process in a heterogeneous environment for a population with social differentiation. Agents were socially divided into two classes and modeled with dissimilar spatial clustering preferences. The model and simulations assessed the importance of gregarious behavior for colonization processes conducted in heterogeneous environments by socially-differentiated populations. Results suggest that in these conditions, the colonization process starts with an agent cluster in the largest and most suitable area. The spatial distribution of agents maintained a tendency toward randomness as simulation time increased, even when gregariousness values increased. The most conspicuous effects in agent clustering were produced by the initial conditions and behavioral adaptations that increased the agent capacity to access more resources and the likelihood of gregariousness. The approach presented here could be used to analyze past human colonization events or support long-term conceptual design of future human colonization processes with small social formations into unfamiliar and uninhabited environments.
Simulating Social Interaction in Times of COVID Restrictions
Oscar de Vries | Published Friday, November 17, 2023Social distancing is a strategy to mitigate the spread of contagious disease, but it bears negative impacts on people’s social well-being, resulting in non-compliance. This paper uses an integrated behavioral simulation model, called HUMAT, to identify a sweet spot
that balances strictness of and obedience to social distancing rules.
A novel agent-based model was developed that aims to explore social interaction while it is constrained by visitor limitations (due to Dutch COVID measures). Specifically, the model aims to capture the interaction between the need for social contact and the support for the visitors measure. The model was developed using the HUMAT integrated framework, which offered a psychological and sociological foundation for the behavior of the agents.
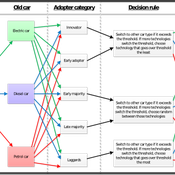
BESTMAP-ABM-DE is an agent-based model to determine the adoption and spatial allocation of selected agri-environmental schemes (AES) by individual farmers in the Mulde River Basin located in Western Saxony, Germany. The selected AES are buffer areas, cover crops, maintaining permanent grassland and conversion of arable land to permanent grassland. While the first three schemes have already been offered in the case study area, the latter scheme is a hypothetical scheme designed to test the impact of potential policy changes. For the first model analyses, only the currently offered schemes are considered. With the model, the effect of different scenarios of policy design on patterns of adoption can be investigated. In particular, the model can be used to study the social-ecological consequences of agricultural policies at different spatial and temporal scales and, in combination with biophysical models, test the ecological implications of different designs of the EU’s Common Agricultural Policy. The model was developed in the BESTMAP project.
Vacunación-Covid Ecuador
Adrian Lara | Published Tuesday, March 22, 2022El modelo a continuación, fue desarrollado para el DATA CHALLENGE 2022. Es un análisis de la información descargada del Portal de datos abiertos de Ecuador. Dentro del modelo podemos realizar una breve exploración de la información así como una simulación respecto al proceso de vacunación en Ecuador.
(De-)Stabilising effect of diffusions
Julia Kasmire Bert Van Meeuwen Cornelis Eikelboom | Published Tuesday, August 11, 2015What is stable: the large but coordinated change during a diffusion or the small but constant and uncoordinated changes during a dynamic equilibrium? This agent-based model of a diffusion creates output that reveal insights for system stability.
MCA-SdA (ABM of mining-community-aquifer interactions in Salar de Atacama, Chile)
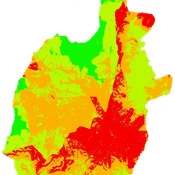
Wenjuan Liu | Published Tuesday, December 01, 2020 | Last modified Thursday, November 04, 2021This model represnts an unique human-aquifer interactions model for the Li-extraction in Salar de Atacama, Chile. It describes the local actors’ experience of mining-induced changes in the socio-ecological system, especially on groundwater changes and social stressors. Social interactions are designed specifically according to a long-term local fieldwork by Babidge et al. (2019, 2020). The groundwater system builds on the FlowLogo model by Castilla-Rho et al. (2015), which was then parameterized and calibrated with local hydrogeological inputs in Salar de Atacama, Chile. The social system of the ABM is defined and customozied based on empirical studies to reflect three major stressors: drought stress, population stress, and mining stress. The model reports evolution of groundwater changes and associated social stress dynamics within the modeled time frame.
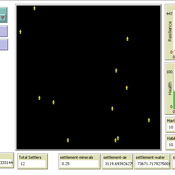
An Agent-Based Model of Space Settlements
Anamaria Berea | Published Wednesday, August 09, 2023 | Last modified Wednesday, November 01, 2023Background: Establishing a human settlement on Mars is an incredibly complex engineering problem. The inhospitable nature of the Martian environment requires any habitat to be largely self-sustaining. Beyond mining a few basic minerals and water, the colonizers will be dependent on Earth resupply and replenishment of necessities via technological means, i.e., splitting Martian water into oxygen for breathing and hydrogen for fuel. Beyond the technical and engineering challenges, future colonists will also face psychological and human behavior challenges.
Objective: Our goal is to better understand the behavioral and psychological interactions of future Martian colonists through an Agent-Based Modeling (ABM simulation) approach. We seek to identify areas of consideration for planning a colony as well as propose a minimum initial population size required to create a stable colony.
Methods: Accounting for engineering and technological limitations, we draw on research regarding high performing teams in isolated and high stress environments (ex: submarines, Arctic exploration, ISS, war) to include the 4 NASA personality types within the ABM. Interactions between agents with different psychological profiles are modeled at the individual level, while global events such as accidents or delays in Earth resupply affect the colony as a whole.
Results: From our multiple simulations and scenarios (up to 28 Earth years), we found that an initial population of 22 was the minimum required to maintain a viable colony size over the long run. We also found that the Agreeable personality type was the one more likely to survive.
Conclusion We developed a simulation with easy to use GUI to explore various scenarios of human interactions (social, labor, economic, psychological) on a future colony on Mars. We included technological and engineering challenges, but our focus is on the behavioral and psychological effects on the sustainability of the colony on the long run. We find, contrary to other literature, that the minimum number of people with all personality types that can lead to a sustainable settlement is in the tens and not hundreds.
Adaptive model of a consumer advice network
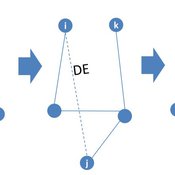
Peng Shao | Published Monday, May 14, 2018In the consumer advice network, users with connections can interact with each other, and the network topology will change during the opinion interaction. When the opinion distance from i to j is greater than the confidence threshold, the two consumers cannot exchange opinions, and the link between them will disconnect with probability DE. Then, a link from node i to node k is established with probability CE and node i learning opinion from node k.
Bayesian Updating Opinion Shared Uncertainty Model.
Johnathan Adams | Published Monday, November 16, 2020 | Last modified Friday, May 14, 2021This is an opinion dynamics model which extends the model found in (Martins 2009). The previous model had an unshared uncertainty assumption in agent-to-agent interaction this model relaxes that assumption. The model only supports a fully connect network where every agent has an equal likelihood of interacting with every other agent at any given time step. The model is highly modular so different social network paradigm can easier be implemented.
Thermostat II
María Pereda Jesús M Zamarreño | Published Thursday, June 12, 2014 | Last modified Monday, June 16, 2014A thermostat is a device that allows to have the temperature in a room near a desire value.
Displaying 10 of 104 results for "Martijn de Vries" clear search