About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 199 results ABM clear search
Selene ABM Suite
ihctdy-f | Published Sunday, January 11, 2026Project Selene ABM Suite
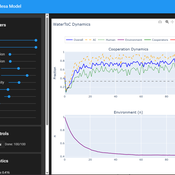
Agent-Based Scenario Exploration for Consortium Cooperation Dynamics
Version: 2.1 (Revised)
Date: January 2026
Status: Exploratory Analysis Tool
Peer reviewed HUMLAND FIRE-IN-THE-HOLE agent-based model
Fulco Scherjon Anastasia Nikulina | Published Monday, October 20, 2025HUMLAND Fire-in-the-Hole is a conceptual agent-based model (ABM) designed to explore the ecological and behavioral consequences of fire-driven hunting strategies employed by hunter-gatherers, specifically Neanderthals, during the Last Interglacial period around the Neumark-Nord (Germany) archaeological site.
This model builds on and specializes the HUMLAND 1.0.0 model (Nikulina et al. 2024), integrating anthropogenic fires, elephant group behavior, and landscape response to simulate interactions between humans, megafauna, and vegetation over time.
Industrial Cooperation and the Hydrogen Transition
Amineh Ghorbani Renske van 't Veer Emre Ates Zofia Lukszo | Published Tuesday, September 23, 2025An Agent Based Model that explores the deployment of hydrogen among a regional industrial cluster in the Netherlands, consisting of 15 companies. The companies seek to decarbonize by replacing their natural gas by hydrogen.
The model integrates technical characteristics as well as company motivations to transition to hydrogen. The baseline model only considers individual investments where company can locally produce hydrogen. If they reach the backbone threshold, companies can also consider buying hydrogen through a connection to the national hydrogen network. The second scenario considers that companies can participate in a joint investment to get an electrolyzer to locally produce the hydrogen.
Two experiments look at the impact of the sectoral configuration and at the impact of subsidy conditions on the region’s hydrogen transition
An agent-based model of scapegoating
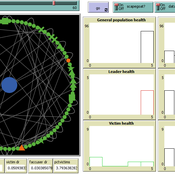
Carlos Paes | Published Thursday, August 28, 2025 | Last modified Thursday, August 28, 2025This agent-based model investigates scapegoating as a social mechanism of crisis management. Inspired by René Girard’s mimetic theory, it simulates how individual tension accumulates and spreads across a small-world network. When tension exceeds certain thresholds, leaders emerge and accuse marginalized agents, who may attempt to transfer blame to substitutes. If scapegoating occurs, collective tension decreases, but victims become isolated while leaders consolidate temporary authority. This simulation provides a conceptual and methodological framework for exploring how collective blame, crisis contagion, and leadership paradoxes emerge in complex networks. It can also be extended with empirical data, such as social media dynamics of online harassment and virtual lynching, offering potential applications for both theoretical research and practical crisis monitoring.
Tragedy of the Commons with Environmental Feedback: A Model of Human-AI Socio-Environmental Water Dilemma
Ivana Malcic Luka Waronig Andrew Crossley | Published Saturday, July 05, 2025 | Last modified Sunday, July 06, 2025This project is an interactive agent-based model simulating consumption of a shared, renewable resource using a game-theoretic framework with environmental feedback. The primary function of this model was to test how resource-use among AI and human agents degrades the environment, and to explore the socio-environmental feedback loops that lead to complex emergent system dynamics. We implemented a classic game theoretic matrix which decides agents´ strategies, and added a feedback loop which switches between strategies in pristine vs degraded environments. This leads to cooperation in bad environments, and defection in good ones.
Despite this use, it can be applicable for a variety of other scenarios including simulating climate disasters, environmental sensitivity to resource consumption, or influence of environmental degradation to agent behaviour.
The ABM was inspired by the Weitz et. al. (2016, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27830651/) use of environmental feedback in their paper, as well as the Demographic Prisoner’s Dilemma on a Grid model (https://mesa.readthedocs.io/stable/examples/advanced/pd_grid.html#demographic-prisoner-s-dilemma-on-a-grid). The main innovation is the added environmental feedback with local resource replenishment.
Beyond its theoretical insights into coevolutionary dynamics, it serves as a versatile tool with several practical applications. For urban planners and policymakers, the model can function as a ”digital sandbox” for testing the impacts of locating high-consumption industrial agents, such as data centers, in proximity to residential communities. It allows for the exploration of different urban densities, and the evaluation of policy interventions—such as taxes on defection or subsidies for cooperation—by directly modifying the agents’ resource consumptions to observe effects on resource health. Furthermore, the model provides a framework for assessing the resilience of such socio-environmental systems to external shocks.
…
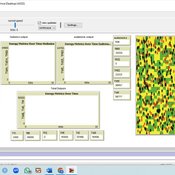
BESTMAP-ABM-DE is an agent-based model to determine the adoption and spatial allocation of selected agri-environmental schemes (AES) by individual farmers in the Mulde River Basin located in Western Saxony, Germany. The selected AES are buffer areas, cover crops, maintaining permanent grassland and conversion of arable land to permanent grassland. While the first three schemes have already been offered in the case study area, the latter scheme is a hypothetical scheme designed to test the impact of potential policy changes. For the first model analyses, only the currently offered schemes are considered. With the model, the effect of different scenarios of policy design on patterns of adoption can be investigated. In particular, the model can be used to study the social-ecological consequences of agricultural policies at different spatial and temporal scales and, in combination with biophysical models, test the ecological implications of different designs of the EU’s Common Agricultural Policy. The model was developed in the BESTMAP project.
This agent-based model (ABM), developed in NetLogo and available on the COMSES repository, simulates a stylized, competitive electricity market to explore the effects of carbon pricing policies under conditions of technological innovation. Unlike traditional models that treat innovation as exogenous, this ABM incorporates endogenous innovation dynamics, allowing clean technology costs to evolve based on cumulative deployment (Wright’s Law) or time (Moore’s Law). Electricity generation companies act as agents, making investment decisions across coal, gas, wind, and solar PV technologies based on expected returns and market conditions. The model evaluates three policy scenarios—No Policy, Emissions Trading System (ETS), and Carbon Tax—within a merit-order market framework. It is partially empirically grounded, using real-world data for technology costs and emissions caps. By capturing emergent system behavior, this model offers a flexible and transparent tool for analyzing the transition to low-carbon electricity systems.
Peer reviewed ABM for Social Cohesion and Wellbeing(ABMSCWB)
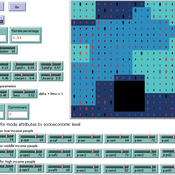
Taseer Salahuddin Hasan Vergil | Published Wednesday, June 25, 2025ABM model studying impact of social cohesion on wellbeing of a society. Ibn Khaldun’s cyclical theory of history is being used as the theoretical lens along with some other theories. Social cohesion is measured as TSC = (TVE + 2 * (TPI * TPL - TNI * TNL))/((TPI+TNI))
Where
TSC total-social-cohesion ; Variable for social cohesion
TPI total-positive-interactions ; Count of positive interactions
TNI total-negative-interactions ; Count of negative interactions
TPL total-positive-learning ; Count of positive learning outcomes
…
A language economics perspective on language spread: Simulating Language Dynamics in a Social Network
Marco Civico | Published Saturday, June 07, 2025This model examines language dynamics within a social network using simulation techniques to represent the interplay of language adoption, social influence, economic incentives, and language policies. The agent-based model (ABM) focuses on interactions between agents endowed with specific linguistic attributes, who engage in communication based on predefined rules. A key feature of our model is the incorporation of network analysis, structuring agent relationships as a dynamic network and leveraging network metrics to capture the evolving inter-agent connections over time. This integrative approach provides nuanced insights into emergent behaviors and system dynamics, offering an analytical framework that extends beyond traditional modeling approaches. By combining agent-based modeling with network analysis, the model sheds light on the underlying mechanisms governing complex language systems and can be effectively paired with sociolinguistic observational data.
Peer reviewed Urban Transport Mode Choices
Kathleen Salazar -Serna Lorena Cadavid Carlos Franco | Published Thursday, May 22, 2025The model represents urban commuters’ transport mode choices among cars, public transit, and motorcycles—a mode highly prevalent in developing countries. Using an agent-based modeling approach, it simulates transport dynamics and serves as a testbed for evaluating policies aimed at improving mobility.
The model simulates an ecosystem of human agents who decide, at each time step, which mode of transportation to use for commuting to work. Their decision is based on a combination of personal satisfaction with their most recent journey—evaluated across a vector of individual needs—the information they crowdsource from their social network, and their personal uncertainty regarding trying new transport options.
Agents are assigned demographic attributes such as sex, age, and income level, and are distributed across city neighborhoods according to their socioeconomic status. To represent social influence in decision-making, agents are connected via a scale-free social network topology, where connections are more likely among agents within the same socioeconomic group, reflecting the tendency of individuals to form social ties with similar others.
…
Displaying 10 of 199 results ABM clear search