About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1252 results Sort by: Recently modified clear search
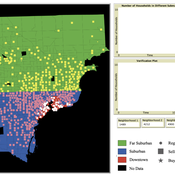
While the world’s total urban population continues to grow, not all cities are witnessing such growth, some are actually shrinking. This shrinkage causes several problems to emerge including population loss, economic depression, vacant properties and the contraction of housing markets. Such problems challenge efforts to make cities sustainable. While there is a growing body of work on study shrinking cities, few explore such a phenomenon from the bottom up using dynamic computational models. To overcome this issue this paper presents an spatially explicit agent-based model stylized on the Detroit Tri-county area, an area witnessing shrinkage. Specifically, the model demonstrates how through the buying and selling of houses can lead to urban shrinkage from the bottom up. The model results indicate that along with the lower level housing transactions being captured, the aggregated level market conditions relating to urban shrinkage are also captured (i.e., the contraction of housing markets). As such, the paper demonstrates the potential of simulation to explore urban shrinkage and potentially offers a means to test polices to achieve urban sustainability.
TunaFisher ABM
Guus Ten Broeke | Published Wednesday, January 13, 2021TunaFisher ABM simulates the decisions of fishing companies and fishing vessels of the Philippine tuna purse seinery operating in the Celebes and Sulu Seas.
High fishing effort remains in many of the world’s fisheries, including the Philippine tuna purse seinery, despite a variety of policies that have been implemented to reduce it. These policies have predominantly focused on models of cause and effect which ignore the possibility that the intended outcomes are altered by social behavior of autonomous agents at lower scales.
This model is a spatially explicit Agent-based Model (ABM) for the Philippine tuna purse seine fishery, specifically designed to include social behavior and to study its effects on fishing effort, fish stock and industry profit. The model includes economic and social factors of decision making by companies and fishing vessels that have been informed by interviews.
…
SimPioN - Simulating Path dependence in inter-organisational Networks
Nanda Wijermans Frithjof Stöppler | Published Monday, January 11, 2021The SimPioN model aims to abstractly reproduce and experiment with the conditions under which a path-dependent process may lead to a (structural) network lock-in in interorganisational networks.
Path dependence theory is constructed around a process argumentation regarding three main elements: a situation of (at least) initially non-ergodic (unpredictable with regard to outcome) starting conditions in a social setting; these become reinforced by the workings of (at least) one positive feedback mechanism that increasingly reduces the scope of conceivable alternative choices; and that process finally results in a situation of lock-in, where any alternatives outside the already adopted options become essentially impossible or too costly to pursue despite (ostensibly) better options theoretically being available.
The purpose of SimPioN is to advance our understanding of lock-ins arising in interorganisational networks based on the network dynamics involving the mechanism of social capital. This mechanism and the lock-ins it may drive have been shown above to produce problematic consequences for firms in terms of a loss of organisational autonomy and strategic flexibility, especially in high-tech knowledge-intensive industries that rely heavily on network organising.
…
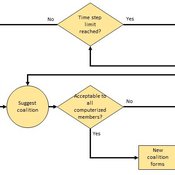
Heuristic Algorithm for Generating Strategic Coalition Structures
Andrew Collins Daniele Vernon-Bido | Published Monday, October 12, 2020The purpose of the model is to generate coalition structures of different glove games, using a specially designed algorithm. The coalition structures can be are later analyzed by comparing them to core partitions of the game used. Core partitions are coalition structures where no subset of players has an incentive to form a new coalition.
The algorithm used in this model is an advancement of the algorithm found in Collins & Frydenlund (2018). It was used used to generate the results in Vernon-Bido & Collins (2021).
VIDA: A simulation model of domestic VIolence in times of social DistAncing
Bernardo Furtado | Published Monday, January 11, 2021Violence against women occurs predominantly in the family and domestic context. The COVID-19 pandemic led Brazil to recommend and, at times, impose social distancing, with the partial closure of economic activities, schools, and restrictions on events and public services. Preliminary evidence shows that intense co- existence increases domestic violence, while social distancing measures may have prevented access to public services and networks, information, and help. We propose an agent-based model (ABM), called VIDA, to illustrate and examine multi-causal factors that influence events that generate violence. A central part of the model is the multi-causal stress indicator, created as a probability trigger of domestic violence occurring within the family environment. Two experimental design tests were performed: (a) absence or presence of the deterrence system of domestic violence against women and measures to increase social distancing. VIDA presents comparative results for metropolitan regions and neighbourhoods considered in the experiments. Results suggest that social distancing measures, particularly those encouraging staying at home, may have increased domestic violence against women by about 10%. VIDA suggests further that more populated areas have comparatively fewer cases per hundred thousand women than less populous capitals or rural areas of urban concentrations. This paper contributes to the literature by formalising, to the best of our knowledge, the first model of domestic violence through agent-based modelling, using empirical detailed socioeconomic, demographic, educational, gender, and race data at the intraurban level (census sectors).
Cascades across networks are sufficient for the formation of echo chambers: An agent-based model
Jan-Philipp Fränken | Published Monday, January 11, 2021An agent-based model of echo chamber formation employing a Bayesian Source Credibility cognitive architecture limiting interactions to a single cascade.
Game of Thrones model
Sean Bergin Claudine Gravel-Miguel | Published Sunday, January 03, 2021 | Last modified Sunday, January 03, 2021This model slowly evolves to become Westeros, with houses fighting for the thrones, and whitewalkers trying to kill all living things. You can download each version to see the evolution of the code, from the Wolf Sheep Predation model to the Game of Thrones model. If you are only interested in the end product, simply download the latest version.
For instructions on each step, see: https://claudinegravelmigu.wixsite.com/got-abm
Ger Grouper
Stefani Crabtree | Published Tuesday, January 05, 2021A “Ger” is a yurt style house used by pastoralists in Mongolia. This model simulates seasonal movements, fission/fusion dynamics, social interaction between households and how these relate to climate impacts.
AmphorABM
Stefani Crabtree | Published Tuesday, January 05, 2021This model examines the economic interaction between Gaulish wheat farmers and Etruscan and Greek wine farming in 7th century B.C. France.
SESPES: socio-ecological systems and payment for ecosystem services model
Eulàlia Baulenas | Published Sunday, December 20, 2020 | Last modified Sunday, December 20, 2020The purpose of this spatially-explicit agent-based model is to intervene in the debate about PES policy design, implementation and context. We use the case for a woodland-for-water payment for ecosystem services (PES) and model its implementation in a local area of Catalonia (NE Spain). The model is based on three sub-models. The structural contains four different designs of a PES policy. The social sub-model includes agent-based factors, by having four types of landowner categories managing or not the forests. This sub-model is based on behavioral studies and assumptions about reception and reaction to incentive policies from European-focused studies. The ecological sub-model is based on climate change data for the area. The output are the evolution of the ecological and social goals of the policy under different policy design scenarios. Our focus in Europe surges from the general context of land abandonment that many Mediterranean areas and Eastern countries are experiencing, and the growing interest from policy-makers and practitioners on the implementation of PES schemes to ameliorate this situation.
Displaying 10 of 1252 results Sort by: Recently modified clear search