About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 145 results C++ clear search
Peer reviewed HUMLAND FIRE-IN-THE-HOLE agent-based model
Fulco Scherjon Anastasia Nikulina | Published Monday, October 20, 2025HUMLAND Fire-in-the-Hole is a conceptual agent-based model (ABM) designed to explore the ecological and behavioral consequences of fire-driven hunting strategies employed by hunter-gatherers, specifically Neanderthals, during the Last Interglacial period around the Neumark-Nord (Germany) archaeological site.
This model builds on and specializes the HUMLAND 1.0.0 model (Nikulina et al. 2024), integrating anthropogenic fires, elephant group behavior, and landscape response to simulate interactions between humans, megafauna, and vegetation over time.
Peer reviewed The effect of homophily on co-offending outcomes
Ruslan Klymentiev Christophe Vandeviver Luis E. C. Rocha | Published Friday, September 26, 2025This Agent-Based Model is designed to simulate how similarity-based partner selection (homophily) shapes the formation of co-offending networks and the diffusion of skills within those networks. Its purpose is to isolate and test the effects of offenders’ preference for similar partners on network structure and information flow, under controlled conditions.
In the model, offenders are represented as agents with an individual attribute and a set of skills. At each time step, agents attempt to select partners based on similarity preference. When two agents mutually select each other, they commit a co-offense, forming a tie and exchanging a skill. The model tracks the evolution of network properties (e.g., density, clustering, and tie strength) as well as the spread of skills over time.
This simple and theoretical model does not aim to produce precise empirical predictions but rather to generate insights and test hypotheses about the trade-off between network stability and information diffusion. It provides a flexible framework for exploring how changes in partner selection preferences may lead to differences in criminal network dynamics. Although the model was developed to simulate offenders’ interactions, in principle, it could be applied to other social processes involving social learning and skills exchange.
…
Peer reviewed E³-MAN. An Institutionally-guided multi-agent. Model for fair and efficient negotiation.
José luis bustelo | Published Monday, September 01, 2025Negotiation plays a fundamental role in shaping human societies, underpinning conflict resolution, institutional design, and economic coordination. This article introduces E³-MAN, a novel multi-agent model for negotiation that integrates individual utility maximization with fairness and institutional legitimacy. Unlike classical approaches grounded solely in game theory, our model incorporates Bayesian opponent modeling, transfer learning from past negotiation domains, and fallback institutional rules to resolve deadlocks. Agents interact in dynamic environments characterized by strategic heterogeneity and asymmetric information, negotiating over multidimensional issues under time constraints. Through extensive simulation experiments, we compare E³-MAN against the Nash bargaining solution and equal-split baselines using key performance metrics: utilitarian efficiency, Nash social welfare, Jain fairness index, Gini coefficient, and institutional compliance. Results show that E³-MAN achieves near-optimal efficiency while significantly improving distributive equity and agreement stability. A legal application simulating multilateral labor arbitration demonstrates that institutional default rules foster more balanced outcomes and increase negotiation success rates from 58% to 98%. By combining computational intelligence with normative constraints, this work contributes to the growing field of socially aware autonomous agents. It offers a virtual laboratory for exploring how simple institutional interventions can enhance justice, cooperation, and robustness in complex socio-legal systems.
An agent-based model of the journey of victim/survivors through local authority domestic abuse support services in the UK
Bruce Edmonds | Published Monday, July 28, 2025This model played a small part in the UK government’s review of the working of local authority implementation of the Domestic Abuse legislation. The model explicitly represents victim-survivor families as they: (a) try to contact the local DA support system, (b) are triaged by the system and (if there is space) allocated to safe temporary accomodation (c) recieve support services from this position and (d) eventually move on to more permenant accomodation. The purpose of the model was to understand some possible ways in which the implementation of DA Duty, might be frustrated in practice, the identification of gaps in the evidence base and to inform the developing Theory of Change. The key measures used for assessing outcomes in the model were the number of families helped and the services that were delivered to them. The exploration was grounded for in two archetypal cases: that of a relatively immature system for the delivery of DA services and a more mature one (based on actual local authority cases, but not based on any single one). See the official report under associated publications for a summary of results.
LogoClim: WorldClim in NetLogo
Daniel Vartanian Leandro Garcia Aline Martins de Carvalho Aline | Published Thursday, July 03, 2025 | Last modified Tuesday, September 16, 2025LogoClim is a NetLogo model for simulating and visualizing global climate conditions. It allows researchers to integrate high-resolution climate data into agent-based models, supporting reproducible research in ecology, agriculture, environmental sciences, and other fields that rely on climate data.
The model utilizes raster data to represent climate variables such as temperature and precipitation over time. It incorporates historical data (1951-2024) and future climate projections (2021-2100) derived from global climate models under various Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSPs, O’Neill et al., 2017). All climate inputs come from WorldClim 2.1, a widely used source of high-resolution, interpolated climate datasets based on weather station observations worldwide (Fick & Hijmans, 2017).
LogoClim follows the FAIR Principles for Research Software (Barker et al., 2022) and is openly available on the CoMSES Network and GitHub. See the Logônia model for an example of its integration into a full NetLogo simulation.
Development of coral reefs under climate change impacts and adaptation options
Nina Preußler | Published Friday, May 30, 2025This NetLogo model simulates how coral reefs around the islands of Palau would develop under different emission scenarios and with selected adaptation strategies. Reef health is indicated by coral cover (%) and is affected by four major climate change impacts: increasing sea surface temperature, sea level rise, ocean acidification, and more intense typhoons. The model differentiates between inner and outer reefs, with the former naturally adapted to warmer, more acidic waters. The simulation includes bleaching events and possible recovery. In addition, the user can choose between different coral transplantation strategies as well as regulate natural thermal adaptation rates.
Peer reviewed soslivestock model
Marco Janssen Irene Perez Ibarra Diego J. Soler-Navarro Alicia Tenza Peral | Published Wednesday, May 28, 2025 | Last modified Tuesday, June 10, 2025The purpose of this model is to analyze how different management strategies affect the wellbeing, sustainability and resilience of an extensive livestock system under scenarios of climate change and landscape configurations. For this purpose, it simulates one cattle farming system, in which agents (cattle) move through the space using resources (grass). Three farmer profiles are considered: 1) a subsistence farmer that emphasizes self-sufficiency and low costs with limited attention to herd management practices, 2) a commercial farmer focused on profit maximization through efficient production methods, and 3) an environmental farmer that prioritizes conservation of natural resources and animal welfare over profit maximization. These three farmer profiles share the same management strategies to adapt to climate and resource conditions, but differ in their goals and decision-making criteria for when, how, and whether to implement those strategies. This model is based on the SequiaBasalto model (Dieguez Cameroni et al. 2012, 2014, Bommel et al. 2014 and Morales et al. 2015), replicated in NetLogo by Soler-Navarro et al. (2023).
One year is 368 days. Seasons change every 92 days. Each step begins with the growth of grass as a function of climate and season. This is followed by updating the live weight of animals according to the grass height of their patch, and grass consumption, which is determined based on the updated live weight. Animals can be supplemented by the farmer in case of severe drought. After consumption, cows grow and reproduce, and a new grass height is calculated. This updated grass height value becomes the starting grass height for the next day. Cows then move to the next area with the highest grass height. After that, cattle prices are updated and cattle sales are held on the first day of fall. In the event of a severe drought, special sales are held. Finally, at the end of the day, the farm balance and the farmer’s effort are calculated.
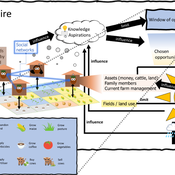
3spire: an agent-based model for exploring aspiration adaptation theory and its implications on smallholder farmers in Ethiopia
ateeuw Yue Dou Markus A Meyer Andrew Nelson | Published Sunday, February 16, 20253spire is an ABM where farming households make management decisions aimed at satisficing along the aspirational dimensions: food self-sufficiency, income, and leisure. Households decision outcomes depend on their social networks, knowledge, assets, household needs, past management, and climate/market trends
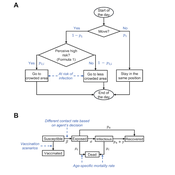
Peer reviewed Behavioral Dynamics of Epidemic Trajectories and Vaccination Strategies: An Agent-Based Model
Ziyuan Zhang | Published Tuesday, December 10, 2024This agent-based model explores the dynamics between human behavior and vaccination strategies during COVID-19 pandemics. It examines how individual risk perceptions influence behaviors and subsequently affect epidemic outcomes in a simulated metropolitan area resembling New York City from December 2020 to May 2021.
Agents modify their daily activities—deciding whether to travel to densely populated urban centers or stay in less crowded neighborhoods—based on their risk perception. This perception is influenced by factors such as risk perception threshold, risk tolerance personality, mortality rate, disease prevalence, and the average number of contacts per agent in crowded settings. Agent characteristics are carefully calibrated to reflect New York City demographics, including age distribution and variations in infection probability and mortality rates across these groups. The agents can experience six distinct health statuses: susceptible, exposed, infectious, recovered from infection, dead, and vaccinated (SEIRDV). The simulation focuses on the Iota and Alpha variants, the dominant strains in New York City during the period.
We simulate six scenarios divided into three main categories:
1. A baseline model without vaccinations where agents exhibit no risk perception and are indifferent to virus transmission and disease prevalence.
…
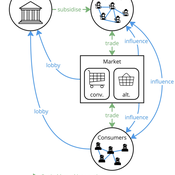
Agent-based model of power dynamics in agri-food systems
Tim Williams | Published Sunday, October 27, 2024 | Last modified Thursday, June 12, 2025This is a stylised agent-based model designed to explore the conditions that lead to lock-ins and transitions in agri-food systems.
The model represents interactions between four different types of agents: farmers, consumers, markets, and the state. Farmers and consumers are heterogeneous, and at each time step decide whether to trade with one of two market agents: the conventional or alternative. The state agent provides subsidies to the farmers at each time step.
The key emergent outcome is the fraction of trade in each time step that flows through the alternative market agent. This arises from the distributed decisions of farmer and consumer agents. A “sustainability transition” is defined as a shift in the dominant practices (and associated balance of power) towards the alternative paradigm.
…
Displaying 10 of 145 results C++ clear search