About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 6 of 6 results farmer decision making clear search
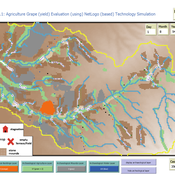
Peer reviewed Agriculture.Grape.yield.Evaluation.using.NetLogo.based.Technology.Simulation (AGENTS): A NetLogo agent-based model developed to assess viticulture efficiency in Byzantine Shivta.
Barak Garty Guy BarOz Gil Gambash Sharona T Levy | Published Friday, December 06, 2024AGENTS model is an agent-based computational framework designed to explore the socio-ecological and economic dynamics of agricultural production in the Byzantine Negev Highlands, with a focus on viticulture. It integrates historical, environmental, and social factors to simulate settlement sustainability, crop yields, and the impacts of varying climate conditions. The model is built in NetLogo and incorporates GIS-based topographical and hydrological data. Key features include the ability to assess climate impacts on crop profitability and settlement strategies, evaluate economic outputs of ancient vineyards, and simulate agent decision-making processes under diverse scenarios.
The AGENTS model is highly flexible, enabling users to simulate agricultural regimes with any two crops: one cash crop (a crop grown for profit, e.g., grapevines) and one staple crop (a crop grown for subsistence, e.g., wheat). While the default setup models viticulture and wheat cultivation in the Byzantine Negev Highlands, users can adapt the model to different environmental and socio-ecological contexts worldwide—both past and present.
Users can load external files to customize precipitation, evaporation, topography, and labor costs (measured as man-days per 0.1ha, converted to kg of wheat per model patch size area), and can also edit key parameters related to yield calculations. This includes modifying crop-specific yield formulas, soil and runoff indices, and any factors influencing crop performance. The model inherently simulates cash crops grown in floodplain regions and staple crops cultivated along riverbanks, providing a powerful tool to investigate societal resilience and responses to climate stressors across diverse environments.
…
Agent-based model of power dynamics in agri-food systems
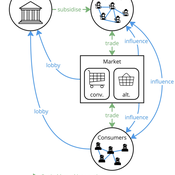
Tim Williams | Published Sunday, October 27, 2024This is a stylised agent-based model designed to explore the conditions that lead to lock-ins and transitions in agri-food systems.
The model represents interactions between four different types of agents: farmers, consumers, markets, and the state. Farmers and consumers are heterogeneous, and at each time step decide whether to trade with one of two market agents: the conventional or alternative. The state agent provides subsidies to the farmers at each time step.
The key emergent outcome is the fraction of trade in each time step that flows through the alternative market agent. This arises from the distributed decisions of farmer and consumer agents. A “sustainability transition” is defined as a shift in the dominant practices (and associated balance of power) towards the alternative paradigm.
…
WEEM (Woodlot Establishment and Expansion Model)
Vianny Ahimbisibwe Jürgen Groeneveld Melvin Lippe Susan Balaba Tumwebaze Eckhard Auch Uta Berger | Published Monday, September 27, 2021The agent-based model WEEM (Woodlot Establishment and Expansion Model) as described in the journal article, has been designed to make use of household socio-demographics (household status, birth, and death events of households), to better understand the temporal dynamics of woodlot in the buffer zones of Budongo protected forest reserve, Masindi district, Uganda. The results contribute to a mechanistic understanding of what determines the current gap between intention and actual behavior in forest land restoration at farm level.
FEARLUS-SPOMM
Gary Polhill Nick Gotts Alistair Law Luis Izquierdio Alessandro Gimona Lee-Ann Sutherland Dawn Parker | Published Friday, March 25, 2016This is a coupled conceptual model of agricultural land decision-making and incentivisation and species metacommunities.
Impact of Seasonal Forecast Use on Agricultural Income in a System with Varying Crop Costs and Returns
Thushara Gunda Josh T Bazuin John Nay Kam L Yeung | Published Tuesday, February 07, 2017The objective of the model is to evaluate the impact of seasonal forecasts on a farmer’s net agricultural income when their crop choices have different and variable costs and returns.
Exploring social psychology theory for modelling farmer decision-making
James Millington | Published Tuesday, September 18, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013To investigate the potential of using Social Psychology Theory in ABMs of natural resource use and show proof of concept, we present an exemplary agent-based modelling framework that explicitly represents multiple and hierarchical agent self-concepts