About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 929 results for "Gert Jan Kramer" clear search
GODS: Gossip-Oriented Dilemma Simulator
Jan Majewski | Published Wednesday, September 04, 2024Model of influence of access to social information spread via social network on decisions in a two-person game.
A model to explore the link between the gender-gap reversal in education and relative divorce risks
Jan Van Bavel Christine Schnor André Grow | Published Thursday, June 30, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, September 13, 2017This model explores a social mechanism that links the reversal of the gender gap in education with changing patterns in relative divorce risks in 12 European countries.
Collective Decision Making for Ecological Restoration
Dean Massey Moira Zellner Cristy Watkins Jeremy Brooks Kristen Ross | Published Friday, December 30, 2011 | Last modified Friday, November 21, 2014We present an agent-based model that maps out and simulates the processes by which individuals within ecological restoration organizations communicate and collectively make restoration decisions.
Peer reviewed Evolution of Sex
Kristin Crouse | Published Sunday, June 05, 2016 | Last modified Monday, February 15, 2021Evolution of Sex is a NetLogo model that illustrates the advantages and disadvantages of sexual and asexual reproductive strategies. It seeks to demonstrate the answer to the question “Why do we have sex?”
Sorghum supply development in Meru County, Kenya
Tim Verwaart Coen Van Wagenberg | Published Wednesday, September 06, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, May 30, 2019Trust between farmers and processors is a key factor in developing stable supply chains including “bottom of the pyramid”, small-scale farmers. This simulation studies a case with 10000 farmers.
Change and Senescence
André Martins | Published Tuesday, November 10, 2020Agers and non-agers agent compete over a spatial landscape. When two agents occupy the same grid, who will survive is decided by a random draw where chances of survival are proportional to fitness. Agents have offspring each time step who are born at a distance b from the parent agent and the offpring inherits their genetic fitness plus a random term. Genetic fitness decreases with time, representing environmental change but effective non-inheritable fitness can increase as animals learn and get bigger.
An Agent Based Model for implementing a double auction financial market
Annalisa Fabretti | Published Thursday, April 14, 2016The model implements a double auction financial markets with two types of agents: rational and noise. The model aims to study the impact of different compensation structure on the market stability and market quantities as prices, volumes, spreads.
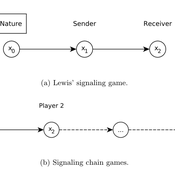
Lewis' Signaling Chains
Giorgio Gosti | Published Wednesday, January 14, 2015 | Last modified Friday, April 03, 2015Signaling chains are a special case of Lewis’ signaling games on networks. In a signaling chain, a sender tries to send a single unit of information to a receiver through a chain of players that do not share a common signaling system.
A model of urban expansion policy scenarios using an agent-based approach—a case of the Guangzhou Metropolitan Region of China
Guangjin Tian | Published Friday, March 21, 2014Three policy scenarios for urban expansion under the influences of the behaviours and decision modes of four agents and their interactions have been applied to predict the future development patterns of the Guangzhou metropolitan region.
Cascades across networks are sufficient for the formation of echo chambers: An agent-based model
Jan-Philipp Fränken | Published Monday, January 11, 2021An agent-based model of echo chamber formation employing a Bayesian Source Credibility cognitive architecture limiting interactions to a single cascade.
Displaying 10 of 929 results for "Gert Jan Kramer" clear search