About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 248 results for "Santiago L Rovere" clear search
BEGET Classic
Kristin Crouse | Published Monday, November 11, 2019 | Last modified Monday, November 25, 2019BEGET Classic includes previous versions used in the classroom and for publication. Please check out the latest version of B3GET here, which has several user-friendly features such as directly importing and exporting genotype and population files.
The classic versions of B3GET include: version one and version three were used in undergraduate labs at the University of Minnesota to demonstrate principles in primate behavioral ecology; version two first demonstrated proof of concept for creating virtual biological organisms using decision-vector algorithms; version four was presented at the 2017 annual meeting at the American Association of Physical Anthropologists; version five was presented in a 2019 publication from the Journal of Human Evolution (Crouse, Miller, and Wilson, 2019).
Armature distribution within the PaleoscapeABM
Claudine Gravel-Miguel | Published Tuesday, March 23, 2021This is a variant of the PaleoscapeABM model available here written by Wren and Janssen. In this variant, we give projectile weapons to hunter and document where they discard them over time. Discard rate and location are influenced by probabilities of hitting/missing the prey, probabilities of damaging the weapon, and probabilities of carrying back embedded projectile armatures to the habitation camp with the body carcass.
Peer reviewed Dynamic Equilibria Prediction: Experience-Weighted Attraction (EWA), Python Implementation
Vinicius Ferraz | Published Friday, December 02, 2022This project is based on a Jupyter Notebook that describes the stepwise implementation of the EWA model in bi-matrix ( 2×2 ) strategic-form games for the simulation of economic learning processes. The output is a dataset with the simulated values of Attractions, Experience, selected strategies, and payoffs gained for the desired number of rounds and periods. The notebook also includes exploratory data analysis over the simulated output based on equilibrium, strategy frequencies, and payoffs.
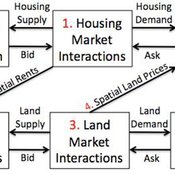
Coupled Housing and Land Markets (CHALMS)
Nicholas Magliocca Virginia Mcconnell Margaret Walls | Published Friday, November 02, 2012 | Last modified Monday, October 27, 2014CHALMS simulates housing and land market interactions between housing consumers, developers, and farmers in a growing ex-urban area.
Land Use in the Chitwan Valley
Alex Zvoleff | Published Monday, June 02, 2014chitwanabm is a spatially explicit agent-based model of population and land use in the Chitwan Valley, Nepal, designed to explore feedbacks between population and environment, with a heavy focus on community context and individual-level variation.
UK Demographic Simulator
Tony Lawson | Published Monday, February 27, 2012 | Last modified Tuesday, October 21, 2014A dynmaic microsimulation model to project the UK population over time
Peer reviewed HUMLAND FIRE-IN-THE-HOLE agent-based model
Fulco Scherjon Anastasia Nikulina | Published Monday, October 20, 2025HUMLAND Fire-in-the-Hole is a conceptual agent-based model (ABM) designed to explore the ecological and behavioral consequences of fire-driven hunting strategies employed by hunter-gatherers, specifically Neanderthals, during the Last Interglacial period around the Neumark-Nord (Germany) archaeological site.
This model builds on and specializes the HUMLAND 1.0.0 model (Nikulina et al. 2024), integrating anthropogenic fires, elephant group behavior, and landscape response to simulate interactions between humans, megafauna, and vegetation over time.
The Agent-Based Wildfire Simulation Environment (ABWiSE) translates the concept of a moving fire front as a set of mobile fire agents that respond to, and interact with, vegetation, wind, and terrain. Presently, the purpose of ABWiSE is to explore how ABM, using simple interactions between agents and a simple atmospheric feedback model, can simulate emergent fire spread patterns.
An age and/or gender-based division of labor during the Last Glacial Maximum in Iberia through rabbit hunting
Liliana Perez Samuel Seuru Ariane Burke | Published Friday, July 07, 2023Many archaeological assemblages from the Iberian Peninsula dated to the Last Glacial Maximum contain large quantities of European rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) remains with an anthropic origin. Ethnographic and historic studies report that rabbits may be mass-collected through warren-based harvesting involving the collaborative participation of several persons.
We propose and implement an Agent-Based Model grounded in the Optimal Foraging Theory and the Diet Breadth Model to examine how different warren-based hunting strategies influence the resulting human diets.
Particularly, this model is developed to test the following hypothesis: What if an age and/or gender-based division of labor was adopted, in which adult men focus on large prey hunting, and women, elders and children exploit warrens?
…
Change and Senescence
André Martins | Published Tuesday, November 10, 2020Agers and non-agers agent compete over a spatial landscape. When two agents occupy the same grid, who will survive is decided by a random draw where chances of survival are proportional to fitness. Agents have offspring each time step who are born at a distance b from the parent agent and the offpring inherits their genetic fitness plus a random term. Genetic fitness decreases with time, representing environmental change but effective non-inheritable fitness can increase as animals learn and get bigger.
Displaying 10 of 248 results for "Santiago L Rovere" clear search