About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 178 results for "Jennifer Fewell" clear search
Setting the Stage for Inequality
Timothy Dennehy | Published Monday, March 11, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013How can a strictly egalitarian social system give way to a stratified society if all of its members punish each other for any type of selfish behavior? This model examines the role of prestige bias in constant and variable environments on the development of hierarchies of wealth.
MiniDemographicABM.jl: A simplified agent-based demographic model of the UK
Atiyah Elsheikh | Published Friday, July 28, 2023 | Last modified Tuesday, December 12, 2023This package implements a simplified artificial agent-based demographic model of the UK. Individuals of an initial population are subject to ageing, deaths, births, divorces and marriages. A specific case-study simulation is progressed with a user-defined simulation fixed step size on a hourly, daily, weekly, monthly basis or even an arbitrary user-defined clock rate. While the model can serve as a base model to be adjusted to realistic large-scale socio-economics, pandemics or social interactions-based studies mainly within a demographic context, the main purpose of the model is to explore and exploit capabilities of the state-of-the-art Agents.jl Julia package as well as other ecosystem of Julia packages like GlobalSensitivity.jl. Code includes examples for evaluating global sensitivity analysis using Morris and Sobol methods and local sensitivity analysis using OFAT and OAT methods. Multi-threaded parallelization is enabled for improved runtime performance.
Impact of Seasonal Forecast Use on Agricultural Income in a System with Varying Crop Costs and Returns
Thushara Gunda Josh T Bazuin John Nay Kam L Yeung | Published Tuesday, February 07, 2017The objective of the model is to evaluate the impact of seasonal forecasts on a farmer’s net agricultural income when their crop choices have different and variable costs and returns.
Simulating the evolution of the human family
Paul Smaldino | Published Wednesday, November 29, 2017The (cultural) evolution of cooperative breeding in harsh environments.
GRASP world
Gert Jan Hofstede | Published Tuesday, April 16, 2019This agent-based model investigates group longevity in a population in a foundational way, using theory on social relations and culture. It is the first application of the GRASP meta-model for social agents, containing elements of Groups, Rituals, Affiliation, Status, and Power. It can be considered an exercise in artificial sociality: a culture-general, content-free base-line trust model from which to engage in more specific studies. Depending on cultural settings for individualism and power distance, as well as settings for xenophobia and for the increase of trust over group life, the GRASP world model generates a variety of patters. Number of groups ranges from one to many, composition from random to segregated, and pattern genesis from rapid to many hundreds of time steps. This makes GRASP world an instrument that plausibly models some basic elements of social structure in different societies.
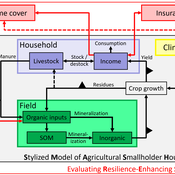
SMASH: Stylized Model of Agricultural Smallholder Households
Tim Williams | Published Tuesday, December 08, 2020The SMASH model is an agent-based model of rural smallholder households. It models households’ evolving income and wealth, which they earn through crop sales. Wealth is carried in the form of livestock, which are grazed on an external rangeland (exogenous) and can be bought/sold as investment/coping mechanisms. The model includes a stylized representation of soil nutrient dynamics, modeling the inflows and outflows of organic and inorganic nitrogen from each household’s field.
The model has been applied to assess the resilience-enhancing effects of two different farm-level adaptation strategies: legume cover cropping and crop insurance. These two strategies interact with the model through different mechanims - legume cover cropping through ecological mechanisms and crop insurance through financial mechanisms. The model can be used to investigate the short- and long-term effects of these strategies, as well as how they may differently benefit different types of household.
A Bottom-Up Simulation on Competition and Displacement of Online Interpersonal Communication Platforms
great-sage-futao | Published Tuesday, December 31, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, December 31, 2019This model aims to simulate Competition and Displacement of Online Interpersonal Communication Platforms process from a bottom-up angle. Individual interpersonal communication platform adoption and abandonment serve as the micro-foundation of the simulation model. The evolution mode of platform user online communication network determines how present platform users adjust their communication relationships as well as how new users join that network. This evolution mode together with innovations proposed by individual interpersonal communication platforms would also have impacts on the platform competition and displacement process and result by influencing individual platform adoption and abandonment behaviors. Three scenes were designed to simulate some common competition situations occurred in the past and current time, that two homogeneous interpersonal communication platforms competed with each other when this kind of platforms first came into the public eye, that a late entrant platform with a major innovation competed with the leading incumbent platform during the following days, as well as that both the leading incumbent and the late entrant continued to propose many small innovations to compete in recent days, respectively.
Initial parameters are as follows: n(Nmax in the paper), denotes the final node number of the online communication network node. mi (m in the paper), denotes the initial degree of those initial network nodes and new added nodes. pc(Pc in the paper), denotes the proportion of links to be removed and added in each epoch. pst(Pv in the paper), denotes the proportion of nodes with a viscosity to some platforms. comeintime(Ti in the paper), denotes the epoch when Platform 2 joins the market. pit(Pi in the paper), denotes the proportion of nodes adopting Platform 2 immediately at epoch comeintime(Ti). ct(Ct in the paper), denotes the Innovation Effective Period length. In Scene 2, There is only one major platform proposed by Platform 2, and ct describes that length. However, in Scene 3, Platform 2 and 1 will propose innovations alternately. And so, we set ct=10000 in simulation program, and every jtt epochs, we alter the innovation proposer from one platform to the other. Hence in this scene, jtt actually denotes the Innovation Effective Period length instead of ct.
Peak-seeking Adder
Julia Kasmire Janne M Korhonen | Published Tuesday, December 02, 2014 | Last modified Friday, February 20, 2015Continuing on from the Adder model, this adaptation explores how rationality, learning and uncertainty influence the exploration of complex landscapes representing technological evolution.
Social norms and the dominance of Low-doers
Antonio Franco | Published Wednesday, July 13, 2016 | Last modified Sunday, December 02, 2018The code for the paper “Social norms and the dominance of Low-doers”
Peer reviewed Flibs’NFarol: Self-Organized Efficiency and Fairness Emergence in an Evolutive Game
Cosimo Leuci | Published Thursday, October 12, 2023According to the philosopher of science K. Popper “All life is problem solving”. Genetic algorithms aim to leverage Darwinian selection, a fundamental mechanism of biological evolution, so as to tackle various engineering challenges.
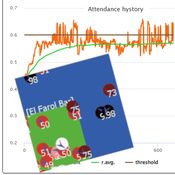
Flibs’NFarol is an Agent Based Model that embodies a genetic algorithm applied to the inherently ill-defined “El Farol Bar” problem. Within this context, a group of agents operates under bounded rationality conditions, giving rise to processes of self-organization involving, in the first place, efficiency in the exploitation of available resources. Over time, the attention of scholars has shifted to equity in resource distribution, as well. Nowadays, the problem is recognized as paradigmatic within studies of complex evolutionary systems.
Flibs’NFarol provides a platform to explore and evaluate factors influencing self-organized efficiency and fairness. The model represents agents as finite automata, known as “flibs,” and offers flexibility in modifying the number of internal flibs states, which directly affects their behaviour patterns and, ultimately, the diversity within populations and the complexity of the system.
Displaying 10 of 178 results for "Jennifer Fewell" clear search