About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 51 results for "Adrian Thomas" clear search
Pedestrian model
Gudrun Wallentin Dana Kaziyeva Martin Loidl Petra Stutz | Published Monday, August 07, 2023The model generates disaggregated traffic flows of pedestrians, simulating their daily mobility behaviour represented as probabilistic rules. Various parameters of physical infrastructure and travel behaviour can be altered and tested. This allows predicting potential shifts in traffic dynamics in a simulated setting. Moreover, assumptions in decision-making processes are general for mid-sized cities and can be applied to similar areas.
Together with the model files, there is the ODD protocol with the detailed description of model’s structure. Check the associated publication for results and evaluation of the model.
Installation
Download GAMA-platform (GAMA1.8.2 with JDK version) from https://gama-platform.github.io/. The platform requires a minimum of 4 GB of RAM.
…
RecovUS: An Agent-Based Model of Post-Disaster Household Recovery
Saeed Moradi | Published Thursday, July 30, 2020The purpose of this model is to explain the post-disaster recovery of households residing in their own single-family homes and to predict households’ recovery decisions from drivers of recovery. Herein, a household’s recovery decision is repair/reconstruction of its damaged house to the pre-disaster condition, waiting without repair/reconstruction, or selling the house (and relocating). Recovery drivers include financial conditions and functionality of the community that is most important to a household. Financial conditions are evaluated by two categories of variables: costs and resources. Costs include repair/reconstruction costs and rent of another property when the primary house is uninhabitable. Resources comprise the money required to cover the costs of repair/reconstruction and to pay the rent (if required). The repair/reconstruction resources include settlement from the National Flood Insurance (NFI), Housing Assistance provided by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA-HA), disaster loan offered by the Small Business Administration (SBA loan), a share of household liquid assets, and Community Development Block Grant Disaster Recovery (CDBG-DR) fund provided by the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). Further, household income determines the amount of rent that it can afford. Community conditions are assessed for each household based on the restoration of specific anchors. ASNA indexes (Nejat, Moradi, & Ghosh 2019) are used to identify the category of community anchors that is important to a recovery decision of each household. Accordingly, households are indexed into three classes for each of which recovery of infrastructure, neighbors, or community assets matters most. Further, among similar anchors, those anchors are important to a household that are located in its perceived neighborhood area (Moradi, Nejat, Hu, & Ghosh 2020).
An Agent-Based Model for Skilled Workers Migration
Hassan Bashiri | Published Thursday, September 21, 2023This documentation provides an overview and explanation of the NetLogo simulation code for modeling skilled workers’ migration in Iran. The simulation aims to explore the dynamics of skilled workers’ migration and their transition through various states, including training, employment, and immigration.
The flow of elite and talent migration, or “brain drain,” is a complex issue with far-reaching implications for developing countries. The decision to migrate is made due to various factors including economic opportunities, political stability, social factors and personal circumstances.
Measuring individual interests in the field of immigration is a complex task that requires careful consideration of various factors. The agent-based model is a useful tool for understanding the complex factors that are involved in talent migration. By considering the various social, economic, and personal factors that influence migration decisions, policymakers can provide more effective strategies to retain skilled and talented labor and promote sustainable growth in developing countries. One of the main challenges in studying the flow of elite migration is the complexity of the decision-making process and a set of factors that lead to migration decisions. Agent-based modeling is a useful tool for understanding how individual decisions can lead to large-scale migration patterns.
Informal Information Transmission Networks among Medieval Genoese Investors
Christopher Frantz | Published Wednesday, October 09, 2013 | Last modified Thursday, October 24, 2013This model represents informal information transmission networks among medieval Genoese investors used to inform each other about cheating merchants they employed as part of long-distance trade operations.
AnimDens NetLogo
Miguel Pais Christine Ward-Paige | Published Friday, February 10, 2017 | Last modified Sunday, February 23, 2020The model demonstrates how non-instantaneous sampling techniques produce bias by overestimating the number of counted animals, when they move relative to the person counting them.
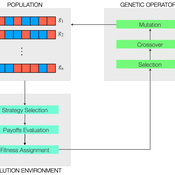
Peer reviewed Evolutionary Economic Learning Simulation: A Genetic Algorithm for Dynamic 2x2 Strategic-Form Games in Python
Vinicius Ferraz Thomas Pitz | Published Friday, April 08, 2022This project combines game theory and genetic algorithms in a simulation model for evolutionary learning and strategic behavior. It is often observed in the real world that strategic scenarios change over time, and deciding agents need to adapt to new information and environmental structures. Yet, game theory models often focus on static games, even for dynamic and temporal analyses. This simulation model introduces a heuristic procedure that enables these changes in strategic scenarios with Genetic Algorithms. Using normalized 2x2 strategic-form games as input, computational agents can interact and make decisions using three pre-defined decision rules: Nash Equilibrium, Hurwicz Rule, and Random. The games then are allowed to change over time as a function of the agent’s behavior through crossover and mutation. As a result, strategic behavior can be modeled in several simulated scenarios, and their impacts and outcomes can be analyzed, potentially transforming conflictual situations into harmony.
An agent-based model to simulate field-specific nitrogen fertilizer applications in grasslands
Maria Haensel Thomas Schmitt Andrea Kaim Sylvia Helena Annuth Thomas Koellner | Published Sunday, February 09, 2025Grasslands have a large share of the world’s land cover and their sustainable management is important for the protection and provisioning of grassland ecosystem services. The question of how to manage grassland sustainably is becoming increasingly important, especially in view of climate change, which on the one hand extends the vegetation period (and thus potentially allows use intensification) and on the other hand causes yield losses due to droughts. Fertilization plays an important role in grassland management and decisions are usually made at farm level. Data on fertilizer application rates are crucial for an accurate assessment of the effects of grassland management on ecosystem services. However, these are generally not available on farm/field scale. To close this gap, we present an agent-based model for Fertilization In Grasslands (FertIG). Based on animal, land-use, and cutting data, the model estimates grassland yields and calculates field-specific amounts of applied organic and mineral nitrogen on grassland (and partly cropland). Furthermore, the model considers different legal requirements (including fertilization ordinances) and nutrient trade among farms. FertIG was applied to a grassland-dominated region in Bavaria, Germany comparing the effects of changes in the fertilization ordinance as well as nutrient trade. The results show that the consideration of nutrient trade improves organic fertilizer distribution and leads to slightly lower Nmin applications. On a regional scale, recent legal changes (fertilization ordinance) had limited impacts. Limiting the maximum applicable amount of Norg to 170 kg N/ha fertilized area instead of farm area as of 2020 hardly changed fertilizer application rates. No longer considering application losses in the calculation of fertilizer requirements had the strongest effects, leading to lower supplementary Nmin applications. The model can be applied to other regions in Germany and, with respective adjustments, in Europe. Generally, it allows comparing the effects of policy changes on fertilization management at regional, farm and field scale.
Peer reviewed Behavior changes through influence
Daria Soboleva | Published Friday, August 30, 2024The model is designed to simulate the behavior and decision-making processes of individuals (agents) in a social network. It aims to represent the changes in individual probability to take any action based on changes in attributes. The action is anything that can be reasonably influenced by the three influencing methods implemented in this model: peer pressure, social media, and state campaigns, and for which the user has a decision-making model. The model is implemented in the multi-agent programmable environment NetLogo 6.3.0.
Exploration and Exploitation: Persistence with local exploration under varying resource distribution, resource availability over time and cost of relocation
Arpan Jani | Published Monday, September 30, 2019Organisms, Individuals and Organizations face the dilemma of exploration vs. exploitation
Identifying the optimal trade-off between the two is a challenge
Too much exploration (e.g. gaining new knowledge) can be detrimental to day-to-day survival and too much exploitation (applying existing knowledge) could be detrimental to long term survival esp. if conditions change over time
The purpose of the model is to investigate how the amount of resources acquired (wealth/success) is related to persistence with the strategy of local exploration under different resource distributions, availability of resources over time and cost of relocation
Peer reviewed Coupled demographic dynamics of herd and household in pastoral systems
Mark Moritz Ian M Hamilton Andrew Yoak Abigail Buffington Chelsea E Hunter Daniel C Peart | Published Saturday, April 08, 2023This purpose of this model is to understand how the coupled demographic dynamics of herds and households constrain the growth of livestock populations in pastoral systems.
Displaying 10 of 51 results for "Adrian Thomas" clear search