About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 292 results for "Aaron C Fisher" clear search
ABM Simulation of Transition from Late Longshan Cultures to Early Erlitou Culture
Carmen Iasiello | Published Sunday, November 26, 2023Within the archeological record for Bronze Age Chinese culture, there continues to be a gap in our understanding of the sudden rise of the Erlitou State from the previous late Longshan chiefdoms. In order to examine this period, I developed and used an agent-based model (ABM) to explore possible socio-politically relevant hypotheses for the gap between the demise of the late Longshan cultures and rise of the first state level society in East Asia. I tested land use strategy making and collective action in response to drought and flooding scenarios, the two plausible environmental hazards at that time. The model results show cases of emergent behavior where an increase in social complexity could have been experienced if a catastrophic event occurred while the population was sufficiently prepared for a different catastrophe, suggesting a plausible lead for future research into determining the life of the time period.
The ABM published here was originally developed in 2016 and its results published in the Proceedings of the 2017 Winter Simulation Conference.
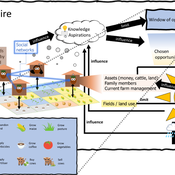
3spire: an agent-based model for exploring aspiration adaptation theory and its implications on smallholder farmers in Ethiopia
ateeuw Yue Dou Markus A Meyer Andrew Nelson | Published Sunday, February 16, 20253spire is an ABM where farming households make management decisions aimed at satisficing along the aspirational dimensions: food self-sufficiency, income, and leisure. Households decision outcomes depend on their social networks, knowledge, assets, household needs, past management, and climate/market trends
AMIRIS
Ulrich Frey Felix Nitsch Christoph Schimeczek Johannes Kochems Kristina Nienhaus Evelyn Sperber Aboubakr Achraf El Ghazi Seyedfarzad Sarfarazi | Published Thursday, February 03, 2022AMIRIS is the Agent-based Market model for the Investigation of Renewable and Integrated energy Systems.
It is an agent-based simulation of electricity markets and their actors.
AMIRIS enables researches to analyse and evaluate energy policy instruments and their impact on the actors involved in the simulation context.
Different prototypical agents on the electricity market interact with each other, each employing complex decision strategies.
AMIRIS allows to calculate the impact of policy instruments on economic performance of power plant operators and marketers.
…
CINCH1 (Covid-19 INfection Control in Hospitals)
Nick Gotts | Published Sunday, August 29, 2021CINCH1 (Covid-19 INfection Control in Hospitals), is a prototype model of physical distancing for infection control among staff in University College London Hospital during the Covid-19 pandemic, developed at the University of Leeds, School of Geography. It models the movement of collections of agents in simple spaces under conflicting motivations of reaching their destination, maintaining physical distance from each other, and walking together with a companion. The model incorporates aspects of the Capability, Opportunity and Motivation of Behaviour (COM-B) Behaviour Change Framework developed at University College London Centre for Behaviour Change, and is aimed at informing decisions about behavioural interventions in hospital and other workplace settings during this and possible future outbreaks of highly contagious diseases. CINCH1 was developed as part of the SAFER (SARS-CoV-2 Acquisition in Frontline Health Care Workers – Evaluation to Inform Response) project
(https://www.ucl.ac.uk/behaviour-change/research/safer-sars-cov-2-acquisition-frontline-health-care-workers-evaluation-inform-response), funded by the UK Medical Research Council. It is written in Python 3.8, and built upon Mesa version 0.8.7 (copyright 2020 Project Mesa Team).
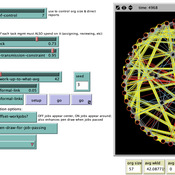
An agent-based simulation of discussion processes in risk workshops
Matthias Meyer Clemens Harten Lucia Bellora-Bienengräber | Published Thursday, September 30, 2021The model measures drivers of effectiveness of risk assessments in risk workshops regarding the correctness and required time. Specifically, we model the limits to information transfer, incomplete discussions, group characteristics, and interaction patterns and investigate their effect on risk assessment in risk workshops.
The model simulates a discussion in the context of a risk workshop with 9 participants. The participants use Bayesian networks to assess a given risk individually and as a group.
Peer reviewed HUMLAND: HUMan impact on LANDscapes agent-based model
Fulco Scherjon Anastasia Nikulina Anhelina Zapolska Maria Antonia Serge Marco Davoli Dave van Wees Katharine MacDonald | Published Monday, October 16, 2023The HUMan impact on LANDscapes (HUMLAND) model has been developed to track and quantify the intensity of different impacts on landscapes at the continental level. This agent-based model focuses on determining the most influential factors in the transformation of interglacial vegetation with a specific emphasis on burning organized by hunter-gatherers. HUMLAND integrates various spatial datasets as input and target for the agent-based model results. Additionally, the simulation incorporates recently obtained continental-scale estimations of fire return intervals and the speed of vegetation regrowth. The obtained results include maps of possible scenarios of modified landscapes in the past and quantification of the impact of each agent, including climate, humans, megafauna, and natural fires.
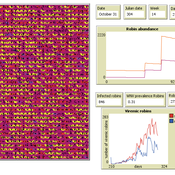
Peer reviewed AMRO_CULEX_WNV
Aniruddha Belsare Jennifer Owen | Published Saturday, February 27, 2021 | Last modified Thursday, March 11, 2021An agent-based model simulating West Nile Virus dynamics in a one host (American robin)-one vector (Culex spp. mosquito) system. ODD improved and code cleaned.
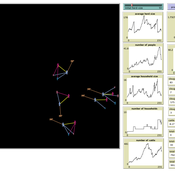
Formal Organization Hierarchy and Informal Networks - "The Company Behind the Org Chart"
Tom Briggs | Published Sunday, April 18, 2021A generalized organizational agent- based model (ABM) containing both formal organizational hierarchy and informal social networks simulates organizational processes that occur over both formal network ties and informal networks.
Peer reviewed Coupled demographic dynamics of herd and household in pastoral systems
Mark Moritz Ian M Hamilton Andrew Yoak Abigail Buffington Chelsea E Hunter Daniel C Peart | Published Saturday, April 08, 2023This purpose of this model is to understand how the coupled demographic dynamics of herds and households constrain the growth of livestock populations in pastoral systems.
Collective Decision Making for Ecological Restoration version 2.0
Dean Massey Moira Zellner Cristy Watkins Jeremy Brooks Kristen Ross Lynne M Westphal | Published Wednesday, November 19, 2014CoDMER v. 2.0 was parameterized with ethnographic data from organizations dealing with prescribed fire and seeding native plants, to advance theory on how collective decisions emerge in ecological restoration.
Displaying 10 of 292 results for "Aaron C Fisher" clear search