About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 259 results for "Carlos Andrés Chiale" clear search
Peer reviewed Simulating the Economic Impact of Boko Haram on a Cameroonian Floodplain
Mark Moritz Nathaniel Henry Sarah Laborde | Published Saturday, October 22, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, June 07, 2017This model examines the potential impact of market collapse on the economy and demography of fishing households in the Logone Floodplain, Cameroon.
MEGADAPT - Socio-hydrological risk model - Theoretical (no data) implementation
Marco Janssen Andres Baeza-Castro Luis Bojorquez Hallie Eakin | Published Wednesday, February 06, 2019The model simulates the decisions of residents and a water authority to respond to socio-hydrological hazards. Residents from neighborhoods are located in a landscape with topographic complexity and two problems: water scarcity in the peripheral neighborhoods at high altitude and high risk of flooding in the lowlands, at the core of the city. The role of the water authority is to decide where investments in infrastructure should be allocated to reduce the risk to water scarcity and flooding events in the city, and these decisions are made via a multi-objective site selection procedure. This procedure accounts for the interdependencies and feedback between the urban landscape and a policy scenario that defines the importance, or priorities, that the authority places on four criteria.
Neighborhoods respond to the water authority decisions by protesting against the lack of investment and the level of exposure to water scarcity and flooding. Protests thus simulate a form of feedback between local-level outcomes (flooding and water scarcity) and higher-level decision-making. Neighborhoods at high altitude are more likely to be exposed to water scarcity and lack infrastructure, whereas neighborhoods in the lowlands tend to suffer from recurrent flooding. The frequency of flooding is also a function of spatially uniform rainfall events. Likewise, neighborhoods at the periphery of the urban landscape lack infrastructure and suffer from chronic risk of water scarcity.
The model simulates the coupling between the decision-making processes of institutional actors, socio-political processes and infrastructure-related hazards. In the documentation, we describe details of the implementation in NetLogo, the description of the procedures, scheduling, and the initial conditions of the landscape and the neighborhoods.
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 1414052, CNH: The Dynamics of Multi-Scalar Adaptation in Megacities (PI Hallie Eakin).
Peer reviewed Coupled demographic dynamics of herd and household in pastoral systems
Mark Moritz Ian M Hamilton Andrew Yoak Abigail Buffington Chelsea E Hunter Daniel C Peart | Published Saturday, April 08, 2023This purpose of this model is to understand how the coupled demographic dynamics of herds and households constrain the growth of livestock populations in pastoral systems.
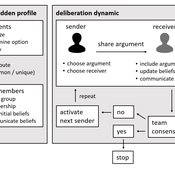
Agent-based model of team decision-making in hidden profile situations
Andreas Flache Jonas Stein Vincenz Frey | Published Thursday, April 20, 2023 | Last modified Friday, November 17, 2023The model presented here is extensively described in the paper ‘Talk less to strangers: How homophily can improve collective decision-making in diverse teams’ (forthcoming at JASSS). A full replication package reproducing all results presented in the paper is accessible at https://osf.io/76hfm/.
Narrative documentation includes a detailed description of the model, including a schematic figure and an extensive representation of the model in pseudocode.
The model develops a formal representation of a diverse work team facing a decision problem as implemented in the experimental setup of the hidden-profile paradigm. We implement a setup where a group seeks to identify the best out of a set of possible decision options. Individuals are equipped with different pieces of information that need to be combined to identify the best option. To this end, we assume a team of N agents. Each agent belongs to one of M groups where each group consists of agents who share a common identity.
The virtual teams in our model face a decision problem, in that the best option out of a set of J discrete options needs to be identified. Every team member forms her own belief about which decision option is best but is open to influence by other team members. Influence is implemented as a sequence of communication events. Agents choose an interaction partner according to homophily h and take turns in sharing an argument with an interaction partner. Every time an argument is emitted, the recipient updates her beliefs and tells her team what option she currently believes to be best. This influence process continues until all agents prefer the same option. This option is the team’s decision.
Diffusion dynamics in small-world networks with heterogeneous consumers
Sebastiano Delre | Published Saturday, September 10, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model simulates diffusion curves and it allows to test how social influence, network structure and consumer heterogeneity affect their spreads and their speeds.
Composite Collective Decision Making - ant colony foraging model
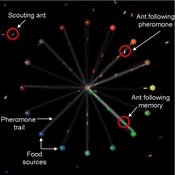
Tomer Czaczkes Benjamin I Czaczkes | Published Thursday, December 17, 2015The model explores how two types of information - social (in the form of pheromone trails) and private (in the form of route memories) affect ant colony level foraging in a variable enviroment.
Agent-based model of WiFi tracking system in urban environment
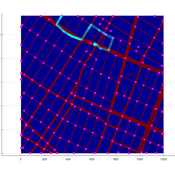
Christopher Thron Khoi Tran | Published Friday, April 21, 2017This code simulates the WiFi user tracking system described in: Thron et al., “Design and Simulation of Sensor Networks for Tracking Wifi Users in Outdoor Urban Environments”. Testbenches used to create the figures in the paper are included.
Impact of topography and climate change on Magdalenian social networks
Claudine Gravel-Miguel | Published Monday, September 11, 2017The model presented here was created as part of my dissertation. It aims to study the impacts of topography and climate change on prehistoric networks, with a focus on the Magdalenian, which is dated to between 20 and 14,000 years ago.
Peer reviewed Empathy & Power
J M Applegate Ned Wellman | Published Monday, November 13, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, December 21, 2017The purpose of this model is to explore the effects of different power structures on a cross-functional team’s prosocial decision making. Are certain power distributions more conducive to the team making prosocial decisions?
Risk-Sharing under Heterogeneity: NetLogo simulation
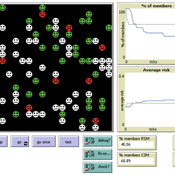
Eva Vriens | Published Monday, February 28, 2022Motivated by the emergence of new Peer-to-Peer insurance organizations that rethink how insurance is organized, we propose a theoretical model of decision-making in risk-sharing arrangements with risk heterogeneity and incomplete information about the risk distribution as core features. For these new, informal organisations, the available institutional solutions to heterogeneity (e.g., mandatory participation or price differentiation) are either impossible or undesirable. Hence, we need to understand the scope conditions under which individuals are motivated to participate in a bottom-up risk-sharing setting. The model puts forward participation as a utility maximizing alternative for agents with higher risk levels, who are more risk averse, are driven more by solidarity motives, and less susceptible to cost fluctuations. This basic micro-level model is used to simulate decision-making for agent populations in a dynamic, interdependent setting. Simulation results show that successful risk-sharing arrangements may work if participants are driven by motivations of solidarity or risk aversion, but this is less likely in populations more heterogeneous in risk, as the individual motivations can less often make up for the larger cost deficiencies. At the same time, more heterogeneous groups deal better with uncertainty and temporary cost fluctuations than more homogeneous populations do. In the latter, cascades following temporary peaks in support requests more often result in complete failure, while under full information about the risk distribution this would not have happened.
Displaying 10 of 259 results for "Carlos Andrés Chiale" clear search