About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 9 of 9 results shock clear search
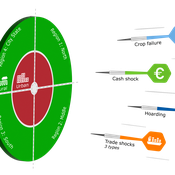
DARTS: modelling effects of shocks on global, regional, urban and rural food security
Geerten Hengeveld Hubert Fonteijn Pepijn van Oort | Published Tuesday, June 18, 2024Food trade networks represent a complex system where food is periodically produced in different regions of the world. Food is continuously stocked and traded. Food security in a globalised world is vulnerable to shocks. We present DARTS, a new agent based model that models monthly dynamics of food production, trade, stocking, consumption and food security for different interconnected world regions and a city state. Agents in different regions differ in their harvest seasons, wealth (rich and poor), degree of urbanisation and connection to domestic and global markets. DARTS was specifically designed to model direct and indirect effects of shocks in the food system. We introduce a new typology of 6 distinct shock types and analyse their impact on food security, modelling local and global effects and short term and longer term effects. An second important scientific novelty of the model is that DARTS can also model indirect effects of shocks (cascading in space and in time, lag effects due to trade and food stock buffering). A third important scientific novelty of the model is its’ capability of modelling food security at different scales, in which the rural/urban divide and differences in (intra-annually varying) production and trade connections play a key role. At the time of writing DARTS is yet insufficiently parameterised for accurate prediction for real world regions and cities. Simulations for a hypothetical in silico world with 3 regions and a city state show that DARTS can reproduce rich and complex dynamics with analogues in the real world. The scientific interest is more on deepening insight in process dynamics and chains of events that lead to ultimate shock effects on food security.
DARTS: an agent-based model of the global food system for studying its resilience to shocks
Hubert Fonteijn | Published Wednesday, November 22, 2023DARTS simulates food systems in which agents produce, consume and trade food. Here, food is a summary item that roughly corresponds to commodity food types (e.g. rice). No other food types are taken into account. Each food system (World) consists of its own distribution of agents, regions and connections between agents. Agents differ in their ability to produce food, earn off-farm income and trade food. The agents aim to satisfy their food requirements (which are fixed and equal across agents) by either their own food production or by food purchases. Each simulation step represents one month, in which agents can produce (if they have productive capacity and it is a harvest month for their region), earn off-farm income, trade food (both buy and sell) and consume food. We evaluate the performance of the food system by averaging the agents’ food satisfaction, which is defined as the ratio of the food consumed by each agent at the end of each month divided by her food requirement. At each step, any of the abovementioned attributes related to the agents’ ability to satisfy their food requirement can (temporarily) be shocked. These shocks include reducing the amount of food they produce, removing their ability to trade locally or internationally and reducing their cash savings. Food satisfaction is quantified (both immediately after the shock and in the year following the shock) to evaluate food security of a particular food system, both at the level of agent types (e.g. the urban poor and the rural poor) and at the systems level. Thus, the effects of shocks on food security can be related to the food system’s structure.
Model of Rental Evictions in Phoenix During the Covid-19 Pandemic
Sean Bergin J M Applegate | Published Saturday, July 31, 2021 | Last modified Friday, October 15, 2021The purpose of this model is to explore the dynamics of residency and eviction for households renting in the greater Phoenix (Arizona) metropolitan area. The model uses a representative population of renters modified from American Community Survey (ACS) data that includes demographic, housing and economic information. Each month, households pay their subsistence, rental and utility bills. If a household is unable to pay their monthly rent or utility bill they apply for financial assistance. This model provides a platform to understand the impact of various economic shock upon households. Also, the model includes conditions that occurred as a result of the Covid-19 pandemic which allows for the study of eviction mitigation strategies that were employed, such as the eviction moratorium and stimulus payments. The model allows us to make preliminary predictions concerning the number of households that may be evicted once the moratorium on evictions ends and the long-term effects on the number of evicted households in the greater Phoenix area going forward.
RiskNetABM
Birgit Müller Jürgen Groeneveld Karin Frank Meike Will Friederike Lenel | Published Monday, July 20, 2020 | Last modified Monday, May 03, 2021The fight against poverty is an urgent global challenge. Microinsurance is promoted as a valuable instrument for buffering income losses due to health or climate-related risks of low-income households in developing countries. However, apart from direct positive effects they can have unintended side effects when insured households lower their contribution to traditional arrangements where risk is shared through private monetary support.
RiskNetABM is an agent-based model that captures dynamics between income losses, insurance payments and informal risk-sharing. The model explicitly includes decisions about informal transfers. It can be used to assess the impact of insurance products and informal risk-sharing arrangements on the resilience of smallholders. Specifically, it allows to analyze whether and how economic needs (i.e. level of living costs) and characteristics of extreme events (i.e. frequency, intensity and type of shock) influence the ability of insurance and informal risk-sharing to buffer income shocks. Two types of behavior with regard to private monetary transfers are explicitly distinguished: (1) all households provide transfers whenever they can afford it and (2) insured households do not show solidarity with their uninsured peers.
The model is stylized and is not used to analyze a particular case study, but represents conditions from several regions with different risk contexts where informal risk-sharing networks between smallholder farmers are prevalent.
…
Peer reviewed BAM: The Bottom-up Adaptive Macroeconomics Model
Alejandro Platas López Alejandro Guerra-Hernández | Published Tuesday, January 14, 2020 | Last modified Sunday, July 26, 2020Overview
Purpose
Modeling an economy with stable macro signals, that works as a benchmark for studying the effects of the agent activities, e.g. extortion, at the service of the elaboration of public policies..
…
A double-layer network and the contagion mechanism of China’s financial systemic risk
zou | Published Tuesday, August 13, 2019We establish a double-layer network for China’s financial system, consisting of an interbank lending network and a cross-shareholding network. The loss of diffusion in an interbank lending channel independently, a cross-shareholding channel independently and a double-layer contagion channel after one of the financial institutions goes bankrupt with an initial shock are simulated to explore the nonlinear evolution mechanism of financial risk and impact factors of financial systemic risk in China.
Network formation on a two-layer multiplex with shocks
Paul Smaldino | Published Monday, November 27, 2017A dynamic model of social network formation on single-layer and multiplex networks with structural incentives that vary over time.
Dynamic Interbank Network Simulator
Valentina Guleva | Published Wednesday, November 23, 2016 | Last modified Monday, April 13, 2020The model provides instruments for the simulation of interbank network evolution. There are tools for dynamic network analysis, allowing to evaluate graph topological invariants, thermodynamic network features and combinational node-based features.
Peer reviewed Simulating the Economic Impact of Boko Haram on a Cameroonian Floodplain
Mark Moritz Nathaniel Henry Sarah Laborde | Published Saturday, October 22, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, June 07, 2017This model examines the potential impact of market collapse on the economy and demography of fishing households in the Logone Floodplain, Cameroon.