About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 247 results for "Julio C%C3%A9sar Acosta%E2%80%93Prado" clear search
Netlogo Earned Value Management Model
Manuel Castañón-Puga Ricardo Fernando Rosales–Cisneros Julio César Acosta–Prado Alfredo Tirado–Ramos Camilo Khatchikian Elías Aburto–Camacllanqui | Published Thursday, November 24, 2022The model aims to illustrate how Earned Value Management (EVM) provides an approach to measure a project’s performance by comparing its actual progress against the planned one, allowing it to evaluate trends to formulate forecasts. The instance performs a project execution and calculates the EVM performance indexes according to a Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB), which integrates the description of the work to do (scope), the deadlines for its execution (schedule), and the calculation of its costs and the resources required for its implementation (cost).
Specifically, we are addressing the following questions: How does the risk of execution delay or advance impact cost and schedule performance? How do the players’ number or individual work capacity impact cost and schedule estimations to finish? Regardless of why workers cause delays or produce overruns in their assignments, does EVM assess delivery performance and help make objective decisions?
To consider our model realistic enough for its purpose, we use the following patterns: The model addresses classic problems of Project Management (PM). It plays the typical task board where workers are assigned to complete a task backlog in project performance. Workers could delay or advance in the task execution, and we calculate the performance using the PMI-recommended Earned Value.
The uFUNK Model
Davide Secchi | Published Monday, August 31, 2020The agent-based simulation is set to work on information that is either (a) functional, (b) pseudo-functional, (c) dysfunctional, or (d) irrelevant. The idea is that a judgment on whether information falls into one of the four categories is based on the agent and its network. In other words, it is the agents who interprets a particular information as being (a), (b), (c), or (d). It is a decision based on an exchange with co-workers. This makes the judgment a socially-grounded cognitive exercise. The uFUNK 1.0.2 Model is set on an organization where agent-employee work on agent-tasks.
Agents’ beliefs and the evolution of institutions for common-pool resource management
Giangiacomo Bravo | Published Friday, December 17, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013C++ and Netlogo models presented in G. Bravo (2011), “Agents’ beliefs and the evolution of institutions for common-pool resource management”. Rationality and Society 23(1).
SLUCEII LUXE (Land Use in an eXurban Environment)
Qingxu Huang Rick L Riolo Shipeng Sun Derek Robinson Dawn Parker Tatiana Filatova Meghan Hutchins Dan Brown | Published Tuesday, September 10, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, October 22, 2022LUXE is a land-use change model featuring different levels of land market implementation. It integrates utility measures, budget constraints, competitive bidding, and market interactions to model land-use change in exurban environment.
00 PSoup V1.22 – Primordial Soup
Garvin Boyle | Published Thursday, April 13, 2017PSoup is an educational program in which evolution is demonstrated, on the desk-top, as you watch. Blind bugs evolve sophisticated heuristic search algorithms to be the best at finding food fast.
The simulation on the study of the optimal business strategy with the interaction between technologies and consumers.
sej-yoo | Published Monday, June 27, 2022 | Last modified Monday, July 04, 2022HOW IT WORKS
This model consists of three agents, and each agent type operates per business theories as below.
a. New technologies(Tech): It evolves per sustaining or disruptive technology trajectory with the constraint of project management triangle (Scope, Time, Quality, and Cost).
b. Entrepreneurs(Entre): It builds up the solution by combining Tech components per its own strategy (Exploration, Exploitation, or Ambidex).
c. Consumer(Consumer): It selects the solution per its own preference due to Diffusion of innovation theory (Innovators, Early Adopters, Early Majority, Late Majority, Laggards)
…
The Bronze Age Collapse model (BACO model)
Marco Vidal-Cordasco | Published Friday, October 09, 2020The Bronze Age Collapse model (BACO model) is written using free NetLogo software v.6.0.3. The purpose of using the BACO model is to develop a tool to identify and analyse the main factors that made the Late Bronze Age and Early Iron Age socio-ecological system resilient or vulnerable in the face of the environmental aridity recorded in the Aegean. The model explores the relationship between dependent and independent variables. Independent variables are: a) inter-annual rainfall variability for the Late Bronze Age and Early Iron Age in the eastern Mediterranean, b) intensity of raiding, c) percentage of marine, agricultural and other calorie sources included in the diet, d) soil erosion processes, e) farming assets, and d) storage capacity. Dependent variables are: a) human pressure for land, b) settlement patterns, c) number of commercial exchanges, d) demographic behaviour, and e) number of migrations.
FEARLUS-SPOMM
Dawn Parker Gary Polhill Nick Gotts Alistair Law Luis Izquierdio Alessandro Gimona Lee-Ann Sutherland | Published Friday, March 25, 2016This is a coupled conceptual model of agricultural land decision-making and incentivisation and species metacommunities.
Peer reviewed Virus Transmission with Super-spreaders
J M Applegate | Published Saturday, September 11, 2021A curious aspect of the Covid-19 pandemic is the clustering of outbreaks. Evidence suggests that 80\% of people who contract the virus are infected by only 19% of infected individuals, and that the majority of infected individuals faile to infect another person. Thus, the dispersion of a contagion, $k$, may be of more use in understanding the spread of Covid-19 than the reproduction number, R0.
The Virus Transmission with Super-spreaders model, written in NetLogo, is an adaptation of the canonical Virus Transmission on a Network model and allows the exploration of various mitigation protocols such as testing and quarantines with both homogenous transmission and heterogenous transmission.
The model consists of a population of individuals arranged in a network, where both population and network degree are tunable. At the start of the simulation, a subset of the population is initially infected. As the model runs, infected individuals will infect neighboring susceptible individuals according to either homogenous or heterogenous transmission, where heterogenous transmission models super-spreaders. In this case, k is described as the percentage of super-spreaders in the population and the differing transmission rates for super-spreaders and non super-spreaders. Infected individuals either recover, at which point they become resistant to infection, or die. Testing regimes cause discovered infected individuals to quarantine for a period of time.
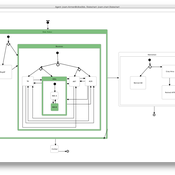
Life Cycle Cost of Military Manpower Model
Jonathan Ozik Todd Combs | Published Monday, January 05, 2015We demonstrate how Repast Simphony statecharts can efficiently encapsulate the deep classification hierarchy of the U.S. Air Force for manpower life cycle costing.
Displaying 10 of 247 results for "Julio C%C3%A9sar Acosta%E2%80%93Prado" clear search