About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 21 results for "Benoit Sarrazin" clear search
TIP TOP Landscape
Patrick Taillandier Nesrine Ayari Claude Janin Benoit Sarrazin Dominique Trévisan | Published Wednesday, September 04, 2019The model aims at reproducing the evolution of the land-use in an agricultural territory at the plot scale. It enables to simulate the affectation of land-use, the crop rotation and technical operations for each plot of the different farms of the territory. It allows as well for crop farms to simulate the daily state of plots (sowed, plowed, harvested, biomass indicator). The model is used as an input for the water pollution model allowing to determine the flow of nitrate, phosphorus and suspended matter in the territory according to the landscape configuration.
FilterBubbles_in_Carley1991
Benoît Desmarchelier | Published Wednesday, May 21, 2025The model is an extension of: Carley K. (1991) “A theory of group stability”, American Sociological Review, vol. 56, pp. 331-354.
The original model from Carley (1991) works as follows:
- Agents know or ignore a series of knowledge facts;
- At each time step, each agent i choose a partner j to interact with at random, with a probability of choice proportional to the degree of knowledge facts they have in common.
- Agents interact synchronously. As such, interaction happens only if the partnert j is not already busy interacting with someone else.
…
CITMOD A Tax-Benefit Modeling System for the average citizen
Philip Truscott | Published Monday, August 15, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Must tax-benefit policy making be limited to the ‘experts’?
Optimal Trading Strategies of Agents in a Population of Firms: An Agent-Based Approach to Soccer Transfer Markets
Kehinde Salau | Published Tuesday, December 16, 2008 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Default Initial skill, read ODD for more info. The purpose of the model presented by Salau is to study the ’player profit vs. club benefit’ dilemma present in professional soccer organizations.
A simple Multi-Agent System of the Tragedy Of the Commons (MASTOC-s)
Julia Schindler | Published Friday, June 29, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a simple model replicating Hardin’s Tragedy of the Commons using reactive agents that have psychological behavioral and social preferences.
A consumer-demand simulation for Smart Metering tariffs (Innovation Diffusion)
Martin Rixin | Published Thursday, August 18, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An Agent-based model simulates consumer demand for Smart Metering tariffs. It utilizes the Bass Diffusion Model and Rogers´s adopter categories. Integration of empirical census microdata enables a validated socio-economic background for each consumer.
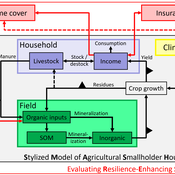
SMASH: Stylized Model of Agricultural Smallholder Households
Tim Williams | Published Tuesday, December 08, 2020The SMASH model is an agent-based model of rural smallholder households. It models households’ evolving income and wealth, which they earn through crop sales. Wealth is carried in the form of livestock, which are grazed on an external rangeland (exogenous) and can be bought/sold as investment/coping mechanisms. The model includes a stylized representation of soil nutrient dynamics, modeling the inflows and outflows of organic and inorganic nitrogen from each household’s field.
The model has been applied to assess the resilience-enhancing effects of two different farm-level adaptation strategies: legume cover cropping and crop insurance. These two strategies interact with the model through different mechanims - legume cover cropping through ecological mechanisms and crop insurance through financial mechanisms. The model can be used to investigate the short- and long-term effects of these strategies, as well as how they may differently benefit different types of household.
The emergence of tag-mediated altruism in structured societies
Shade Shutters David Hales | Published Tuesday, January 20, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, March 02, 2023This abstract model explores the emergence of altruistic behavior in networked societies. The model allows users to experiment with a number of population-level parameters to better understand what conditions contribute to the emergence of altruism.
Peer reviewed ABM for Social Cohesion and Wellbeing(ABMSCWB)
Taseer Salahuddin Hasan Vergil | Published Wednesday, June 25, 2025ABM model studying impact of social cohesion on wellbeing of a society. Ibn Khaldun’s cyclical theory of history is being used as the theoretical lens along with some other theories. Social cohesion is measured as TSC = (TVE + 2 * (TPI * TPL - TNI * TNL))/((TPI+TNI))
Where
TSC total-social-cohesion ; Variable for social cohesion
TPI total-positive-interactions ; Count of positive interactions
TNI total-negative-interactions ; Count of negative interactions
TPL total-positive-learning ; Count of positive learning outcomes
…
U-TRANS Modelling Urban Transition with Coupled Housing and Labour Markets
Bernardo Furtado Jiaqi Ge | Published Monday, July 31, 2023We develop an agent-based model (U-TRANS) to simulate the transition of an abstract city under an industrial revolution. By coupling the labour and housing markets, we propose a holistic framework that incorporates the key interacting factors and micro processes during the transition. Using U-TRANS, we look at five urban transition scenarios: collapse, weak recovery, transition, enhanced training and global recruit, and find the model is able to generate patterns observed in the real world. For example, We find that poor neighbourhoods benefit the most from growth in the new industry, whereas the rich neighbourhoods do better than the rest when the growth is slow or the situation deteriorates. We also find a (subtle) trade-off between growth and equality. The strategy to recruit a large number of skilled workers globally will lead to higher growth in GDP, population and human capital, but it will also entail higher inequality and market volatility, and potentially create a divide between the local and international workers. The holistic framework developed in this paper will help us better understand urban transition and detect early signals in the process. It can also be used as a test-bed for policy and growth strategies to help a city during a major economic and technological revolution.
Displaying 10 of 21 results for "Benoit Sarrazin" clear search