About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 117 results structure clear search
City Sandbox
Javier Sandoval | Published Thursday, January 09, 2020This model grows land use patterns that emerge as a result of land-use compatibilities stablished in urban development plans, land topography, and street networks. It contains urban brushes to paint streets and land uses as a way to learn about urban pattern emergence through free experimentation.
A Pastoral Stoking Strategy Model with Fodder Import and Loan Scenarios
Yanbo Li | Published Tuesday, December 24, 2019This model was built to estimate the impacts of exogenous fodder input and credit loans services on livelihood, rangeland health and profits of pastoral production in a small holder pastoral household in the arid steppe rangeland of Inner Mongolia, China. The model simulated the long-term dynamic of herd size and structure, the forage demand and supply, the cash flow, and the situation of loan debt under three different stocking strategies: (1) No external fodder input, (2) fodders were only imported when natural disaster occurred, and (3) frequent import of external fodder, with different amount of available credit loans. Monte-Carlo method was used to address the influence of climate variability.
Peer reviewed MIOvCWD
Aniruddha Belsare | Published Friday, December 13, 2019MIOvCWD is a spatially-explicit, agent-based model designed to simulate the spread of chronic wasting disease (CWD) in Michigan’s white-tailed deer populations. CWD is an emerging prion disease of North American cervids (white-tailed deer Odocoileus virginianus, mule deer Odocoileus hemionus, and elk Cervus elaphus) that is being actively managed by wildlife agencies in most states and provinces in North America, including Michigan. MIOvCWD incorporates features like deer population structure, social organization and behavior that are particularly useful to simulate CWD dynamics in regional deer populations.
Cultural Evolution of Sustainable Behaviours: Landscape of Affordances Model
Nikita Strelkovskii Roope Oskari Kaaronen | Published Wednesday, December 04, 2019 | Last modified Wednesday, December 04, 2019This NetLogo model illustrates the cultural evolution of pro-environmental behaviour patterns. It illustrates how collective behaviour patterns evolve from interactions between agents and agents (in a social network) as well as agents and the affordances (action opportunities provided by the environment) within a niche. More specifically, the cultural evolution of behaviour patterns is understood in this model as a product of:
- The landscape of affordances provided by the material environment,
- Individual learning and habituation,
- Social learning and network structure,
- Personal states (such as habits and attitudes), and
…
Prisoner's Tournament
Kristin Crouse | Published Wednesday, November 06, 2019 | Last modified Wednesday, December 15, 2021This model replicates the Axelrod prisoner’s dilemma tournaments. The model takes as input a file of strategies and pits them against each other to see who achieves the best payoff in the end. Change the payoff structure to see how it changes the tournament outcome!
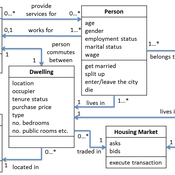
Demography, Industry and Residential Choice (DIReC) model
Jiaqi Ge | Published Wednesday, September 04, 2019The integrated and spatially-explicit ABM, called DIReC (Demography, Industry and Residential Choice), has been developed for Aberdeen City and the surrounding Aberdeenshire (Ge, Polhill, Craig, & Liu, 2018). The model includes demographic (individual and household) models, housing infrastructure and occupancy, neighbourhood quality and evolution, employment and labour market, business relocation, industrial structure, income distribution and macroeconomic indicators. DIReC includes a detailed spatial housing model, basing preference models on house attributes and multi-dimensional neighbourhood qualities (education, crime, employment etc.).
The dynamic ABM simulates the interactions between individuals, households, the labour market, businesses and services, neighbourhoods and economic structures. It is empirically grounded using multiple data sources, such as income and gender-age distribution across industries, neighbourhood attributes, business locations, and housing transactions. It has been used to study the impact of economic shocks and structural changes, such as the crash of oil price in 2014 (the Aberdeen economy heavily relies on the gas and oil sector) and the city’s transition from resource-based to a green economy (Ge, Polhill, Craig, & Liu, 2018).
Peer reviewed Organizational behavior in the hierarchy model
Smarzhevskiy Ivan | Published Tuesday, June 18, 2019 | Last modified Wednesday, July 31, 2019In a two-level hierarchical structure (consisting of the positions of managers and operators), persons holding these positions have a certain performance and the value of their own (personal perception in this, simplified, version of the model) perception of each other. The value of the perception of each other by agents is defined as a random variable that has a normal distribution (distribution parameters are set by the control elements of the interface).
In the world of the model, which is the space of perceptions, agents implement two strategies: rapprochement with agents that perceive positively and distance from agents that perceive negatively (both can be implemented, one of these strategies, or neither, the other strategy, which makes the agent stationary). Strategies are implemented in relation to those agents that are in the radius of perception (PerRadius).
The manager (Head) forms a team of agents. The performance of the group (the sum of the individual productivities of subordinates, weighted by the distance from the leader) varies depending on the position of the agents in space and the values of their individual productivities. Individual productivities, in the current version of the model, are set as a random variable distributed evenly on a numerical segment from 0 to 100. The manager forms the team 1) from agents that are in (organizational) radius (Op_Radius), 2) among agents that the manager perceives positively and / or negatively (both can be implemented, one of the specified rules, or neither, which means the refusal of the command formation).
Agents can (with a certain probability, given by the variable PrbltyOfDecisn%), in case of a negative perception of the manager, leave his group permanently.
It is possible in the model to change on the fly radii values, update the perception value across the entire population and the perception of an individual agent by its neighbors within the perception radius, and the probability values for a subordinate to make a decision about leaving the group.
You can also change the set of strategies for moving agents and strategies for recruiting a team manager. It is possible to add a randomness factor to the movement of agents (Stoch_Motion_Speed, the default is set to 0, that is, there are no random movements).
…
MERCURY extension: population
Tom Brughmans | Published Thursday, May 23, 2019This model is an extended version of the original MERCURY model (https://www.comses.net/codebases/4347/releases/1.1.0/ ) . It allows for experiments to be performed in which empirically informed population sizes of sites are included, that allow for the scaling of the number of tableware traders with the population of settlements, and for hypothesised production centres of four tablewares to be used in experiments.
Experiments performed with this population extension and substantive interpretations derived from them are published in:
Hanson, J.W. & T. Brughmans. In press. Settlement scale and economic networks in the Roman Empire, in T. Brughmans & A.I. Wilson (ed.) Simulating Roman Economies. Theories, Methods and Computational Models. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
…
GRASP world
Gert Jan Hofstede | Published Tuesday, April 16, 2019This agent-based model investigates group longevity in a population in a foundational way, using theory on social relations and culture. It is the first application of the GRASP meta-model for social agents, containing elements of Groups, Rituals, Affiliation, Status, and Power. It can be considered an exercise in artificial sociality: a culture-general, content-free base-line trust model from which to engage in more specific studies. Depending on cultural settings for individualism and power distance, as well as settings for xenophobia and for the increase of trust over group life, the GRASP world model generates a variety of patters. Number of groups ranges from one to many, composition from random to segregated, and pattern genesis from rapid to many hundreds of time steps. This makes GRASP world an instrument that plausibly models some basic elements of social structure in different societies.
Opinion Dynamics with various confidence distributions
Jonas Lindblad | Published Friday, September 28, 2018Project for the course “Introduction to Agent-Based Modeling”.
The NetLogo model implements an Opinion Dynamics model with different confidence distributions, inspired by the Bounded Confidence model presented by Hegselmann and Krause in 2002. Hegselmann and Krause used a model with uniform distribution of confidence, but one could imagine agents that are more confident in their own opinions than others. Confidence with triangular, semi-circular, and Gaussian distributions are implemented. Moreover, network structure is optional and can be taken into account in the agent’s confidence such that agents assign less confidence the further away from them other agents are.
Displaying 10 of 117 results structure clear search