About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1112 results for "Oto Hudec" clear search
Peer reviewed Urban Transport Mode Choices
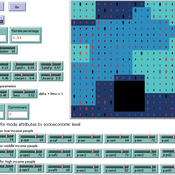
Kathleen Salazar -Serna Lorena Cadavid Carlos Franco | Published Thursday, May 22, 2025The model represents urban commuters’ transport mode choices among cars, public transit, and motorcycles—a mode highly prevalent in developing countries. Using an agent-based modeling approach, it simulates transport dynamics and serves as a testbed for evaluating policies aimed at improving mobility.
The model simulates an ecosystem of human agents who decide, at each time step, which mode of transportation to use for commuting to work. Their decision is based on a combination of personal satisfaction with their most recent journey—evaluated across a vector of individual needs—the information they crowdsource from their social network, and their personal uncertainty regarding trying new transport options.
Agents are assigned demographic attributes such as sex, age, and income level, and are distributed across city neighborhoods according to their socioeconomic status. To represent social influence in decision-making, agents are connected via a scale-free social network topology, where connections are more likely among agents within the same socioeconomic group, reflecting the tendency of individuals to form social ties with similar others.
…
An agent-based model of the journey of victim/survivors through local authority domestic abuse support services in the UK
Bruce Edmonds | Published Monday, July 28, 2025This model played a small part in the UK government’s review of the working of local authority implementation of the Domestic Abuse legislation. The model explicitly represents victim-survivor families as they: (a) try to contact the local DA support system, (b) are triaged by the system and (if there is space) allocated to safe temporary accomodation (c) recieve support services from this position and (d) eventually move on to more permenant accomodation. The purpose of the model was to understand some possible ways in which the implementation of DA Duty, might be frustrated in practice, the identification of gaps in the evidence base and to inform the developing Theory of Change. The key measures used for assessing outcomes in the model were the number of families helped and the services that were delivered to them. The exploration was grounded for in two archetypal cases: that of a relatively immature system for the delivery of DA services and a more mature one (based on actual local authority cases, but not based on any single one). See the official report under associated publications for a summary of results.
The Cardial Spread Model
Sean Bergin | Published Friday, September 29, 2017 | Last modified Monday, February 04, 2019The purpose of this model is to provide a platform to test and compare four conceptual models have been proposed to explain the spread of the Impresso-Cardial Neolithic in the west Mediterranean.
Growing Unpopular Norms. A Network-Situated ABM of Norm Choice.
C Merdes | Published Tuesday, November 22, 2016 | Last modified Saturday, March 17, 2018The model’s purpose is to provide a potential explanation for the emergence, sustenance and decline of unpopular norms based on pluralistic ignorance on a social network.
Simulation of the Governance of Complex Systems
Fabian Adelt Johannes Weyer Robin D Fink Andreas Ihrig | Published Monday, December 18, 2017 | Last modified Friday, March 02, 2018Simulation-Framework to study the governance of complex, network-like sociotechnical systems by means of ABM. Agents’ behaviour is based on a sociological model of action. A set of basic governance mechanisms helps to conduct first experiments.
Crowdworking Model
Georg Jäger | Published Wednesday, September 25, 2019The purpose of this agent-based model is to compare different variants of crowdworking in a general way, so that the obtained results are independent of specific details of the crowdworking platform. It features many adjustable parameters that can be used to calibrate the model to empirical data, but also when not calibrated it yields essential results about crowdworking in general.
Agents compete for contracts on a virtual crowdworking platform. Each agent is defined by various properties like qualification and income expectation. Agents that are unable to turn a profit have a chance to quit the crowdworking platform and new crowdworkers can replace them. Thus the model has features of an evolutionary process, filtering out the ill suited agents, and generating a realistic distribution of agents from an initially random one. To simulate a stable system, the amount of contracts issued per day can be set constant, as well as the number of crowdworkers. If one is interested in a dynamically changing platform, the simulation can also be initialized in a way that increases or decreases the number of crowdworkers or number of contracts over time. Thus, a large variety of scenarios can be investigated.
Exploring social psychology theory for modelling farmer decision-making
James Millington | Published Tuesday, September 18, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013To investigate the potential of using Social Psychology Theory in ABMs of natural resource use and show proof of concept, we present an exemplary agent-based modelling framework that explicitly represents multiple and hierarchical agent self-concepts
9 Maturity levels in Empirical Validation - An innovation diffusion example
Martin Rixin | Published Wednesday, October 19, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Several taxonomies for empirical validation have been published. Our model integrates different methods to calibrate an innovation diffusion model, ranging from simple randomized input validation to complex calibration with the use of microdata.
CONSERVAT
Pieter Van Oel | Published Monday, April 13, 2015The CONSERVAT model evaluates the effect of social influence among farmers in the Lake Naivasha basin (Kenya) on the spatiotemporal diffusion pattern of soil conservation effort levels and the resulting reduction in lake sedimentation.
Segregation and Opinion Polarization
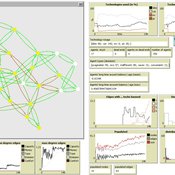
Thomas Feliciani Andreas Flache Jochem Tolsma | Published Wednesday, April 13, 2016This is a tool to explore the effects of groups´ spatial segregation on the emergence of opinion polarization. It embeds two opinion formation models: a model of negative (and positive) social influence and a model of persuasive argument exchange.
Displaying 10 of 1112 results for "Oto Hudec" clear search