About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 318 results for "J Hall" clear search
An agent-based model to simulate meat consumption behaviour of consumers in Britain
Andrea Scalco | Published Friday, October 18, 2019The current rate of production and consumption of meat poses a problem both to peoples’ health and to the environment. This work aims to develop a simulation of peoples’ meat consumption behaviour in Britain using agent-based modelling. The agents represent individual consumers. The key variables that characterise agents include sex, age, monthly income, perception of the living cost, and concerns about the impact of meat on the environment, health, and animal welfare. A process of peer influence is modelled with respect to the agents’ concerns. Influence spreads across two eating networks (i.e. co-workers and household members) depending on the time of day, day of the week, and agents’ employment status. Data from a representative sample of British consumers is used to empirically ground the model. Different experiments are run simulating interventions of application of social marketing campaigns and a rise in price of meat. The main outcome is the average weekly consumption of meat per consumer. A secondary outcome is the likelihood of eating meat.
Team Structure and Task Performance
Davide Secchi Martin Neumann | Published Monday, August 05, 2024This model was designed to study resilience in organizations. Inspired by ethnographic work, it follows the simple goal to understand whether team structure affects the way in which tasks are performed. In so doing, it compares the ‘hybrid’ data-inspired structure with three more traditional structures (i.e. hierarchy, flexible/relaxed hierarchy, and anarchy/disorganization).
Two agent-based models of cooperation in dynamic groups and fixed social networks
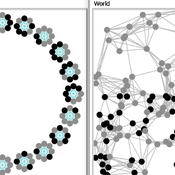
Carlos A. de Matos Fernandes | Published Thursday, January 20, 2022Both models simulate n-person prisoner dilemma in groups (left figure) where agents decide to C/D – using a stochastic threshold algorithm with reinforcement learning components. We model fixed (single group ABM) and dynamic groups (bad-barrels ABM). The purpose of the bad-barrels model is to assess the impact of information during meritocratic matching. In the bad-barrels model, we incorporated a multidimensional structure in which agents are also embedded in a social network (2-person PD). We modeled a random and homophilous network via a random spatial graph algorithm (right figure).
Forager mobility and interaction
L S Premo | Published Thursday, January 10, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a relatively simple foraging-radius model, as described first by Robert Kelly, that allows one to quantify the effect of increased logistical mobility (as represented by increased effective foraging radius, r_e) on the likelihood that 2 randomly placed central place foragers will encounter one another within 5000 time steps.
Peer reviewed Neighbor Influenced Energy Retrofit (NIER) agent-based model
Eric Boria | Published Friday, April 03, 2020The NIER model is intended to add qualitative variables of building owner types and peer group scales to existing energy efficiency retrofit adoption models. The model was developed through a combined methodology with qualitative research, which included interviews with key stakeholders in Cleveland, Ohio and Detroit and Grand Rapids, Michigan. The concepts that the NIER model adds to traditional economic feasibility studies of energy retrofit decision-making are differences in building owner types (reflecting strategies for managing buildings) and peer group scale (neighborhoods of various sizes and large-scale Districts). Insights from the NIER model include: large peer group comparisons can quickly raise the average energy efficiency values of Leader and Conformist building owner types, but leave Stigma-avoider owner types as unmotivated to retrofit; policy interventions such as upgrading buildings to energy-related codes at the point of sale can motivate retrofits among the lowest efficient buildings, which are predominantly represented by the Stigma-avoider type of owner; small neighborhood peer groups can successfully amplify normal retrofit incentives.
PopComp
Andre Costopoulos | Published Thursday, December 10, 2020PopComp by Andre Costopoulos 2020
[email protected]
Licence: DWYWWI (Do whatever you want with it)
I use Netlogo to build a simple environmental change and population expansion and diffusion model. Patches have a carrying capacity and can host two kinds of populations (APop and BPop). Each time step, the carrying capacity of each patch has a given probability of increasing or decreasing up to a maximum proportion.
…
Musical Chairs
Andreas Angourakis | Published Wednesday, February 03, 2016 | Last modified Friday, March 11, 2016This Agent-Based model intends to explore the conditions for the emergence and change of land use patterns in Central Asian oases and similar contexts.
World of Cows - Exploring land-use policies for a dairy-farm world (teaching modeling complex human-environment systems)
Maria Haensel Thomas Michael Schmitt Jakob Bogenreuther | Published Wednesday, January 11, 2023In the “World of Cows”, dairy farmers run their farms and interact with each other, the surrounding agricultural landscape, and the economic and political framework. The model serves as an exemplary case of an interdependent human-environment system.
With the model, users can analyze the influence of policies and markets on land use decisions of dairy farms. The land use decisions taken by farms determine the delivered ecosystem services on the landscape level. Users can choose a combination of five policy options and how strongly market prices fluctuate. Ideally, the choice of policy options fulfills the following three “political goals” 1) dairy farming stays economically viable, 2) the provision of ecosystem services is secured, and 3) government spending on subsidies is as low as possible.
The model has been designed for students to practice agent-based modeling and analyze the impacts of land use policies.
Peer reviewed HUMLAND: HUMan impact on LANDscapes agent-based model
Fulco Scherjon Anastasia Nikulina Anhelina Zapolska Maria Antonia Serge Marco Davoli Dave van Wees Katharine MacDonald | Published Monday, October 16, 2023The HUMan impact on LANDscapes (HUMLAND) model has been developed to track and quantify the intensity of different impacts on landscapes at the continental level. This agent-based model focuses on determining the most influential factors in the transformation of interglacial vegetation with a specific emphasis on burning organized by hunter-gatherers. HUMLAND integrates various spatial datasets as input and target for the agent-based model results. Additionally, the simulation incorporates recently obtained continental-scale estimations of fire return intervals and the speed of vegetation regrowth. The obtained results include maps of possible scenarios of modified landscapes in the past and quantification of the impact of each agent, including climate, humans, megafauna, and natural fires.
Peer reviewed The Andean Resource Management Model (ARMM)
Olga Palacios | Published Tuesday, January 20, 2026ARMM is a theoretical agent-based model that formalizes Murra’s Theory of Verticality (Murra, 1972) to explore how multi-zonal resource management systems emerge in mountain landscapes. The model identifies the social, political, and economic mechanisms that enable vertical complementarity across ecological gradients.
Built in NetLogo, ARMM employs an abstract 111×111 grid divided into four Andean ecological zones (Altiplano, Highland, Lowland, Coast), each containing up to 18 resource types distributed according to ecological suitability. To test general theoretical principles rather than replicate specific geography, resource locations are randomized at each model initialization.
Settlement agents pursue one of two economic strategies: diversification (seeking resource variety, maximum 2 units per type) or accumulation (maximising total quantity, maximum 30 units). Agents move between adjacent zones through hierarchical decision-making, first attempting peaceful interactions—coexistence (governed by tolerance) and trading (governed by cooperation)—before resorting to conflict (theft or takeover, governed by belligerence).
The model demonstrates that vertical complementarity can emerge through fundamentally different mechanisms: either through autonomous mobility under political decentralization or through state-coordinated redistribution under centralization. Sensitivity analysis reveals that belligerence and economic strategy explain approximately 25% of outcome variance, confirming that structural inequalities between zones result from political-economic organization rather than environmental constraints alone.
As a preliminary theoretical model, ARMM intentionally maintains simplicity to isolate core mechanisms and generate testable hypotheses. This foundational framework will guide future empirically-calibrated versions that incorporate specific archaeological settlement data and geographic features from the Carangas region (Bolivia-Chile border), enabling direct comparison between theoretical predictions and observed historical patterns.
Displaying 10 of 318 results for "J Hall" clear search