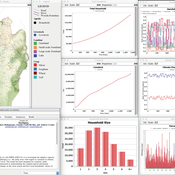
About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 124 results agent-based modeling clear search
Peer reviewed ELTAP-Egy model (Energy Landscape Transition Analysis and Planning in Egypt)
Mostafa Shaaban Jürgen Scheffran Jürgen Böhner Mohamed Salah Elsobki | Published Saturday, December 29, 2018The model investigates conditions, scenarios and strategies for future planning of energy in Egypt, with an emphasis on alternative energy pathways and a sustainable electricity supply mix as part of an energy roadmap till the year 2100. It combines the multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) with agent-based modeling (ABM) and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) visualization to integrate the interactions of the decisions of multi-agents, the multi-criteria evaluation of sustainability, the time factor and the site factors to assess the transformation of energy landscapes.
word-of-mouth dynamics with information seeking
Samuel Thiriot | Published Wednesday, October 24, 2018Studies on word-of-mouth identify two behaviors leading to transmission of information between individuals: proactive transmission of information, and information seeking. Individuals who are aware might be curious of it and start seeking for information; they might find around them the expertise held by another individual. Field studies indicate individuals do not adopt an innovation if they don’t hold the corresponding expertise. This model describes this information seeking behavior, and enables the exploration of the dynamics which emerges out of it.
Opinion Dynamics with various confidence distributions
Jonas Lindblad | Published Friday, September 28, 2018Project for the course “Introduction to Agent-Based Modeling”.
The NetLogo model implements an Opinion Dynamics model with different confidence distributions, inspired by the Bounded Confidence model presented by Hegselmann and Krause in 2002. Hegselmann and Krause used a model with uniform distribution of confidence, but one could imagine agents that are more confident in their own opinions than others. Confidence with triangular, semi-circular, and Gaussian distributions are implemented. Moreover, network structure is optional and can be taken into account in the agent’s confidence such that agents assign less confidence the further away from them other agents are.
An Agent-Based Simulation of Continuous-Time Public Goods Games
Tuong Manh Vu | Published Thursday, May 17, 2018 | Last modified Tuesday, April 02, 2019To our knowledge, this is the first agent-based simulation of continuous-time PGGs (where participants can change contributions at any time) which are much harder to realise within both laboratory and simulation environments.
Work related to this simulation has been published in the following journal article:
Vu, Tuong Manh, Wagner, Christian and Siebers, Peer-Olaf (2019) ‘ABOOMS: Overcoming the Hurdles of Continuous-Time Public Goods Games with a Simulation-Based Approach’ Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation 22 (2) 7 http://jasss.soc.surrey.ac.uk/22/2/7.html. doi: 10.18564/jasss.3995
Abstract:
…
PolicySpace: agent-based modeling
Francisco Miguel Quesada Bernardo Furtado Isaque Daniel Rocha Eberhardt | Published Tuesday, March 06, 2018PolicySpace models public policies within an empirical, spatial environment using data from 46 metropolitan regions in Brazil. The model contains citizens, markets, residences, municipalities, commuting and a the tax scheme. In the associated publications (book in press and https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.00259) we validate the model and demonstrate an application of the fiscal analysis. Besides providing the basics of the platform, our results indicate the relevance of the rules of taxes transfer for cities’ quality of life.
Team Problem Solving and Motivation under Disorganization
Dinuka Herath | Published Sunday, August 13, 2017The model combines the two elements of disorganization and motivation to explore their impact on teams. Effects of disorganization on team task performance (problem solving)
OMOLAND-CA: An Agent-Based Modeling of Rural Households’ Adaptation to Climate Change
Atesmachew Hailegiorgis Andrew Crooks Claudio Cioffi-Revilla | Published Tuesday, July 25, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, July 10, 2018The purpose of the OMOLAND-CA is to investigate the adaptive capacity of rural households in the South Omo zone of Ethiopia with respect to variation in climate, socioeconomic factors, and land-use at the local level.
Peer reviewed MOOvPOP
Matthew Gompper Aniruddha Belsare Joshua J Millspaugh | Published Monday, April 10, 2017 | Last modified Saturday, April 19, 2025MOOvPOP is designed to simulate population dynamics (abundance, sex-age composition and distribution in the landscape) of white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) for a selected sampling region.
Peer reviewed MOOvPOPsurveillance
Matthew Gompper Aniruddha Belsare Joshua J Millspaugh | Published Tuesday, April 04, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, May 12, 2020MOOvPOPsurveillance was developed as a tool for wildlife agencies to guide collection and analysis of disease surveillance data that relies on non-probabilistic methods like harvest-based sampling.
LimnoSES - social-ecological lake management undergoing regime shifts
Romina Martin | Published Thursday, November 24, 2016 | Last modified Friday, January 18, 2019LimnoSES is a coupled system dynamics, agent-based model to simulate social-ecological feedbacks in shallow lake use and management.
Displaying 10 of 124 results agent-based modeling clear search