About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 21 results for "Mohamed Salah Elsobki" clear search
MCA-SdA (ABM of mining-community-aquifer interactions in Salar de Atacama, Chile)
Wenjuan Liu | Published Tuesday, December 01, 2020 | Last modified Thursday, November 04, 2021This model represnts an unique human-aquifer interactions model for the Li-extraction in Salar de Atacama, Chile. It describes the local actors’ experience of mining-induced changes in the socio-ecological system, especially on groundwater changes and social stressors. Social interactions are designed specifically according to a long-term local fieldwork by Babidge et al. (2019, 2020). The groundwater system builds on the FlowLogo model by Castilla-Rho et al. (2015), which was then parameterized and calibrated with local hydrogeological inputs in Salar de Atacama, Chile. The social system of the ABM is defined and customozied based on empirical studies to reflect three major stressors: drought stress, population stress, and mining stress. The model reports evolution of groundwater changes and associated social stress dynamics within the modeled time frame.
Peer reviewed ELTAP-Egy model (Energy Landscape Transition Analysis and Planning in Egypt)
Mostafa Shaaban Jürgen Scheffran Jürgen Böhner Mohamed Salah Elsobki | Published Saturday, December 29, 2018The model investigates conditions, scenarios and strategies for future planning of energy in Egypt, with an emphasis on alternative energy pathways and a sustainable electricity supply mix as part of an energy roadmap till the year 2100. It combines the multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) with agent-based modeling (ABM) and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) visualization to integrate the interactions of the decisions of multi-agents, the multi-criteria evaluation of sustainability, the time factor and the site factors to assess the transformation of energy landscapes.
Optimal Trading Strategies of Agents in a Population of Firms: An Agent-Based Approach to Soccer Transfer Markets
Kehinde Salau | Published Tuesday, December 16, 2008 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Default Initial skill, read ODD for more info. The purpose of the model presented by Salau is to study the ’player profit vs. club benefit’ dilemma present in professional soccer organizations.
ABM for Underwater optical wireless communication in a water tank
Mohamed ABID | Published Sunday, May 29, 2022This model simulates the propagation of photons in a water tank. A source of light emits an impulse of photons with equal energy represented by yellow dots. These photons are then scattered by water particles before possibly reaching the photo-detector represented by a gray line. Different types of water are considered. For each one of them we calculate the total received energy.
The water tank is represented by a blue rectangle with fixed dimensions. It’s exposed to the air interface and has totally absorbent barriers. Four types of water are supported. Each one is characterized by its absorption and scattering coefficients.
At the source, the photons are generated uniformly with a random direction within the beamwidth. Each photon travels a random distance drawn from a distribution depending on the water characteristics before encountering a water particle.
Based on the updated position of the photon, three situations may occur:
-The photon hits the barrier of the tank on its trajectory. In this case it’s considered as lost since the barriers are assumed totally absorbent.
…
SLUCEII LUXE (Land Use in an eXurban Environment)
Qingxu Huang Rick L Riolo Shipeng Sun Derek Robinson Dawn Parker Tatiana Filatova Meghan Hutchins Dan Brown | Published Tuesday, September 10, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, October 22, 2022LUXE is a land-use change model featuring different levels of land market implementation. It integrates utility measures, budget constraints, competitive bidding, and market interactions to model land-use change in exurban environment.
Heterogeneity of preferences and the dynamics of voluntary contributions to public goods
Engi Amin Amal Soliman Mohamed Abouelela | Published Thursday, August 18, 2016 | Last modified Thursday, January 25, 2018This model simulates the heterogeneity of preferences in a PG game and how the interaction between them affects the dynamics of voluntary contributions. Model is based on the results of a human-based experiment.
The purpose of this model is to enhance a basic ABM through a simple set of rules identified using the activity-driven models in order to produce more realistic patterns of pedestrian movement.
TRAINING AND TURNOVER
Kehinde Salau | Published Tuesday, December 16, 2008 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The purpose of the model presented by Glance et al is to study the ‘contribute vs. free-ride’ dilemma present in organizations.
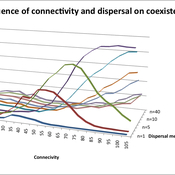
Varying effects of connectivity and dispersal on interacting species dynamics
Kehinde Salau | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An agent-based model of species interaction on fragmented landscape is developed to address the question, how do population levels of predators and prey react with respect to changes in the patch connectivity as well as changes in the sharpness of threshold dispersal?
This model presents an autonomous, two-lane driving environment with a single lane-closure that can be toggled. The four driving scenarios - two baseline cases (based on the real-world) and two experimental setups - are as follows:
- Baseline-1 is where cars are not informed of the lane closure.
- Baseline-2 is where a Red Zone is marked wherein cars are informed of the lane closure ahead.
- Strategy-1 is where cars use a co-operative driving strategy - FAS. <sup>[1]</sup>
- Strategy-2 is a variant of Strategy-1 and uses comfortable deceleration values instead of the vehicle’s limit.
…
Displaying 10 of 21 results for "Mohamed Salah Elsobki" clear search