About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 164 results for "Joshua J Millspaugh" clear search
Thoughtless conformity and spread of norms in an artificial society
Muhammad Azfar Nisar | Published Tuesday, May 27, 2014This model is based on Joshua Epstein’s (2001) model on development of thoughtless conformity in an artificial society of agents.
In-group favoritism due to friend selection strategies based on fixed tag and within-group reputation
Yutaka Nakai | Published Friday, March 28, 2014 | Last modified Friday, March 28, 2014An agent-based model simulates emergence of in-group favoritism. Agents adopt friend selection strategies using an invariable tag and reputations meaning how cooperative others are to a group. The reputation can be seen as a kind of public opinion.
Peer reviewed MOOvPOPsurveillance
Matthew Gompper Aniruddha Belsare Joshua J Millspaugh | Published Tuesday, April 04, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, May 12, 2020MOOvPOPsurveillance was developed as a tool for wildlife agencies to guide collection and analysis of disease surveillance data that relies on non-probabilistic methods like harvest-based sampling.
Peer reviewed MOOvPOP
Matthew Gompper Aniruddha Belsare Joshua J Millspaugh | Published Monday, April 10, 2017 | Last modified Saturday, April 19, 2025MOOvPOP is designed to simulate population dynamics (abundance, sex-age composition and distribution in the landscape) of white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) for a selected sampling region.
Thoughtless conformity and spread of norms in an artificial society (Grid Model)
Muhammad Azfar Nisar | Published Tuesday, May 27, 2014This model is a small extension (rectangular layout) of Joshua Epstein’s (2001) model on development of thoughtless conformity in an artificial society of agents.
Replication of the Demographic Prisoner's Dilemma
Wolfgang Radax | Published Thursday, May 02, 2013The provided source code is the result of our efforts in replicating Epstein’s Demographic Prisoner’s Dilemma. The simulation model is written in Repast/J 3.1.
FilterBubbles_in_Carley1991
Benoît Desmarchelier | Published Wednesday, May 21, 2025The model is an extension of: Carley K. (1991) “A theory of group stability”, American Sociological Review, vol. 56, pp. 331-354.
The original model from Carley (1991) works as follows:
- Agents know or ignore a series of knowledge facts;
- At each time step, each agent i choose a partner j to interact with at random, with a probability of choice proportional to the degree of knowledge facts they have in common.
- Agents interact synchronously. As such, interaction happens only if the partnert j is not already busy interacting with someone else.
…
Peer reviewed Garbage can model Excel reconstruction
Smarzhevskiy Ivan | Published Tuesday, August 19, 2014 | Last modified Tuesday, July 30, 2019Reconstruction of the original code M. Cohen, J. March, and J. Olsen garbage can model, realized by means of Microsoft Office Excel 2010
Adaptive model of a consumer advice network
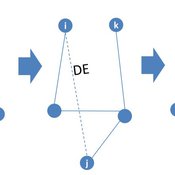
Peng Shao | Published Monday, May 14, 2018In the consumer advice network, users with connections can interact with each other, and the network topology will change during the opinion interaction. When the opinion distance from i to j is greater than the confidence threshold, the two consumers cannot exchange opinions, and the link between them will disconnect with probability DE. Then, a link from node i to node k is established with probability CE and node i learning opinion from node k.
MERCURY extension: transport-cost
Tom Brughmans | Published Monday, July 23, 2018This is extended version of the MERCRUY model (Brughmans 2015) incorporates a ‘transport-cost’ variable, and is otherwise unchanged. This extended model is described in this publication: Brughmans, T., 2019. Evaluating the potential of computational modelling for informing debates on Roman economic integration, in: Verboven, K., Poblome, J. (Eds.), Structural Determinants in the Roman World.
Brughmans, T., 2015. MERCURY: an ABM of tableware trade in the Roman East. CoMSES Comput. Model Libr. URL https://www.comses.net/codebases/4347/releases/1.1.0/
Displaying 10 of 164 results for "Joshua J Millspaugh" clear search