About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 2 of 2 results Metropolises clear search
Peer reviewed PolicySpace2: modeling markets and endogenous public policies
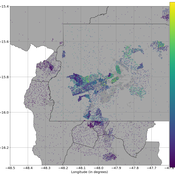
Bernardo Furtado | Published Thursday, February 25, 2021 | Last modified Friday, January 14, 2022Policymakers decide on alternative policies facing restricted budgets and uncertain future. Designing public policies is further difficult due to the need to decide on priorities and handle effects across policies. Housing policies, specifically, involve heterogeneous characteristics of properties themselves and the intricacy of housing markets and the spatial context of cities. We propose PolicySpace2 (PS2) as an adapted and extended version of the open source PolicySpace agent-based model. PS2 is a computer simulation that relies on empirically detailed spatial data to model real estate, along with labor, credit, and goods and services markets. Interaction among workers, firms, a bank, households and municipalities follow the literature benchmarks to integrate economic, spatial and transport scholarship. PS2 is applied to a comparison among three competing public policies aimed at reducing inequality and alleviating poverty: (a) house acquisition by the government and distribution to lower income households, (b) rental vouchers, and (c) monetary aid. Within the model context, the monetary aid, that is, smaller amounts of help for a larger number of households, makes the economy perform better in terms of production, consumption, reduction of inequality, and maintenance of financial duties. PS2 as such is also a framework that may be further adapted to a number of related research questions.
PolicySpace: agent-based modeling
Francisco Miguel Quesada Bernardo Furtado Isaque Daniel Rocha Eberhardt | Published Tuesday, March 06, 2018PolicySpace models public policies within an empirical, spatial environment using data from 46 metropolitan regions in Brazil. The model contains citizens, markets, residences, municipalities, commuting and a the tax scheme. In the associated publications (book in press and https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.00259) we validate the model and demonstrate an application of the fiscal analysis. Besides providing the basics of the platform, our results indicate the relevance of the rules of taxes transfer for cities’ quality of life.