About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 42 results power clear
Peer reviewed Empathy & Power
J Applegate Ned Wellman | Published Monday, November 13, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, December 21, 2017The purpose of this model is to explore the effects of different power structures on a cross-functional team’s prosocial decision making. Are certain power distributions more conducive to the team making prosocial decisions?
Agent-based model of WiFi tracking system in urban environment
Christopher Thron Khoi Tran | Published Friday, April 21, 2017This code simulates the WiFi user tracking system described in: Thron et al., “Design and Simulation of Sensor Networks for Tracking Wifi Users in Outdoor Urban Environments”. Testbenches used to create the figures in the paper are included.
03 MppLab V1.09 – Maximum Power Principle Laboratory
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, April 15, 2017Using webs of replicas of Atwood’s Machine, we explore implications of the Maximum Power Principle. This is one of a series of models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, CmLab.
02 OamLab V1.10 - Open Atwood Machine Laboratory
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, January 31, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, April 13, 2017Using chains of replicas of Atwood’s Machine, this model explores implications of the Maximum Power Principle. It is one of a series of models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, EiLab.
Interplay between stakeholders of the management of a river
Christophe Sibertin-Blanc Pascal Roggero Bertrand Baldet | Published Wednesday, November 12, 2014This model describes and analyses the outcomes of the confrontation of interests, some conflicting, some common, about the management of a small river in SW France
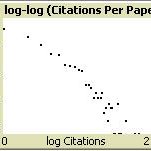
Citation Agents: A model of collective learning through scientific publication
Christopher Watts | Published Friday, July 31, 2015Simulates the construction of scientific journal publications, including authors, references, contents and peer review. Also simulates collective learning on a fitness landscape. Described in: Watts, Christopher & Nigel Gilbert (forthcoming) “Does cumulative advantage affect collective learning in science? An agent-based simulation”, Scientometrics.
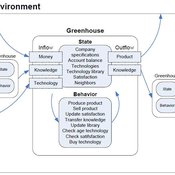
Universal Darwinism in Dutch Greenhouses
Julia Kasmire | Published Wednesday, May 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An ABM, derived from a case study and a series of surveys with greenhouse growers in the Westland, Netherlands. Experiments using this model showshow that the greenhouse horticulture industry displays diversity, adaptive complexity and an uneven distribution, which all suggest that the industry is an evolving system.
WeDiG Sim
Reza Shamsaee | Published Monday, May 14, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013WeDiG Sim- Weighted Directed Graph Simulator - is an open source application that serves to simulate complex systems. WeDiG Sim reflects the behaviors of those complex systems that put stress on scale-free, weightedness, and directedness. It has been implemented based on “WeDiG model” that is newly presented in this domain. The WeDiG model can be seen as a generalized version of “Barabási-Albert (BA) model”. WeDiG not only deals with weighed directed systems, but also it can handle the […]
Societal Simulator v203
Tim Gooding | Published Tuesday, October 01, 2013 | Last modified Friday, November 28, 2014Designed to capture the evolutionary forces of global society.
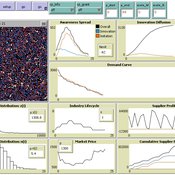
(Policy induced) Diffusion of Innovations - An integrated demand-supply Model based on Cournot Competition
Martin Rixin | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Objective is to simulate policy interventions in an integrated demand-supply model. The underlying demand function links both sides. Diffusion proceeds if interactions distribute awareness (Epidemic effect) and rivalry reduces the market price (Probit effect). Endogeneity is given due to the fact that consumer awareness as well as their willingness-to-pay drives supply-side rivalry. Firm´s entry and exit decisions as well as quantity and price settings are driven by Cournot competition.
Displaying 10 of 42 results power clear