About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 183 results for "Wil Hennen" clear search
06b EiLab_Model_I_V5.00 NL
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, October 05, 2019EiLab - Model I - is a capital exchange model. That is a type of economic model used to study the dynamics of modern money which, strangely, is very similar to the dynamics of energetic systems. It is a variation on the BDY models first described in the paper by Dragulescu and Yakovenko, published in 2000, entitled “Statistical Mechanics of Money”. This model demonstrates the ability of capital exchange models to produce a distribution of wealth that does not have a preponderance of poor agents and a small number of exceedingly wealthy agents.
This is a re-implementation of a model first built in the C++ application called Entropic Index Laboratory, or EiLab. The first eight models in that application were labeled A through H, and are the BDY models. The BDY models all have a single constraint - a limit on how poor agents can be. That is to say that the wealth distribution is bounded on the left. This ninth model is a variation on the BDY models that has an added constraint that limits how wealthy an agent can be? It is bounded on both the left and right.
EiLab demonstrates the inevitable role of entropy in such capital exchange models, and can be used to examine the connections between changing entropy and changes in wealth distributions at a very minute level.
…
Behavioural model
Aulia Imania Sukma | Published Friday, November 07, 2025This repository serves as a design proof for agent-based modeling simulation in heat adaptation behavior. This model was developed as part of the UrbanAir project theme. This repository will be kept updated in the four-year timeline (2025 until 2029).
Alternative Fuel Design/Consumer Choice Model
Rosanna Garcia | Published Wednesday, September 22, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a model of the diffusion of alternative fuel vehicles based on manufacturer designs and consumer choices of those designs. It is written in Netlogo 4.0.3. Because it requires data to upload
Livestock drought insurance model
Birgit Müller Felix John Jürgen Groeneveld Karin Frank Russell Toth | Published Tuesday, December 19, 2017 | Last modified Saturday, April 14, 2018The model analyzes the economic and ecological effects of a provision of livestock drought insurance for dryland pastoralists. More precisely, it yields qualitative insights into how long-term herd and pasture dynamics change through insurance.
Patch choice model from Optimal Foraging Theory (Human Behavioral Ecology)
C Michael Barton | Published Saturday, November 22, 2008 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013NetLogo model of patch choice model from optimal foraging theory (human behavioral ecology).
Consumats on a network
Marco Janssen | Published Tuesday, January 14, 2020 | Last modified Tuesday, May 30, 2023Consumer agents make choices which products to choose using the consumat approach. In this approach agents will make choices using deliberation, repetition, imitation or social comparison dependent on the level of need satisfaction and uncertainty.
The model is discussed in Introduction to Agent-Based Modeling by Marco Janssen. For more information see https://intro2abm.com/
Evolutionary Dynamics of the Warring States Period: Initial Unification in Ancient China (475 BC to 221 BC)
zhuo zhang | Published Sunday, August 07, 2022If you have any questions about the model run, please send me an email and I will respond as soon as possible.
Under complex system perspectives, we build the multi-agent system to back-calculate this unification process of the Warring State period, from 32 states in 475 BC to 1 state (Qin) in 221 BC.
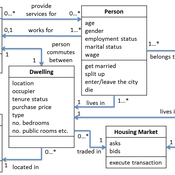
Demography, Industry and Residential Choice (DIReC) model
Jiaqi Ge | Published Wednesday, September 04, 2019The integrated and spatially-explicit ABM, called DIReC (Demography, Industry and Residential Choice), has been developed for Aberdeen City and the surrounding Aberdeenshire (Ge, Polhill, Craig, & Liu, 2018). The model includes demographic (individual and household) models, housing infrastructure and occupancy, neighbourhood quality and evolution, employment and labour market, business relocation, industrial structure, income distribution and macroeconomic indicators. DIReC includes a detailed spatial housing model, basing preference models on house attributes and multi-dimensional neighbourhood qualities (education, crime, employment etc.).
The dynamic ABM simulates the interactions between individuals, households, the labour market, businesses and services, neighbourhoods and economic structures. It is empirically grounded using multiple data sources, such as income and gender-age distribution across industries, neighbourhood attributes, business locations, and housing transactions. It has been used to study the impact of economic shocks and structural changes, such as the crash of oil price in 2014 (the Aberdeen economy heavily relies on the gas and oil sector) and the city’s transition from resource-based to a green economy (Ge, Polhill, Craig, & Liu, 2018).
SMILI: Small-scale fisheries Institutions and Local Interactions
Emilie Lindkvist Maja Schlüter Xavier Basurto | Published Thursday, March 09, 2017The model represents an archetypical fishery in a co-evolutionary social-ecological environment, capturing different dimensions of trust between fishers and fish buyers for the establishment and persistence of self-governance arrangements.
The Opportunistic Acquisition Model of Stone Tool Raw Material Procurement
Marco Janssen Simen Oestmo Haley Cawthra | Published Friday, April 21, 2017 | Last modified Sunday, March 10, 2019The Opportunistic Acquisition Model (OAM) posits that the archaeological lithic raw material frequencies are due to opportunistic encounters with sources while randomly walking in an environment.
Displaying 10 of 183 results for "Wil Hennen" clear search