About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 191 results decision clear search
Peer reviewed The Andean Resource Management Model (ARMM)
Olga Palacios | Published Tuesday, January 20, 2026ARMM is a theoretical agent-based model that formalizes Murra’s Theory of Verticality (Murra, 1972) to explore how multi-zonal resource management systems emerge in mountain landscapes. The model identifies the social, political, and economic mechanisms that enable vertical complementarity across ecological gradients.
Built in NetLogo, ARMM employs an abstract 111×111 grid divided into four Andean ecological zones (Altiplano, Highland, Lowland, Coast), each containing up to 18 resource types distributed according to ecological suitability. To test general theoretical principles rather than replicate specific geography, resource locations are randomized at each model initialization.
Settlement agents pursue one of two economic strategies: diversification (seeking resource variety, maximum 2 units per type) or accumulation (maximising total quantity, maximum 30 units). Agents move between adjacent zones through hierarchical decision-making, first attempting peaceful interactions—coexistence (governed by tolerance) and trading (governed by cooperation)—before resorting to conflict (theft or takeover, governed by belligerence).
The model demonstrates that vertical complementarity can emerge through fundamentally different mechanisms: either through autonomous mobility under political decentralization or through state-coordinated redistribution under centralization. Sensitivity analysis reveals that belligerence and economic strategy explain approximately 25% of outcome variance, confirming that structural inequalities between zones result from political-economic organization rather than environmental constraints alone.
As a preliminary theoretical model, ARMM intentionally maintains simplicity to isolate core mechanisms and generate testable hypotheses. This foundational framework will guide future empirically-calibrated versions that incorporate specific archaeological settlement data and geographic features from the Carangas region (Bolivia-Chile border), enabling direct comparison between theoretical predictions and observed historical patterns.
FRAMe (Flood Resilience Agent-Based Model)
Wenhan Feng | Published Wednesday, October 22, 2025The FRAMe (Flood Resilience Agent-Based Model) serves as a framework designed to simulate flood resilience dynamics at the community level, focusing on a rural settlement in the Mekong River Basin. Integrating empirical data from extensive surveys, Bayesian networks, and hydrological simulations, the framework quantifies resilience as a trade-off between robustness (resistance to damage) and adaptability (capacity for dynamic response). Agents include households, governments, and other actors, linked by social and governance networks that facilitate knowledge transfer, resource distribution, and risk communication. FRAMe incorporates mechanisms for flood forecasting, policy interventions (education, aid, insurance), and individual and collective decision-making, grounded in Protection Motivation Theory and MoHuB frameworks. The framework’s spatially explicit design leverages GIS data, which supports scenario testing of governance structures and stakeholder interactions. By examining policy scenarios and agent behavior, FRAMe aims to inform adaptive flood management strategies and enhance community resilience.
Peer reviewed E³-MAN. An Institutionally-guided multi-agent. Model for fair and efficient negotiation.
José luis bustelo | Published Monday, September 01, 2025Negotiation plays a fundamental role in shaping human societies, underpinning conflict resolution, institutional design, and economic coordination. This article introduces E³-MAN, a novel multi-agent model for negotiation that integrates individual utility maximization with fairness and institutional legitimacy. Unlike classical approaches grounded solely in game theory, our model incorporates Bayesian opponent modeling, transfer learning from past negotiation domains, and fallback institutional rules to resolve deadlocks. Agents interact in dynamic environments characterized by strategic heterogeneity and asymmetric information, negotiating over multidimensional issues under time constraints. Through extensive simulation experiments, we compare E³-MAN against the Nash bargaining solution and equal-split baselines using key performance metrics: utilitarian efficiency, Nash social welfare, Jain fairness index, Gini coefficient, and institutional compliance. Results show that E³-MAN achieves near-optimal efficiency while significantly improving distributive equity and agreement stability. A legal application simulating multilateral labor arbitration demonstrates that institutional default rules foster more balanced outcomes and increase negotiation success rates from 58% to 98%. By combining computational intelligence with normative constraints, this work contributes to the growing field of socially aware autonomous agents. It offers a virtual laboratory for exploring how simple institutional interventions can enhance justice, cooperation, and robustness in complex socio-legal systems.
An Agent-Based Model of Farmland Trading Partners Selection
Hang Xiong Chen Yuxin Xinfan Wang | Published Tuesday, August 19, 2025This base model uses an agent-based approach to represent heterogeneous farmers’ trading partners selection among multiple recipients (other farmers, village collectives, and firms). Each period, a potential transfer-out farmer decides whether to transfer based on a net-return versus transaction-cost trade-off; if transferring, the farmer selects the counterparty with the highest expected profit. Meanwhile, social learning—operationalized as logistic accumulation of neighborhood experience—continuously updates uncertainty, which in turn shapes transaction costs and subsequent decisions.
An agent-based model of the journey of victim/survivors through local authority domestic abuse support services in the UK
Bruce Edmonds | Published Monday, July 28, 2025This model played a small part in the UK government’s review of the working of local authority implementation of the Domestic Abuse legislation. The model explicitly represents victim-survivor families as they: (a) try to contact the local DA support system, (b) are triaged by the system and (if there is space) allocated to safe temporary accomodation (c) recieve support services from this position and (d) eventually move on to more permenant accomodation. The purpose of the model was to understand some possible ways in which the implementation of DA Duty, might be frustrated in practice, the identification of gaps in the evidence base and to inform the developing Theory of Change. The key measures used for assessing outcomes in the model were the number of families helped and the services that were delivered to them. The exploration was grounded for in two archetypal cases: that of a relatively immature system for the delivery of DA services and a more mature one (based on actual local authority cases, but not based on any single one). See the official report under associated publications for a summary of results.
BESTMAP-ABM-DE is an agent-based model to determine the adoption and spatial allocation of selected agri-environmental schemes (AES) by individual farmers in the Mulde River Basin located in Western Saxony, Germany. The selected AES are buffer areas, cover crops, maintaining permanent grassland and conversion of arable land to permanent grassland. While the first three schemes have already been offered in the case study area, the latter scheme is a hypothetical scheme designed to test the impact of potential policy changes. For the first model analyses, only the currently offered schemes are considered. With the model, the effect of different scenarios of policy design on patterns of adoption can be investigated. In particular, the model can be used to study the social-ecological consequences of agricultural policies at different spatial and temporal scales and, in combination with biophysical models, test the ecological implications of different designs of the EU’s Common Agricultural Policy. The model was developed in the BESTMAP project.
Peer reviewed soslivestock model
Marco Janssen Irene Perez Ibarra Diego J. Soler-Navarro Alicia Tenza Peral | Published Wednesday, May 28, 2025 | Last modified Tuesday, June 10, 2025The purpose of this model is to analyze how different management strategies affect the wellbeing, sustainability and resilience of an extensive livestock system under scenarios of climate change and landscape configurations. For this purpose, it simulates one cattle farming system, in which agents (cattle) move through the space using resources (grass). Three farmer profiles are considered: 1) a subsistence farmer that emphasizes self-sufficiency and low costs with limited attention to herd management practices, 2) a commercial farmer focused on profit maximization through efficient production methods, and 3) an environmental farmer that prioritizes conservation of natural resources and animal welfare over profit maximization. These three farmer profiles share the same management strategies to adapt to climate and resource conditions, but differ in their goals and decision-making criteria for when, how, and whether to implement those strategies. This model is based on the SequiaBasalto model (Dieguez Cameroni et al. 2012, 2014, Bommel et al. 2014 and Morales et al. 2015), replicated in NetLogo by Soler-Navarro et al. (2023).
One year is 368 days. Seasons change every 92 days. Each step begins with the growth of grass as a function of climate and season. This is followed by updating the live weight of animals according to the grass height of their patch, and grass consumption, which is determined based on the updated live weight. Animals can be supplemented by the farmer in case of severe drought. After consumption, cows grow and reproduce, and a new grass height is calculated. This updated grass height value becomes the starting grass height for the next day. Cows then move to the next area with the highest grass height. After that, cattle prices are updated and cattle sales are held on the first day of fall. In the event of a severe drought, special sales are held. Finally, at the end of the day, the farm balance and the farmer’s effort are calculated.
Peer reviewed Urban Transport Mode Choices
Kathleen Salazar -Serna Lorena Cadavid Carlos Franco | Published Thursday, May 22, 2025The model represents urban commuters’ transport mode choices among cars, public transit, and motorcycles—a mode highly prevalent in developing countries. Using an agent-based modeling approach, it simulates transport dynamics and serves as a testbed for evaluating policies aimed at improving mobility.
The model simulates an ecosystem of human agents who decide, at each time step, which mode of transportation to use for commuting to work. Their decision is based on a combination of personal satisfaction with their most recent journey—evaluated across a vector of individual needs—the information they crowdsource from their social network, and their personal uncertainty regarding trying new transport options.
Agents are assigned demographic attributes such as sex, age, and income level, and are distributed across city neighborhoods according to their socioeconomic status. To represent social influence in decision-making, agents are connected via a scale-free social network topology, where connections are more likely among agents within the same socioeconomic group, reflecting the tendency of individuals to form social ties with similar others.
…
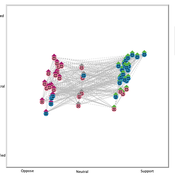
Gaming Polarisation: Using Agent-Based Simulations as A Dialogue Tool
Shaoni Wang | Published Friday, May 09, 2025This model aims to replicate the evolution of opinions and behaviours on a communal plan over time. It also aims to foster community dialogue on simulation outcomes, promoting inclusivity and engagement. Individuals (referred to as agents), grouped based on Sinus Milieus (Groh-Samberg et al., 2023), face a binary choice: support or oppose the plan. Motivated by experiential, social, and value needs (Antosz et al., 2019), their decision is influenced by how well the plan aligns with these fundamental needs.
Agent-Based Model for Multiple Team Membership (ABMMTM)
Andrew Collins | Published Thursday, April 03, 2025The Agent-Based Model for Multiple Team Membership (ABMMTM) simulates design teams searching for viable design solutions, for a large design project that requires multiple design teams that are working simultaneously, under different organizational structures; specifically, the impact of multiple team membership (MTM). The key mechanism under study is how individual agent-level decision-making impacts macro-level project performance, specifically, wage cost. Each agent follows a stochastic learning approach, akin to simulated annealing or reinforcement learning, where they iteratively explore potential design solutions. The agent evaluates new solutions based on a random-walk exploration, accepting improvements while rejecting inferior designs. This iterative process simulates real-world problem-solving dynamics where designers refine solutions based on feedback.
As a proof-of-concept demonstration of assessing the macro-level effects of MTM in organizational design, we developed this agent-based simulation model which was used in a simulation experiment. The scenario is a system design project involving multiple interdependent teams of engineering designers. In this scenario, the required system design is split into three separate but interdependent systems, e.g., the design of a satellite could (trivially) be split into three components: power source, control system, and communication systems; each of three design team is in charge of a design of one of these components. A design team is responsible for ensuring its proposed component’s design meets the design requirement; they are not responsible for the design requirements of the other components. If the design of a given component does not affect the design requirements of the other components, we call this the uncoupled scenario; otherwise, it is a coupled scenario.
Displaying 10 of 191 results decision clear search