About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 83 results for "Isaque Daniel Rocha Eberhardt" clear search
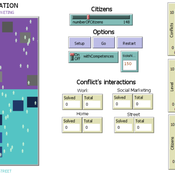
Citizenship competences and conflict resolution styles
Cecilia Avila Manuel Balaguera Valentina Tabares | Published Monday, February 03, 2020This model represents an agent-based social simulation for citizenship competences. In this model people interact by solving different conflicts and a conflict is solved or not considering two possible escenarios: when individual citizenship competences are considered and when not. In both cases the TKI conflict resolution styles are considered. Each conflict has associated a competence and the information about the conflicts and their competences is retrieved from an ontology which was developed in Protégé. To do so, a NetLogo extension was developed using the Java programming language and the JENA API (to make queries over the ontology).
Generalized Trust in the Mirror - a model on the Dynamics of Trust
Dominik Klein Johannes Marx | Published Friday, January 12, 2018This model studies the emergence and dynamics of generalized trust. It does so by modeling agents that engage in trust games and, based on their experience, slowly determine whether others are, in general, trustworthy.
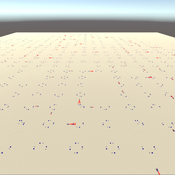
3D Urban Traffic Simulator (ABM) in Unity
Daniel Birks Sedar Olmez Obi Thompson Sargoni Alison Heppenstall Annabel Whipp Ed Manley | Published Friday, January 22, 2021 | Last modified Monday, March 22, 2021The Urban Traffic Simulator is an agent-based model developed in the Unity platform. The model allows the user to simulate several autonomous vehicles (AVs) and tune granular parameters such as vehicle downforce, adherence to speed limits, top speed in mph and mass. The model allows researchers to tune these parameters, run the simulator for a given period and export data from the model for analysis (an example is provided in Jupyter Notebook).
The data the model is currently able to output are the following:
…
Peer reviewed Labor and environment in global value chains: An evolutionary policy study with a three-sector and two-region agent-based macroeconomic model
Lena Gerdes Manuel Scholz-Wäckerle Bernhard Rengs | Published Wednesday, December 22, 2021With this model, we investigate resource extraction and labor conditions in the Global South as well as implications for climate change originating from industry emissions in the North. The model serves as a testbed for simulation experiments with evolutionary political economic policies addressing these issues. In the model, heterogeneous agents interact in a self-organizing and endogenously developing economy. The economy contains two distinct regions – an abstract Global South and Global North. There are three interlinked sectors, the consumption good–, capital good–, and resource production sector. Each region contains an independent consumption good sector, with domestic demand for final goods. They produce a fictitious consumption good basket, and sell it to the households in the respective region. The other sectors are only present in one region. The capital good sector is only found in the Global North, meaning capital goods (i.e. machines) are exclusively produced there, but are traded to the foreign as well as the domestic market as an intermediary. For the production of machines, the capital good firms need labor, machines themselves and resources. The resource production sector, on the other hand, is only located in the Global South. Mines extract resources and export them to the capital firms in the North. For the extraction of resources, the mines need labor and machines. In all three sectors, prices, wages, number of workers and physical capital of the firms develop independently throughout the simulation. To test policies, an international institution is introduced sanctioning the polluting extractivist sector in the Global South as well as the emitting industrial capital good producers in the North with the aim of subsidizing innovation reducing environmental and social impacts.
Cooperation Under Resources Pressure (CURP)
María Pereda José Manuel Galán Ordax José Santos | Published Monday, November 21, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, April 25, 2018This is an agent-based model designed to explore the evolution of cooperation under changes in resources availability for a given population
Mesoscopic Effects in an Agent-Based Bargaining Model in Regular Lattices
David Poza José Manuel Galán Ordax José Santos Adolfo López-Paredes | Published Thursday, February 02, 2017 | Last modified Wednesday, April 25, 2018We propose an agent-based model where a fixed finite population of tagged agents play iteratively the Nash demand game in a regular lattice. The model extends the bargaining model by Axtell, Epstein and Young.
Cooling in simulated annealing using Metropolis' algorithm (version a & b)
María Pereda José Santos José Manuel Galán Virginia Ahedo | Published Monday, March 15, 2021Netlogo model that shows how the cooling process determines the quality of a solution in simulated annealing using Metropolis algorithm.
SimPLS - The PLS Agent
Iris Lorscheid Sandra Schubring Matthias Meyer Christian Ringle | Published Monday, April 18, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, May 17, 2016The simulation model SimPLS shows an application of the PLS agent concept, using SEM as empirical basis for the definition of agent architectures. The simulation model implements the PLS path model TAM about the decision of using innovative products.
Human-in-the-loop Experiment of the Strategic Coalition Formation using the glove game
Andrew Collins | Published Monday, November 23, 2020 | Last modified Wednesday, June 22, 2022The purpose of the model is to collect information on human decision-making in the context of coalition formation games. The model uses a human-in-the-loop approach, and a single human is involved in each trial. All other agents are controlled by the ABMSCORE algorithm (Vernon-Bido and Collins 2020), which is an extension of the algorithm created by Collins and Frydenlund (2018). The glove game, a standard cooperative game, is used as the model scenario.
The intent of the game is to collection information on the human players behavior and how that compares to the computerized agents behavior. The final coalition structure of the game is compared to an ideal output (the core of the games).
Equity Constrained Dispatching Model of Emergency Medical Services
Sreekanth V K Ram Babu Roy | Published Thursday, September 08, 2016 | Last modified Monday, May 01, 2017Model for evaluating various ambulance dispatching policies of an equity constrained emergency medical services under bounded rationality.
Displaying 10 of 83 results for "Isaque Daniel Rocha Eberhardt" clear search