About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 64 results for "Emre Ates" clear search
CONSERVAT
Pieter Van Oel | Published Monday, April 13, 2015The CONSERVAT model evaluates the effect of social influence among farmers in the Lake Naivasha basin (Kenya) on the spatiotemporal diffusion pattern of soil conservation effort levels and the resulting reduction in lake sedimentation.
CITMOD A Tax-Benefit Modeling System for the average citizen
Philip Truscott | Published Monday, August 15, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Must tax-benefit policy making be limited to the ‘experts’?
04 TpLab V2.08 – Teleological Pruning Laboratory
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, April 15, 2017Our societal belief systems are pruned by evolution, informing our unsustainable economies. This is one of a series of models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, CmLab.
02 OamLab V1.10 - Open Atwood Machine Laboratory
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, January 31, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, April 13, 2017Using chains of replicas of Atwood’s Machine, this model explores implications of the Maximum Power Principle. It is one of a series of models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, EiLab.
03 MppLab V1.09 – Maximum Power Principle Laboratory
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, April 15, 2017Using webs of replicas of Atwood’s Machine, we explore implications of the Maximum Power Principle. This is one of a series of models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, CmLab.
Peer reviewed The foraging potential of the Holocene Cape South Coast of South Africa without the Palaeo-Agulhas Plain
Marco Janssen Colin Wren | Published Monday, August 12, 2019The Palaeo-Agulhas Plain formed an important habitat exploited by Pleistocene hunter-gatherer populations during periods of lower sea level. This productive, grassy habitat would have supported numerous large-bodied ungulates accessible to a population of skilled hunters with the right hunting technology. It also provided a potentially rich location for plant food collection, and along its shores a coastline that moved with the rise and fall of sea levels. The rich archaeological and paleontological records of Pleistocene sites along the modern Cape south coast of South Africa, which would have overlooked the Palaeo-Agulhas Plain during Pleistocene times of lower sea level, provides a paleoarchive of this extinct ecosystem. In this paper, we present a first order illustration of the “palaeoscape modeling” approach advocated by Marean et al. (2015). We use a resourcescape model created from modern studies of habitat productivity without the Palaeo-Agulhas Plain. This is equivalent to predominant Holocene conditions. We then run an agent-based model of the human foraging system to investigate several research questions. Our agent-based approach uses the theoretical framework of optimal foraging theory to model human foraging decisions designed to optimize the net caloric gains within a complex landscape of spatially and temporally variable resources. We find that during the high sea-levels of MIS 5e (+5-6 m asl) and the Holocene, the absence of the Plain left a relatively poor food base supporting a much smaller population relying heavily on edible plant resources from the current Cape flora. Despite high species diversity of plants with edible storage organs, and marine invertebrates, encounter rates with highly profitable resources were low. We demonstrate that without the Palaeo-Agulhas Plain, human populations must have been small and low density, and exploited plant, mammal, and marine resources with relatively low caloric returns. The exposure and contraction of the Palaeo-Agulhas Plain was likely the single biggest driver of behavioral change during periods of climate change through the Pleistocene and into the transition to the Holocene.
Peer reviewed Monogamous Reproduction in Small Populations and the Enforcement of the Incest Taboo
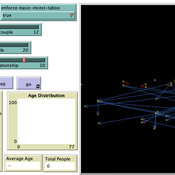
Ian Stuart | Published Wednesday, January 18, 2023This program was developed to simulate monogamous reproduction in small populations (and the enforcement of the incest taboo).
Every tick is a year. Adults can look for a mate and enter a relationship. Adult females in a Relationship (under the age of 52) have a chance to become pregnant. Everyone becomes not alive at 77 (at which point people are instead displayed as flowers).
User can select a starting-population. The starting population will be adults between the ages of 18 and 42.
…
Peer reviewed Behavioral Dynamics of Epidemic Trajectories and Vaccination Strategies: An Agent-Based Model
Ziyuan Zhang | Published Tuesday, December 10, 2024This agent-based model explores the dynamics between human behavior and vaccination strategies during COVID-19 pandemics. It examines how individual risk perceptions influence behaviors and subsequently affect epidemic outcomes in a simulated metropolitan area resembling New York City from December 2020 to May 2021.
Agents modify their daily activities—deciding whether to travel to densely populated urban centers or stay in less crowded neighborhoods—based on their risk perception. This perception is influenced by factors such as risk perception threshold, risk tolerance personality, mortality rate, disease prevalence, and the average number of contacts per agent in crowded settings. Agent characteristics are carefully calibrated to reflect New York City demographics, including age distribution and variations in infection probability and mortality rates across these groups. The agents can experience six distinct health statuses: susceptible, exposed, infectious, recovered from infection, dead, and vaccinated (SEIRDV). The simulation focuses on the Iota and Alpha variants, the dominant strains in New York City during the period.
We simulate six scenarios divided into three main categories:
1. A baseline model without vaccinations where agents exhibit no risk perception and are indifferent to virus transmission and disease prevalence.
…
NarrABS
Tilman Schenk | Published Thursday, September 20, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An agent based simulation of a political process based on stakeholder narratives
Agent-Based Model of a Circular Food Packaging Ecosystem to assess Packaging Waste Dynamics
Annoek Reitsema | Published Friday, October 11, 2024Reducing packaging waste is a critical challenge that requires organizations to collaborate within circular ecosystems, considering social, economic, and technical variables like decision-making behavior, material prices, and available technologies. Agent-Based Modeling (ABM) offers a valuable methodology for understanding these complex dynamics. In our research, we have developed an ABM to explore circular ecosystems’ potential in reducing packaging waste, using a case study of the Dutch food packaging ecosystem. The model incorporates three types of agents—beverage producers, packaging producers, and waste treaters—who can form closed-loop recycling systems.
Beverage Producer Agents: These agents represent the beverage company divided into five types based on packaging formats: cans, PET bottles, glass bottles, cartons, and bag-in-boxes. Each producer has specific packaging demands based on product volume, type, weight, and reuse potential. They select packaging suppliers annually, guided by deterministic decision styles: bargaining (seeking the lowest price) or problem-solving (prioritizing high recycled content).
Packaging Producer Agents: These agents are responsible for creating packaging using either recycled or virgin materials. The model assumes a mix of monopolistic and competitive market situations, with agents calculating annual material needs. Decision styles influence their choices: bargaining agents compare recycled and virgin material costs, while problem-solving agents prioritize maximum recycled content. They calculate recycled content in packaging and set prices accordingly, ensuring all produced packaging is sold within or outside the model.
…
Displaying 10 of 64 results for "Emre Ates" clear search