About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 62 results adaptive clear search
Resource distribution effects on optimal foraging theory
Marco Janssen Kim Hill | Published Friday, January 27, 2017The original Ache model is used to explore different distributions of resources on the landscape and it’s effect on optimal strategies of the camps on hunting and camp movement.
An adaptive model of homing pigeons: A genetic algorithm approach
Gudrun Wallentin Francis Oloo | Published Friday, January 27, 2017In this model, we simulate the navigation behavior of homing pigeons. Specifically we use genetic algorithms to optimize the navigation and flocking parameters of pigeon agents.
Peter Diamond's Coconut Model (Heterogeneity and Learning)
Sven Banisch Eckehard Olbrich | Published Monday, May 30, 2016Agent-based version of the simple search and barter economy conceived by Peter Diamond in 1982. The model is also known as Coconut Model.
How to not get stuck – an ant model showing how negative feedback due to crowding maintains flexibility in ant foraging
Tomer Czaczkes | Published Thursday, December 17, 2015Positive feedback can lead to “trapping” in local optima. Adding a simple negative feedback effect, based on ant behaviour, prevents this trapping
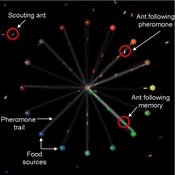
Composite Collective Decision Making - ant colony foraging model
Tomer Czaczkes Benjamin I Czaczkes | Published Thursday, December 17, 2015The model explores how two types of information - social (in the form of pheromone trails) and private (in the form of route memories) affect ant colony level foraging in a variable enviroment.
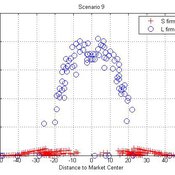
Micro-level Adaptation, Macro-level Selection, and the Dynamics of Market Partitioning
César García-Díaz | Published Monday, October 19, 2015 | Last modified Monday, October 19, 2015This model simulates the emergence of a dual market structure from firm-level interaction. Firms are profit-seeking, and demand is represented by a unimodal distribution of consumers along a set of taste positions.
FlowLogo: An agent-based platform for simulating complex human-aquifer interactions in managed groundwater systems
Juan Castilla-Rho | Published Sunday, August 30, 2015FlowLogo integrates agent-based and groundwater flow simulation. It aims to simplify the process of developing participatory ABMs in the groundwater space and begin the exploration of novel, bottom-up solutions to conflicts in shared aquifers.
06 EiLab V1.36 – Entropic Index Laboratory
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, January 31, 2015 | Last modified Friday, April 14, 2017EiLab explores the role of entropy in simple economic models. EiLab is one of several models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, and CmLab.
Peer reviewed Ideal Free Distribution of Mobile Pastoralists in the Logone Floodplain, Cameroon
Jeff Cronley Andrew Yoak Mark Moritz Hongyang Pi Ian M Hamilton Paul Maddock | Published Thursday, June 19, 2014 | Last modified Saturday, January 06, 2018The purpose of the model is to examine whether and how mobile pastoralists are able to achieve an Ideal Free Distribution (IFD).
A test-bed ecological model
Bruce Edmonds | Published Sunday, May 04, 2014 | Last modified Wednesday, May 15, 2019This is a multi-patch meta-population ecological model. It intended as a test-bed in which to test the impact of humans with different kinds of social structure.
Displaying 10 of 62 results adaptive clear search