About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 521 results for "Jingjing Cai" clear search
A data-informed bounded-confidence opinion dynamics model
Bruce Edmonds | Published Wednesday, March 10, 2021The simulation is a variant of the “ToRealSim OD variants - base v2.7” base model, which is based on the standard DW opinion dynamics model (but with the differences that rather than one agent per tick randomly influencing another, all agents randomly influence one other per tick - this seems to make no difference to the outcomes other than to scale simulation time). Influence can be made one-way by turning off the two-way? switch
Various additional variations and sources of noise are possible to test robustness of outcomes to these (compared to DW model).
In this version agent opinions change following the empirical data collected in some experiments (Takács et al 2016).
Such an algorithm leaves no role for the uncertainties in other OD models. [Indeed the data from (Takács et al 2016) indicates that there can be influence even when opinion differences are large - which violates a core assumption of these]. However to allow better comparison with other such models there is a with-un? switch which allows uncertainties to come into play. If this is on, then influence (according to above algorithm) is only calculated if the opinion difference is less than the uncertainty. If an agent is influenced uncertainties are modified in the same way as standard DW models.
An Agent-Based Model for Skilled Workers Migration
Hassan Bashiri | Published Thursday, September 21, 2023This documentation provides an overview and explanation of the NetLogo simulation code for modeling skilled workers’ migration in Iran. The simulation aims to explore the dynamics of skilled workers’ migration and their transition through various states, including training, employment, and immigration.
The flow of elite and talent migration, or “brain drain,” is a complex issue with far-reaching implications for developing countries. The decision to migrate is made due to various factors including economic opportunities, political stability, social factors and personal circumstances.
Measuring individual interests in the field of immigration is a complex task that requires careful consideration of various factors. The agent-based model is a useful tool for understanding the complex factors that are involved in talent migration. By considering the various social, economic, and personal factors that influence migration decisions, policymakers can provide more effective strategies to retain skilled and talented labor and promote sustainable growth in developing countries. One of the main challenges in studying the flow of elite migration is the complexity of the decision-making process and a set of factors that lead to migration decisions. Agent-based modeling is a useful tool for understanding how individual decisions can lead to large-scale migration patterns.
Hyperconnectivity, and Fact-Checking- Modeling Witnessing as a Traditional Coast Salish Mechanism
Adam Rorabaugh | Published Thursday, May 01, 2025An unintended consequence of low cost maritime travel may be hyperconnectedness, creating social situations where information can be readily passed before it is verified- an issue not limited to modern digitally connected societies. In traditional Coast Salish societies, the peoples of what is now Western Washington and Southwestern British Columbia, oral traditions were vertified through a process called witnessing. Witnesses would be trained to recount and verify oral history and traditional teachings at high fidelity. Here, a simple model based on dual inheritance approaches to genes and culture, is used to compare this specific form of verifying socially important information compared to modern mass communication. The model suggests that witnessing is a high fidelity form of transmitting knowledge with a low error rate, more in line with modern apprenticeships than mass communication. Social mechanisms such as witnessing provide solutions to issues faced in contemporary discourse where the validity of information and even fact checking mechanisms may be biased or counterfactual. This effort also demonstrates the utillity of using modeling approaches to highlight how specific, historically contingent institutions such as witnesses can be drawn upon to model potential solutions to contemporary issues solved in the past in traditional Coast Salish practice.
Network formation on a two-layer multiplex with shocks
Paul Smaldino | Published Monday, November 27, 2017A dynamic model of social network formation on single-layer and multiplex networks with structural incentives that vary over time.
The Mobility Model
Emilie Lindkvist | Published Wednesday, September 27, 2017 | Last modified Friday, October 06, 2017The Mobility Model is a model of a small-scale fishery with the purpose to study the movement of fishers between different sub-regions within a larger region, as they move between different regions to fish.
FeedUS - A global food trade model
Jiaqi Ge | Published Thursday, February 25, 2021 | Last modified Friday, February 26, 2021The purpose of the model is to study the impact of global food trade on food and nutrition security in countries around the world. It will incorporate three main aspects of trade between countries, including a country’s wealth, geographic location, and its trade relationships with other countries (past and ongoing), and can be used to study food and nutrition security across countries in various scenarios, such as climate change, sustainable intensification, waste reduction and dietary change.
Introductory SIR Model
Kit Martin Amber Cesare Matthew Johnson | Published Tuesday, September 28, 2021This is a basic Susceptible, Infected, Recovered (SIR) model. This model explores the spread of disease in a space. In particular, it explores how changing assumptions about the number of susceptible people, starting number of infected people, as well as the disease’s infection probability, and average duration of infection. The model shows that the interactions of agents can drastically affect the results of the model.
We used it in our course on COVID-19: https://www.csats.psu.edu/science-of-covid19
Weighted Balance Model of Issue Alignment and Polarization
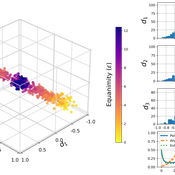
David Garcia Simon Schweighofer | Published Sunday, October 08, 2023This model is pertinent to our JASSS publication “Raising the Spectrum of Polarization: Generating Issue Alignment with a Weighted Balance Opinion Dynamics Model”. It shows how, based on the mechanisms of our Weighted Balance Theory (a development of Fritz Heider’s Cognitive Balance Theory), agents can self-organize in a multi-dimensional opinion space and form an emergent ideological spectrum. The degree of issue alignment and polarization realized by the model depends mainly on the agent-specific ‘equanimity parameter’ epsilon.
DIAL is a model of group dynamics and opinion dynamics. It features dialogues, in which agents put their reputation at stake. Intra-group radicalisation of opinions appears to be an emergent phenomenon.
Institutions and Cooperation in an Ecology of Games
Paul Smaldino | Published Wednesday, November 29, 2017Dynamic bipartite network model of agents and games in which agents can participate in multiple public goods games.
Displaying 10 of 521 results for "Jingjing Cai" clear search