About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 112 results interaction clear search
Prisoner's Dilemma Game on Complex Networks with Agents' Adaptive Expectations
Bo Xianyu | Published Wednesday, November 16, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model studies the effect of the agents’ adaptive expectation on cooperation frequency in the prisoner’s dilemma game in complex networks from an agent based approach. The model is implemented in Repast simphony 1.2.
Spatiotemporal Visualization of Emotional and Emotional-related Mental States
Luis Macedo | Published Monday, November 07, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013A system that receives from an agent-based social simulation the agent’s emotional data, their emotional-related data such as motivations and beliefs, as well as their location, and visualizes of all this information in a two dimensional map of the geographic region the agents inhabit as well as on graphs along the time dimension.
Peer reviewed Hominin ecodynamics v.1
C Michael Barton | Published Saturday, October 01, 2011 | Last modified Friday, March 28, 2014Biobehavioral interactions between two populations under different movement strategies.
Hominin ecodynamics v.2
C Michael Barton | Published Monday, September 19, 2011 | Last modified Friday, March 28, 2014Simulates biobehavioral interactions between 2 populations of hominins.
ADAM: Agent-based Demand and Assignment Model
D Levinson | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The core algorithm is an agent-based model, which simulates travel patterns on a network based on microscopic decision-making by each traveler.
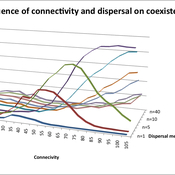
Varying effects of connectivity and dispersal on interacting species dynamics
Kehinde Salau | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An agent-based model of species interaction on fragmented landscape is developed to address the question, how do population levels of predators and prey react with respect to changes in the patch connectivity as well as changes in the sharpness of threshold dispersal?
Village Ecodynamics Project
ipem | Published Friday, May 13, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The Village Project is designed to help archaeologists understand the factors influencing settlement patterns of small-scale agrarian peoples. Although such societies are becoming increasingly rare, they represent the norm throughout most of the Neolithic period the world over.
A Computational Model of Workers Protest
Jae-Woo Kim | Published Friday, May 13, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013We present an agent-based model of worker protest informed by Epstein (2002). Workers have varying degrees of grievance depending on the difference between their wage and the average of their neighbors. They protest with probabilities proportional to grievance, but are inhibited by the risk of being arrested – which is determined by the ratio of coercive agents to probable rebels in the local area. We explore the effect of similarity perception on the dynamics of collective behavior. If […]
An agent-based model for assessing strategies of adaptation to climate and tourism demand changes in an alpine destination
Stefano Balbi Marco Alberti | Published Monday, February 14, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The model is then used for assessing three hypothetical and contrasted infrastructure-oriented adaptation strategies for the winter tourism industry, that have been previously discussed with local stakeholders, as possible alternatives to the “business-as-usual” situation.
Relational Social Interaction Model of Migration (RSIMM)
Christopher Roberts Sean Bergin | Published Monday, February 07, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Current trends suggest that when individuals of different cultural backgrounds encounter one another, their social categories become entangled and create new hybridized or creole identities.
Displaying 10 of 112 results interaction clear search