About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 6 of 6 results human evolution clear search
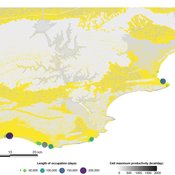
PaleoscapeABM: coastal occupation and shellfish discard
Claudine Gravel-Miguel | Published Tuesday, February 08, 2022This model builds on the Armature distribution within the PaleoscapeABM model, which is itself a variant of the PaleoscapeABM available here written by Wren and Janssen, and.
This model aims to explore where and how much shellfish is discarded at coastal and non-coastal locations by daily coastal foraging. We use this model’s output to test the idea that we can confidently use the archaeological record to evaluate the importance of shellfish in prehistoric people’s diets.
The recognition that aquatic adaptations likely had significant impacts on human evolution triggered an explosion of research on that topic. Recognizing coastal foraging in the past relies on the archaeological signature of that behavior. We use this model to explore why some coastal sites are very intensely occupied and see if it is due to the shellfish productivity of the coast.
Peer reviewed B3GET
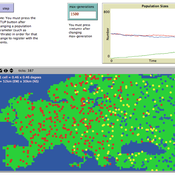
Kristin Crouse | Published Thursday, November 14, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, September 20, 2022B3GET simulates populations of virtual organisms evolving over generations, whose evolutionary outcomes reflect the selection pressures of their environment. The model simulates several factors considered important in biology, including life history trade-offs, investment in fighting ability and aggression, sperm competition, infanticide, and competition over access to food and mates. Downloaded materials include starting genotype and population files. Edit the these files and see what changes occur in the behavior of virtual populations!
View the B3GET user manual here.
BEGET Classic
Kristin Crouse | Published Monday, November 11, 2019 | Last modified Monday, November 25, 2019BEGET Classic includes previous versions used in the classroom and for publication. Please check out the latest version of B3GET here, which has several user-friendly features such as directly importing and exporting genotype and population files.
The classic versions of B3GET include: version one and version three were used in undergraduate labs at the University of Minnesota to demonstrate principles in primate behavioral ecology; version two first demonstrated proof of concept for creating virtual biological organisms using decision-vector algorithms; version four was presented at the 2017 annual meeting at the American Association of Physical Anthropologists; version five was presented in a 2019 publication from the Journal of Human Evolution (Crouse, Miller, and Wilson, 2019).
The role of spatial foresight in models of hominin dispersal
Colin Wren | Published Monday, February 24, 2014 | Last modified Monday, July 14, 2014The natural selection of foresight, an accuracy at assess the environment, under degrees of environmental heterogeneity. The model is designed to connect local scale mobility, from foraging, with the global scale phenomenon of population dispersal.
Peer reviewed Hominin ecodynamics v.1
C Michael Barton | Published Saturday, October 01, 2011 | Last modified Friday, March 28, 2014Biobehavioral interactions between two populations under different movement strategies.
Hominin ecodynamics v.2
C Michael Barton | Published Monday, September 19, 2011 | Last modified Friday, March 28, 2014Simulates biobehavioral interactions between 2 populations of hominins.