About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 8 of 8 results cattle clear search
Peer reviewed Mission Cattle
Isaac Ullah | Published Monday, December 15, 2025The model examines cattle herd dynamics on a patchy grassland subject to two exogenous pressures: periodic raiding events that remove animals and scheduled management culling that can target males and/or females. It is intended for comparative experiments on how raiding frequency, culling schedules, vegetation dynamics, and life-history parameters interact to shape herd persistence. The model was specifically designed to test the scenario of cattle herding in the arid grasslands of southern Arizona and northern Sonora during the mission period (late 17th through late 18th centuries, CE). In this period, herds were locally managed by Spanish mission personnel and local O’odham groups. Herds were culled mostly for local consumption of meat, hides, and tallow, but the mission herds were often targets for raiding by neighboring groups. The main purpose of the model is to examine herd dynamics in a seasonally variable, arid environment where herds are subject to both intentional internal harvest (culling) and external harvest (raiding).
Peer reviewed soslivestock model
Marco Janssen Irene Perez Ibarra Diego J. Soler-Navarro Alicia Tenza Peral | Published Wednesday, May 28, 2025 | Last modified Tuesday, June 10, 2025The purpose of this model is to analyze how different management strategies affect the wellbeing, sustainability and resilience of an extensive livestock system under scenarios of climate change and landscape configurations. For this purpose, it simulates one cattle farming system, in which agents (cattle) move through the space using resources (grass). Three farmer profiles are considered: 1) a subsistence farmer that emphasizes self-sufficiency and low costs with limited attention to herd management practices, 2) a commercial farmer focused on profit maximization through efficient production methods, and 3) an environmental farmer that prioritizes conservation of natural resources and animal welfare over profit maximization. These three farmer profiles share the same management strategies to adapt to climate and resource conditions, but differ in their goals and decision-making criteria for when, how, and whether to implement those strategies. This model is based on the SequiaBasalto model (Dieguez Cameroni et al. 2012, 2014, Bommel et al. 2014 and Morales et al. 2015), replicated in NetLogo by Soler-Navarro et al. (2023).
One year is 368 days. Seasons change every 92 days. Each step begins with the growth of grass as a function of climate and season. This is followed by updating the live weight of animals according to the grass height of their patch, and grass consumption, which is determined based on the updated live weight. Animals can be supplemented by the farmer in case of severe drought. After consumption, cows grow and reproduce, and a new grass height is calculated. This updated grass height value becomes the starting grass height for the next day. Cows then move to the next area with the highest grass height. After that, cattle prices are updated and cattle sales are held on the first day of fall. In the event of a severe drought, special sales are held. Finally, at the end of the day, the farm balance and the farmer’s effort are calculated.
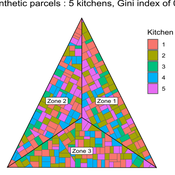
MeReDiem : Fallow Land Simulations to examine the conditions of sustainable village livelihood
Etienne DELAY Paul Chapron Mathieu | Published Monday, January 20, 2025 | Last modified Tuesday, January 21, 2025The MeReDiem model aims to simulate the effect of socio-agricultural practices of farmers and pastors on the food sustainability and soil fertility of a serrer village, in Senegal. The model is a central part of a companion modeling and exploration approach, described in a paper, currently under review)
The village population is composed of families (kitchens). Kitchens cultivate their land parcels to feed their members, aiming for food security at the family level. On a global level , the village tries to preserve the community fallow land as long as possible.
Kitchens sizes vary depending on the kitchens food production, births and migration when food is insufficient.
…
TRUE GRASP (Tree Recruitment Under Exotic GRAsses in a Savanna-Pineland)
is a socio-ecological agent-based model (ABM) and role playing game (RPG) for farmers and other stakeholders involved in rural landscape planning.
The purpose of this model is to allow actors to explore the individual and combined effects - as well as tradeoffs - of three methods of controlling exotic grasses in pine savannas: fire, weeding, and grazing cattle.
Design of TRUE GRASP is based on 3 years of socio-ecological fieldwork in a human-induced pine savanna in La Sepultura Biosphere Reserve (SBR) in the Mexican state of Chiapas. In this savanna, farmers harvest resin from Pinus oocarpa, which is used to produce turpentine and other products. However, long term persistence of this activity is jeopardized by low tree recruitment due to exotic tall grass cover in the forest understory (see Braasch et al., 2017). The TRUE GRASP model provides the user with different management strategies for controlling exotic grass cover and avoiding possible regime shifts, which in the case of the SBR would jeopardize resin harvesting.
RaMDry - Rangeland Model in Drylands
Pascal Fust Eva Schlecht | Published Friday, January 05, 2018 | Last modified Friday, April 01, 2022RaMDry allows to study the dynamic use of forage ressources by herbivores in semi-arid savanna with an emphasis on effects of change of climate and management. Seasonal dynamics affects the amount and the nutritional values of the available forage.
Livestock drought insurance model
Birgit Müller Felix John Jürgen Groeneveld Karin Frank Russell Toth | Published Tuesday, December 19, 2017 | Last modified Saturday, April 14, 2018The model analyzes the economic and ecological effects of a provision of livestock drought insurance for dryland pastoralists. More precisely, it yields qualitative insights into how long-term herd and pasture dynamics change through insurance.
Kulayinjana
Christophe Le Page Arthur Perrotton Michel De Garine-Wichatitsky Barry Bitu Killion Koyisi Ferdinand Mwamba Cephus Ncube Victor Ncube Siphusisiwe Ndlovu Raphael Ngwenya Ambu Nyathi Fumbane Nyathi Patrick Sibanda Zenzo Sibanda | Published Monday, October 03, 2016a computer-based role-playing game simulating the interactions between farming activities, livestock herding and wildlife in a virtual landscape reproducing local socioecological dynamics at the periphery of Hwange National Park (Zimbabwe).
Peer reviewed Family Herd Demography
Mark Moritz Ian M Hamilton Andrew Yoak Rebecca Garabed Abigail Buffington | Published Monday, August 15, 2016 | Last modified Saturday, January 06, 2018The model examines the dynamics of herd growth in African pastoral systems. We used it to examine the role of scale (herd size) stochasticity (in mortality, fertility, and offtake) on herd growth.