About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 136 results for "José I Santos" clear search
The Coevolution of the Firm and the Product Attribute Space
César García-Díaz | Published Friday, May 22, 2020This model inspects the performance of firms as the product attribute space changes, which evolves as a consequence of firms’ actions. Firms may create new product variants by dragging demand from other existing variants. Firms decide whether to open new product variants, to invade existing ones, or to keep their variant portfolio. At each variant there is a Cournot competition each round. Competition is nested since many firms compete at many variants simultaneously, affecting firm composition at each location (variant).
After the Cournot outcomes, at each round firms decide whether to (i) keep their existing product variant niche, (ii) invade an existing variant, (iii) create a new variant, or (iv) abandon a variant. Firms’ profits across their niche take into consideration the niche-width cost and the cost of opening a new variant.
02 OamLab V1.10 - Open Atwood Machine Laboratory
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, January 31, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, April 13, 2017Using chains of replicas of Atwood’s Machine, this model explores implications of the Maximum Power Principle. It is one of a series of models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, EiLab.
03 MppLab V1.09 – Maximum Power Principle Laboratory
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, April 15, 2017Using webs of replicas of Atwood’s Machine, we explore implications of the Maximum Power Principle. This is one of a series of models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, CmLab.
The S-uFUNK Model
Davide Secchi | Published Friday, March 17, 2023This version 2.1.0 of the uFunk model is about setting a business strategy (the S in the name) for an organization. A team of managers (or executives) meet and discuss various options on the strategy for the firm. There are three aspects that they have to agree on to set the strategic positioning of the organization.
The discussion is on market, stakeholders, and resources. The team (it could be a business strategy task force) considers various aspects of these three elements. The resources they use to develop the discussion can come from a traditional approach to strategy or from non-traditional means (e.g., so-called serious play, creativity and imagination techniques).
The S-uFunk 2.1.0 Model wants to understand to which extent cognitive means triggered by traditional and non-traditional resources affect the making of the strategy process.
Between Pleasure and Contentment: Evolutionary Dynamics of Some Possible Parameters of Happiness
Yue Gao Shimon Edelman | Published Saturday, March 12, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, March 16, 2016We build a computational model to investigate, in an evolutionary setting, a series of questions pertaining to happiness.
Agent-based Simulation of Innovation Diffusion
Theresa Elbracht | Published Monday, May 19, 2025The agent-based simulation of innovation diffusion is based on the idea of the Bass model (1969).
The adoption of an agent is driven two parameters: its innovativess p and its prospensity to conform with others. The model is designed for a computational experiment building up on the following four model variations:
(i) the agent population it fully connected and all agents share the same parameter values for p and q
(ii) the agent population it fully connected and agents are heterogeneous, i.e. individual parameter values are drawn from a normal distribution
(iii) the agents population is embeded in a social network and all agents share the same parameter values for p and q
…
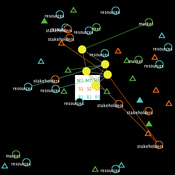
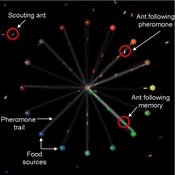
Composite Collective Decision Making - ant colony foraging model
Tomer Czaczkes Benjamin I Czaczkes | Published Thursday, December 17, 2015The model explores how two types of information - social (in the form of pheromone trails) and private (in the form of route memories) affect ant colony level foraging in a variable enviroment.
An Agent-Based Model of Flood Risk and Insurance
J Dubbelboer I Nikolic K Jenkins J Hall | Published Monday, July 27, 2015 | Last modified Monday, October 03, 2016A model to show the effects of flood risk on a housing market; the role of flood protection for risk reduction; the working of the existing public-private flood insurance partnership in the UK, and the proposed scheme ‘Flood Re’.
Exploring Transitions towards Sustainable Construction
Jesus Rosales-Carreon César García-Díaz | Published Wednesday, October 30, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, January 31, 2015This model illustrates actor interaction in the construction sector, according to information gathered in NL. It offers a simple frame to represent diverse interests, interdependencies and effects on the number of built sustainable houses.
Displaying 10 of 136 results for "José I Santos" clear search