About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 940 results for "George Ak Van Voorn" clear search
BarterNet is a platform for modeling early barter networks with the aim of learning how supply and demand for a good determine if traders will learn to use that good as a form of money. Traders use a good as money when they offer to trade for it even if they can’t consume it, but believe that they can subsequently trade it for a good they can consume in the near future.
A Computational Model of Workers Protest
Jae-Woo Kim | Published Friday, May 13, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013We present an agent-based model of worker protest informed by Epstein (2002). Workers have varying degrees of grievance depending on the difference between their wage and the average of their neighbors. They protest with probabilities proportional to grievance, but are inhibited by the risk of being arrested – which is determined by the ratio of coercive agents to probable rebels in the local area. We explore the effect of similarity perception on the dynamics of collective behavior. If […]
A Complex Model of Voter Turnout
Bruce Edmonds Laurence Lessard-Phillips Ed Fieldhouse | Published Monday, October 13, 2014 | Last modified Tuesday, August 18, 2015This is a complex “Data Integration Model”, following a “KIDS” rather than a “KISS” methodology - guided by the available evidence. It looks at the complex mix of social processes that may determine why people vote or not.
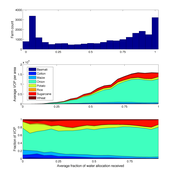
Irrigation Equity and Efficiency
Andrew Bell | Published Tuesday, August 30, 2016The purpose of this model is to examine equity and efficiency in crop production across a system of irrigated farms, as a function of maintenance costs, assessed water fees, and the capacity of farmers to trade water rights among themselves.
Design principles for a redistributive collective action institution in times of crisis
Aashis Joshi | Published Friday, September 15, 2023What policy measures are effective in redistributing essential resources during crisis situations such as climate change impacts? We model a collective action institution with different rules for designing and organizing it, and make our analysis specific to various societal contexts.
Our model captures a generic societal context of unequal vulnerability and climate change impact in a stylized form. We represent a community of people who harvest and consume an essential resource to maintain their well-being. However, their ability to harvest the resource is not equal; people are characterized by a ‘resource access’ attribute whose values are uniformly distributed from 0 to 1 in the population. A person’s resource access value determines the amount of resource units they are able to harvest, and therefore the welfare levels they are able to attain. People travel to the centralized resource region and derive well-being or welfare, represented as an energy gain, by harvesting and consuming resource units.
The community is subject to a climate change impact event that occurs with a certain periodicity and over a certain duration. The capacity of resource units to regenerate diminishes during the impact events. Unequal capacities to access the essential resource results in unequal vulnerability among people with regards to their ability to maintain a sufficient welfare level, especially during impact events.
…
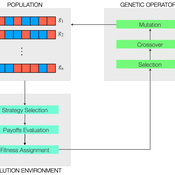
Peer reviewed Evolutionary Economic Learning Simulation: A Genetic Algorithm for Dynamic 2x2 Strategic-Form Games in Python
Vinicius Ferraz Thomas Pitz | Published Friday, April 08, 2022This project combines game theory and genetic algorithms in a simulation model for evolutionary learning and strategic behavior. It is often observed in the real world that strategic scenarios change over time, and deciding agents need to adapt to new information and environmental structures. Yet, game theory models often focus on static games, even for dynamic and temporal analyses. This simulation model introduces a heuristic procedure that enables these changes in strategic scenarios with Genetic Algorithms. Using normalized 2x2 strategic-form games as input, computational agents can interact and make decisions using three pre-defined decision rules: Nash Equilibrium, Hurwicz Rule, and Random. The games then are allowed to change over time as a function of the agent’s behavior through crossover and mutation. As a result, strategic behavior can be modeled in several simulated scenarios, and their impacts and outcomes can be analyzed, potentially transforming conflictual situations into harmony.
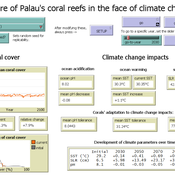
Development of coral reefs under climate change impacts and adaptation options
Nina Preußler | Published Friday, May 30, 2025This NetLogo model simulates how coral reefs around the islands of Palau would develop under different emission scenarios and with selected adaptation strategies. Reef health is indicated by coral cover (%) and is affected by four major climate change impacts: increasing sea surface temperature, sea level rise, ocean acidification, and more intense typhoons. The model differentiates between inner and outer reefs, with the former naturally adapted to warmer, more acidic waters. The simulation includes bleaching events and possible recovery. In addition, the user can choose between different coral transplantation strategies as well as regulate natural thermal adaptation rates.
Customers going to a restaurant
hdouss | Published Tuesday, September 25, 2018The model is about customers going to a restaurant when they are hungry. They wait in the queue if no tables are available. Customers can leave the restaurant and got upset and decide to never return to the restaurant. The model tries to show 2 things: 1.the main caracteristics of the people that decided to never return to the restaurant and 2.the main factors that can impact the total number of customers that decided to never return to the restaurant.
Netlogo model ` Effect of Network Homophily and Partisanship on Social Media to “Oil Spill” Polarizations’
takuya nagura | Published Saturday, September 13, 2025This model was utilized for the simulation in the paper titled Effect of Network Homophily and Partisanship on Social Media to “Oil Spill” Polarizations. It allows you to examine whether oil spill polarization occurs through people’s communication under various conditions.
・Choose the network construction conditions you’d like to examine from the “rewire-style” chooser box.
・Select the desired strength of partisanship from the “partisanlevel” chooser box. You can also set the strength manually in the code tab.
・You can set the number of dynamic topics using the “number-of-topics” slider.
・Use the “divers-of-opinion” slider to set the number of preference types for each dynamic topic.
…
Biodynamica
Klaus Jaffe | Published Saturday, December 24, 2016Agent based simulation model for the study of the genetic evolution of sexual recombination and social behavior
Displaying 10 of 940 results for "George Ak Van Voorn" clear search