About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 3 of 3 results voting behavior clear search
PaCE Austria Pilot Model
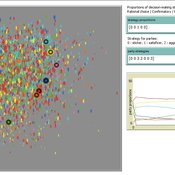
Ruth Meyer | Published Tuesday, June 30, 2020The objective of building a social simulation in the Populism and Civic Engagement (PaCE) project is to study the phenomenon of populism by mapping individual level political behaviour and explain the influence of agents on, and their interdependence with the respective political parties. Voters, political parties and – to some extent – the media can be viewed as forming a complex adaptive system, in which parties compete for citizens’ votes, voters decide on which party to vote for based on their respective positions with regard to particular issues, and the media may influence the salience of issues in the public debate.
This is the first version of a model exploring voting behaviour in Austria. It focusses on modelling the interaction of voters and parties in a political landscape; the effects of the media are not yet represented. Austria was chosen as a case study because it has an established populist party (the “Freedom Party” FPO), which has even been part of the government over the years.
A Complex Model of Voter Turnout
Bruce Edmonds Laurence Lessard-Phillips Ed Fieldhouse | Published Monday, October 13, 2014 | Last modified Tuesday, August 18, 2015This is a complex “Data Integration Model”, following a “KIDS” rather than a “KISS” methodology - guided by the available evidence. It looks at the complex mix of social processes that may determine why people vote or not.
John Q. Public (JQP): A Model of Political Judgment and Behavior
Sung-Youn Kim | Published Monday, March 14, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The model integrates major theories of political judgment and behavior within the classical cognitive paradigm embedded in the ACT-R cognitive architecture. It models preferences and beliefs of political candidates, parties, and groups.