About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 50 results for "Thomas Michael Schmitt" clear search
Carington
William Kennedy Emily S Ihara Catherine J Tompkins Michael E Wolf-Branigin | Published Thursday, July 13, 2017The Carington model is designed to provide insights into the factors affecting informal health care for older adults. It encompasses older adults, caregivers, and factors affecting informal health care. The Carington model includes no submodels.
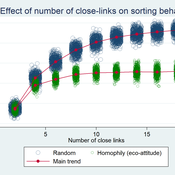
Waste separation in small-world networks
František Kalvas Michaela Kudrnáčová | Published Monday, September 30, 2019The model answers the question how homophily and number of close-links in small-world network influences behavior of consumats. The results show that the more close-links the more probable the consumat follows the major behavior, but homophilly blocks the major behavior and supports survival of the minor behavior.
Peer reviewed Historical Letters
Bernardo Buarque Malte Vogl Jascha Merijn Schmitz Aleksandra Kaye | Published Thursday, May 16, 2024 | Last modified Friday, May 24, 2024A letter sending model with historically informed initial positions to reconstruct communication and archiving processes in the Republic of Letters, the 15th to 17th century form of scholarship.
The model is aimed at historians, willing to formalize historical assumptions about the letter sending process itself and allows in principle to set heterogeneous social roles, e.g. to evaluate the role of gender or social status in the formation of letter exchange networks. The model furthermore includes a pruning process to simulate the loss of letters to critically asses the role of biases e.g. in relation to gender, geographical regions, or power structures, in the creation of empirical letter archives.
Each agent has an initial random topic vector, expressed as a RGB value. The initial positions of the agents are based on a weighted random draw based on data from [2]. In each step, agents generate two neighbourhoods for sending letters and potential targets to move towards. The probability to send letters is a self-reinforcing process. After each sending the internal topic of the receiver is updated as a movement in abstract space by a random amount towards the letters topic.
…
Neolithic Spread Model Version 1.0
Sean Bergin Salvador Pardo Gordo Joan Bernabeu Auban Michael Barton | Published Thursday, December 11, 2014 | Last modified Monday, December 31, 2018This model simulates different spread hypotheses proposed for the introduction of agriculture on the Iberian peninsula. We include three dispersal types: neighborhood, leapfrog, and ideal despotic distribution (IDD).
Incentives for data sharing
Flaminio Squazzoni Federico Bianchi Thomas Klebel Tony Ross-Hellauer | Published Thursday, October 02, 2025Although beneficial to scientific development, data sharing is still uncommon in many research areas. Various organisations, including funding agencies that endorse open science, aim to increase its uptake. However, estimating the large-scale implications of different policy interventions on data sharing by funding agencies, especially in the context of intense competition among academics, is difficult empirically. Here, we built an agent-based model to simulate the effect of different funding schemes (i.e., highly competitive large grants vs. distributive small grants), and varying intensity of incentives for data sharing on the uptake of data sharing by academic teams strategically adapting to the context.
Managing networked landscapes: conservation in fragmented, regionally connected world
Jacopo A. Baggio Michael Schoon Sechindra Vallury | Published Monday, December 09, 2019Exploring how learning and social-ecological networks influence management choice set and their ability to increase the likelihood of species coexistence (i.e. biodiversity) on a fragmented landscape controlled by different managers.
SimDrink: An agent-based NetLogo model of young, heavy drinkers for conducting alcohol policy experiments
Nick Scott James Wilson Michael Livingston Aaron Hart David Moore Paul Dietze | Published Friday, September 25, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, October 15, 2015A proof-of-concept agent-based model ‘SimDrink’, which simulates a population of 18-25 year old heavy alcohol drinkers on a night out in Melbourne to provide a means for conducting policy experiments to inform policy decisions.
Simulating Components of the Reinforcing Spirals Model and Spiral of Silence
František Kalvas Michael D. Slater Ashley Sanders-Jackson | Published Friday, November 05, 2021Communication processes occur in complex dynamic systems impacted by person attitudes and beliefs, environmental affordances, interpersonal interactions and other variables that all change over time. Many of the current approaches utilized by Communication researchers are unable to consider the full complexity of communication systems or the over time nature of our data. We apply agent-based modeling to the Reinforcing Spirals Model and the Spiral of Silence to better elucidate the complex and dynamic nature of this process. Our preliminary results illustrate how environmental affordances (i.e. social media), closeness of the system and probability of outspokenness may impact how attitudes change over time. Additional analyses are also proposed.
The Pampas Model: An agent-based model of agricultural systems in the Argentinean Pampas
Michael North Federico Bert Guillermo P Podestá Santiago L Rovere Charles Macal | Published Tuesday, July 16, 2013 | Last modified Tuesday, February 17, 2015The Pampas Model is an Agent-Based Model intended to explore the dynamics of structural and land use changes in agricultural systems of the Argentine Pampas in response to climatic, technological economic, and political drivers.
Sunshine or Shield?: Secret Voting Procedures and Legislative Accountability
Matthew Taylor Michele Buttò Carlos Pereira | Published Tuesday, June 24, 2014 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019An agent-based model is used to simulate legislators’ behavior under secret voting rules, as influenced by the power of the accused politician, the composition of the voting body, and the publicity of the accusations.
Displaying 10 of 50 results for "Thomas Michael Schmitt" clear search