About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 376 results for "Huw Vasey" clear search
Local extinctions, connectedness, and cultural evolution in structured populations
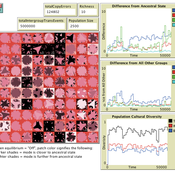
Luke Premo | Published Tuesday, May 25, 2021This model is designed to address the following research question: How does the amount and topology of intergroup cultural transmission modulate the effect of local group extinction on selectively neutral cultural diversity in a geographically structured population? The experimental design varies group extinction rate, the amount of intergroup cultural transmission, and the topology of intergroup cultural transmission while measuring the effects of local group extinction on long-term cultural change and regional cultural differentiation in a constant-size, spatially structured population. The results show that for most of the intergroup social network topologies tested here, increasing the amount of intergroup cultural transmission (similar to increasing gene flow in a genetic model) erases the negative effect of local group extinction on selectively neutral cultural diversity. The stochastic (i.e., preference attachment) network seems to stand out as an exception.
Biodiversity and Adoption of Small-scale Agroforestry in Rwanda (BASAR)
Beatrice Nöldeke Etti Winter Elisée Bahati Ntawuhiganayo | Published Friday, July 15, 2022The BASAR model aims to investigate different approaches to describe small-scale farmers’ decision-making in the context of diversified agroforestry adoption in rural Rwanda. Thereby, it compares random behaviour with perfect rationality (non-discounted and discounted utility maximization), bounded rationality (satisficing and fast and frugal decision tree heuristics), Theory of Planned Behaviour, and a probabilistic regression-based approach. It is aimed at policy-makers, extension agents, and cooperatives to better understand how rural farmers decide about implementing innovative agricultural practices such as agroforestry and at modelers to support them in selecting an approach to represent human decision-making in ABMs of Social-Ecological Systems. The overall objective is to identify a suitable approach to describe human decision-making and therefore improve forecasts of adoption rates and support the development and implementation of interventions that aim to raise low adoption rates.
Activation Regimes in Opinion Dynamics
Meysam Alizadeh Claudio Cioffi-Revilla | Published Tuesday, September 01, 2015We compare the effect of four activation regimes by measuring the appropriate opinion clustering statistics and also the number of emergent extremists.
Food supply chain innovations under public pressure
Tim Verwaart Wil Hennen Jan Buurma | Published Friday, April 15, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, November 27, 2018Aroused public opinion has led to public debates on social responsibility issues in food supply chains. This model based op opinion dynamics and the linkages between involved actors simulates the public debate leading to the transitions.
Simulation of the Effects of Disorganization on Goals and Problem Solving
Dinuka Herath | Published Sunday, August 13, 2017 | Last modified Sunday, August 13, 2017This is a model of the occurrence of disorganization and its impact on individual goal setting and problem-solving. This model therefore, explores the effects of disorganization on goal achievement.
Population size limits the coefficient of variation in continuous traits affected by proportional copying error
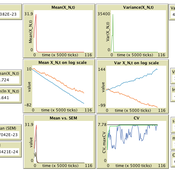
Luke Premo | Published Thursday, June 18, 2020This version of the accumulated copying error (ACE) model is designed to address the following research question: how does finite population size (N) affect the coefficient of variation (CV) of a continuous cultural trait under the assumptions that the only source of copying error is visual perception error and that the continuous trait can take any positive value (i.e., it has no upper bound)? The model allows one to address this question while assuming the continuous trait is transmitted via vertical transmission, unbiased transmission, prestige biased transmission, mean conformist transmission, or median conformist transmission. By varying the parameter, p, one can also investigate the effect of population size under a mix of vertical and non-vertical transmission, whereby on average (1-p)N individuals learn via vertical transmission and pN individuals learn via either unbiased transmission, prestige biased transmission, mean conformist transmission, or median conformist transmission.
SMASH: Stylized Model of Agricultural Smallholder Households
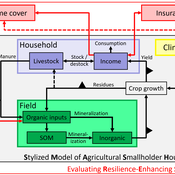
Tim Williams | Published Tuesday, December 08, 2020The SMASH model is an agent-based model of rural smallholder households. It models households’ evolving income and wealth, which they earn through crop sales. Wealth is carried in the form of livestock, which are grazed on an external rangeland (exogenous) and can be bought/sold as investment/coping mechanisms. The model includes a stylized representation of soil nutrient dynamics, modeling the inflows and outflows of organic and inorganic nitrogen from each household’s field.
The model has been applied to assess the resilience-enhancing effects of two different farm-level adaptation strategies: legume cover cropping and crop insurance. These two strategies interact with the model through different mechanims - legume cover cropping through ecological mechanisms and crop insurance through financial mechanisms. The model can be used to investigate the short- and long-term effects of these strategies, as well as how they may differently benefit different types of household.
World of Cows - Exploring land-use policies for a dairy-farm world (teaching modeling complex human-environment systems)
Maria Haensel Thomas Michael Schmitt Jakob Bogenreuther | Published Wednesday, January 11, 2023In the “World of Cows”, dairy farmers run their farms and interact with each other, the surrounding agricultural landscape, and the economic and political framework. The model serves as an exemplary case of an interdependent human-environment system.
With the model, users can analyze the influence of policies and markets on land use decisions of dairy farms. The land use decisions taken by farms determine the delivered ecosystem services on the landscape level. Users can choose a combination of five policy options and how strongly market prices fluctuate. Ideally, the choice of policy options fulfills the following three “political goals” 1) dairy farming stays economically viable, 2) the provision of ecosystem services is secured, and 3) government spending on subsidies is as low as possible.
The model has been designed for students to practice agent-based modeling and analyze the impacts of land use policies.
An Agent Based Model of International Capital Flows
Harvey Baldovino | Published Thursday, April 06, 2023This is a preliminary attempt in creating an Agent-Based Model of capital flows. This is based on the theory of capital flows based on interest-rate differentials. Foreign capital flows to a country with higher interest rates relative to another. The model shows how capital volatilty and wealth concentration are affected by the speed of capital flow, number of investors, magnitude of changes in interest rate due to capital flows and the interest differential threshold that investors set in deciding whether to move capital or not. Investors in the model are either “regional” investors (only investing in neighboring countries) and “global” investors (those who invest anywhere in the world).
In the future, the author hopes to extend this model to incorporate capital flow based on changes in macroeconomic fundamentals, exchange rate volatility, behavioral finance (for instance, herding behavior) and the presence of capital controls.
An agent-based model exploring the biodiversity-agriculture-nutrition dynamics in Eastern Madagascar resulting from alternative land uses
Romain Clercq-Roques Jessica Williams Katja Perez Guzman Marta Kozicka Kristine Belesova Zaid Chalabi | Published Wednesday, July 23, 2025This agent-based model simulates the interactions between smallholder farming households, land-use dynamics, and ecosystem services in a rural landscape of Eastern Madagascar. It explores how alternative agricultural practices —shifting agriculture, rice cultivation, and agroforestry—combined with varying levels of forest protection, influence food production, food security, dietary diversity, and forest biodiversity over time. The landscape is represented as a grid of spatially explicit patches characterized by land use, ecological attributes, and regeneration dynamics. Agents make yearly decisions on land management based on demographic pressures, agricultural returns, and institutional constraints. Crop yields are affected by stochastic biotic and abiotic disruptions, modulated by local ecosystem regulation functions. The model additionally represents foraging as a secondary food source and pressure on biodiversity. The model supports the analysis of long-term trade-offs between agricultural productivity, human nutrition, and conservation under different policy and land-use scenarios.
Displaying 10 of 376 results for "Huw Vasey" clear search