About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 229 results NetLogo clear search
01b ModEco NLG V1.39 – Model Economies – The PMM
Garvin Boyle | Published Friday, April 14, 2017It is very difficult to model a sustainable intergenerational biophysical/financial economy. ModEco NLG is one of a series of models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, CmLab.
A social network model to analyze team assembly mechanisms
Andreas Koch | Published Monday, April 10, 2017This model simulates networking mechanisms of an empirical social network. It correlates event determinants with place-based geography and social capital production.
Peer reviewed CHIME ABM Hurricane Evacuation Model
Joshua Watts | Published Friday, March 03, 2017 | Last modified Wednesday, May 29, 2019The CHIME ABM explores information distribution networks and agents’ protective decision making in the context of hurricane landfall.
This is an agent-based model that simulates the structural evolution in food supply chain.
Increased costs of cooperation help cooperators in the long run
Paul Smaldino | Published Wednesday, March 01, 2017A spatial prisoner’s dilemma model with mobile agents, de-coupled birth-death events, and harsh environments.
Peer reviewed ana-wag
Géraldine Abrami Mamadou Diallo Stefano Farolfi Bruno Bonté Nils Ferrand Wanda Aquae Gaudi | Published Monday, February 13, 2017 | Last modified Friday, May 10, 2019The ana-wag model, for Analyse Wat-A-Game (WAG), is a NetLogo version of the WAG role playing game. It enables to model a river catchment with the graphical modelling language WAG and to play it as a network-game (each player is a water user).
AnimDens NetLogo
Miguel Pais Christine Ward-Paige | Published Friday, February 10, 2017 | Last modified Sunday, February 23, 2020The model demonstrates how non-instantaneous sampling techniques produce bias by overestimating the number of counted animals, when they move relative to the person counting them.
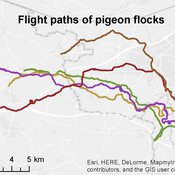
Homing pigeon model
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Saturday, October 29, 2016This model represents the flight paths of a flock of homing pigeons according to their flocking-, orientation- and leadership behaviour.
Heterogeneity of preferences and the dynamics of voluntary contributions to public goods
Engi Amin Amal Soliman Mohamed Abouelela | Published Thursday, August 18, 2016 | Last modified Thursday, January 25, 2018This model simulates the heterogeneity of preferences in a PG game and how the interaction between them affects the dynamics of voluntary contributions. Model is based on the results of a human-based experiment.
Peer reviewed Family Herd Demography
Mark Moritz Ian M Hamilton Andrew Yoak Rebecca Garabed Abigail Buffington | Published Monday, August 15, 2016 | Last modified Saturday, January 06, 2018The model examines the dynamics of herd growth in African pastoral systems. We used it to examine the role of scale (herd size) stochasticity (in mortality, fertility, and offtake) on herd growth.
Displaying 10 of 229 results NetLogo clear search