About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
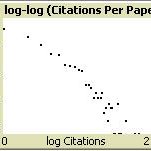
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 212 results Data clear search
Endogenous dynamics of firms made up by networked agents: an exploratory analysis
Bernardo Alves Furtado Isaque Daniel Rocha Eberhardt | Published Wednesday, March 23, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, October 05, 2016This is an adaptation and extension of Robert Axtell’s model (2013) of endogenous firms, in Python 3.4
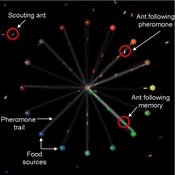
Composite Collective Decision Making - ant colony foraging model
Tomer Czaczkes Benjamin I Czaczkes | Published Thursday, December 17, 2015The model explores how two types of information - social (in the form of pheromone trails) and private (in the form of route memories) affect ant colony level foraging in a variable enviroment.
STECCAR: a simulation of the diffusion of electric cars
A Kangur Lc Verbrugge W Jager M Bockarjova | Published Sunday, November 29, 2015In this Repast model the ‘Consumat’ cognitive framework is applied to an ABM of the Dutch car market. Different policy scenarios can be selected or created to examine their effect on the diffusion of EVs.
The purpose of this model is to enhance a basic ABM through a simple set of rules identified using the activity-driven models in order to produce more realistic patterns of pedestrian movement.
Citation Agents: A model of collective learning through scientific publication
Christopher Watts | Published Friday, July 31, 2015Simulates the construction of scientific journal publications, including authors, references, contents and peer review. Also simulates collective learning on a fitness landscape. Described in: Watts, Christopher & Nigel Gilbert (forthcoming) “Does cumulative advantage affect collective learning in science? An agent-based simulation”, Scientometrics.
MedLanD Modeling Laboratory
C Michael Barton Sean Bergin Isaac Ullah Gary Mayer Hessam Sarjoughian Helena Mitasova | Published Friday, May 08, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, December 14, 2017The MML is a hybrid modeling environment that couples an agent-based model of small-holder agropastoral households and a cellular landscape evolution model that simulates changes in erosion/deposition, soils, and vegetation.
Social and ecological feedback in greening behavior
Athena Aktipis | Published Thursday, February 19, 2015We construct an agent-based model to investigate and understand the roles of green attachment, engagement in local ecological investment (i.e., greening), and social feedback.
Effect of communication in irrigation games
Jacopo A. Baggio Marco Janssen | Published Wednesday, January 14, 2015 | Last modified Wednesday, August 09, 2017The model includes different formulations how agents make decisions in irrigation games and this is compared with empirical data. The aim is to test different theoretical models, especially explaining effect of communication.
Collective Decision Making for Ecological Restoration version 2.0
Dean Massey Moira Zellner Cristy Watkins Jeremy Brooks Kristen Ross Lynne M Westphal | Published Wednesday, November 19, 2014CoDMER v. 2.0 was parameterized with ethnographic data from organizations dealing with prescribed fire and seeding native plants, to advance theory on how collective decisions emerge in ecological restoration.
Interplay between stakeholders of the management of a river
Christophe Sibertin-Blanc Pascal Roggero Bertrand Baldet | Published Wednesday, November 12, 2014This model describes and analyses the outcomes of the confrontation of interests, some conflicting, some common, about the management of a small river in SW France
Displaying 10 of 212 results Data clear search