About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 67 results for "Sarah Wise" clear search
The purpose of this model is to enhance a basic ABM through a simple set of rules identified using the activity-driven models in order to produce more realistic patterns of pedestrian movement.
SLUCEII LUXE (Land Use in an eXurban Environment)
Qingxu Huang Rick L Riolo Shipeng Sun Derek Robinson Dawn Parker Tatiana Filatova Meghan Hutchins Dan Brown | Published Tuesday, September 10, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, October 22, 2022LUXE is a land-use change model featuring different levels of land market implementation. It integrates utility measures, budget constraints, competitive bidding, and market interactions to model land-use change in exurban environment.
Viticulture development in emerging markets: Małopolska region
Marcin Czupryna Bogumił Kamiński Paweł Oleksy Piotr Przybek | Published Tuesday, November 28, 2017 | Last modified Saturday, June 16, 2018Model explains both the final state and the dynamics of the development process of the wine sector in the Małopolska region in Poland. Model admits heterogeneous agents (regular farms,large and small vineyards).
Peer reviewed MOOvPOPsurveillance
Matthew Gompper Aniruddha Belsare Joshua J Millspaugh | Published Tuesday, April 04, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, May 12, 2020MOOvPOPsurveillance was developed as a tool for wildlife agencies to guide collection and analysis of disease surveillance data that relies on non-probabilistic methods like harvest-based sampling.
An epidemiological-economic agent-based model of Huanglongbing and Asian citrus psyllid control in California
Jonathan Kaplan | Published Wednesday, June 01, 2022This model simulates economic and epidemiological interaction between citrus production and the disease Huanglongbing (HLB), which is vectored by the Asian citrus psyllid. The model is used to evaluate area-wide coordinated spraying when free-riding is possible given individuals’ beliefs in other grower participation in area-wide spraying and in the information provided by extension on the threat as HLB spread.
Peer reviewed Agent-Based Ramsey growth model with Brown and Green capital (ABRam-BG)
Sarah Wolf Aida Sarai Figueroa Alvarez | Published Monday, December 09, 2024The purpose of the ABRam-BG model is to study belief dynamics as a potential driver of green (growth) transitions and illustrate their dynamics in a closed, decentralized economy populated by utility maximizing agents with an environmental attitude. The model is built using the ABRam-T model (for model visit: https://doi.org/10.25937/ep45-k084) and introduces two types of capital – green (low carbon intensity) and brown (high carbon intensity) – with their respective technological progress levels. ABRam-BG simulates a green transition as an emergent phenomenon resulting from well-known opinion dynamics along the economic process.
Climate Change Adaptation in Coastal Regions
Emma Cutler | Published Thursday, June 01, 2017This generic model simulates climate change adaptation in the form of resistance, accommodation, and retreat in coastal regions vulnerable to sea level rise and flooding. It tracks how population changes as households retreat to higher ground.
AmphorABM
Stefani Crabtree | Published Tuesday, January 05, 2021This model examines the economic interaction between Gaulish wheat farmers and Etruscan and Greek wine farming in 7th century B.C. France.
Peer reviewed Multilevel Group Selection I
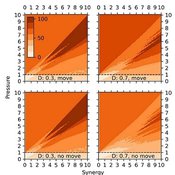
Wayne W. Wakeland Thaddeus Shannon Garry Sotnik | Published Tuesday, April 21, 2020 | Last modified Saturday, July 03, 2021New theoretical agent-based model of population-wide adoption of prosocial common-pool behavior with four parameters (initial percent of adopters, pressure to change behavior, synergy from behavior, and population density); dynamics in behavior, movement, freeriding, and group composition and size; and emergence of multilevel group selection. Theoretical analysis of model’s dynamics identified six regions in model’s parameter space, in which pressure-synergy combinations lead to different outcomes: extinction, persistence, and full adoption. Simulation results verified the theoretical analysis and demonstrated that increases in density reduce number of pressure-synergy combinations leading to population-wide adoption; initial percent of contributors affects underlying behavior and final outcomes, but not size of regions or transition zones between them; and random movement assists adoption of prosocial common-pool behavior.
An agent-based approach to weighted decision making in the spatially and temporally variable South African Paleoscape
Colin Wren | Published Thursday, December 29, 2016This model simulates a foraging system based on Middle Stone Age plant and shellfish foraging in South Africa.
Displaying 10 of 67 results for "Sarah Wise" clear search