About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 150 results strategies clear search
Lakeland 2 is a simple version of the original Lakeland of Jager et al. (2000) Ecological Economics 35(3): 357-380. The model can be used to explore the consequences of different behavioral assumptions on resource and social dynamics.
InnovationGame
Madeline Tyson | Published Thursday, August 24, 2017This model includes an innovation search environment. Agents search and can share their findings. It’s implemented in Netlogo-Hubnet & a parallel Netlogo model. This allows for validation of search strategies against experimental findings.
RAGE RAngeland Grazing Model
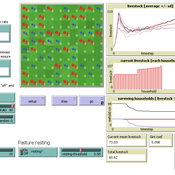
Carsten M Buchmann Jule Thober Birgit Müller Karin Frank Cheng Guo Jürgen Groeneveld Gunnar Dressler Niklas Hase | Published Monday, July 17, 2017 | Last modified Friday, October 26, 2018RAGE models a stylized common property grazing system. Agents follow a certain behavioral type. The model allows analyzing how household behavior with respect to a social norm on pasture resting affects long-term social-ecological system dynamics.
A model on feeding and social interaction behaviour of pigs
Iris J.M.M. Boumans | Published Thursday, May 04, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, February 27, 2018The model simulates interaction between internal physiological factors (e.g. energy balance) and external social factors (e.g. competition level) underlying feeding and social interaction behaviour of commercially group-housed pigs.
Success bias imitation increases the probability of effectively dealing with ecological disturbances
Jacopo A. Baggio Vicken Hillis | Published Thursday, April 13, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, August 02, 2018This model aims to investigate how different type of learning (social system) and disturbance specific attributes (ecological system) influence adoption of treatment strategies to treat the effects of ecological disturbances.
Peer reviewed MOOvPOPsurveillance
Matthew Gompper Aniruddha Belsare Joshua J Millspaugh | Published Tuesday, April 04, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, May 12, 2020MOOvPOPsurveillance was developed as a tool for wildlife agencies to guide collection and analysis of disease surveillance data that relies on non-probabilistic methods like harvest-based sampling.
Peer reviewed DogFoxCDVspillover
Aniruddha Belsare Matthew Gompper | Published Thursday, March 16, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, April 04, 2017The purpose of this model is to better understand the dynamics of a multihost pathogen in two host system comprising of high densities of domestic hosts and sympatric wildlife hosts susceptible to the pathogen.
LBD Model: Learning-by-doing for sustainable management of renewable resources
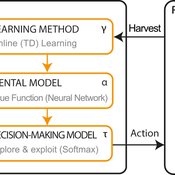
Emilie Lindkvist Örjan Ekeberg Jon Norberg | Published Thursday, March 09, 2017This is a simulation model of an intelligent agent that has the objective to learn sustainable management of a renewable resource, such as a fish stock.
Resource distribution effects on optimal foraging theory
Marco Janssen Kim Hill | Published Friday, January 27, 2017The original Ache model is used to explore different distributions of resources on the landscape and it’s effect on optimal strategies of the camps on hunting and camp movement.
Institutional change
Abigail Sullivan | Published Friday, October 07, 2016 | Last modified Sunday, December 02, 2018This model builds on another model in this library (“diffusion of culture”).
Displaying 10 of 150 results strategies clear search