About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1252 results Sort by: Recently modified clear search
Telephone Game
Julia Kasmire | Published Friday, January 10, 2020This is a model of a game of Telephone (also known as Chinese Whishpers in the UK), with agents representing people that can be asked, to play. The first player selects a word from their internal vocabulary and “whispers” it to the next player, who may mishear it depending on the current noise level, who whispers that word to the next player, and so on.
When the game ends, the word chosen by the first player is compared to the word heard by the last player. If they match exactly, all players earn large prize. If the words do not match exactly, a small prize is awarded to all players for each part of the words that do match. Players change color to reflect their current prize-count. A histogram shows the distribution of colors over all the players.
The user can decide on factors like
* how many players there are,
…
City Sandbox
Javier Sandoval | Published Thursday, January 09, 2020This model grows land use patterns that emerge as a result of land-use compatibilities stablished in urban development plans, land topography, and street networks. It contains urban brushes to paint streets and land uses as a way to learn about urban pattern emergence through free experimentation.
Spatio-Temporal Dynamic of Risk Model
J Jumadi | Published Tuesday, October 22, 2019 | Last modified Sunday, January 05, 2020This model aims to simlulate the dynamic of risk over time and space.
A Bottom-Up Simulation on Competition and Displacement of Online Interpersonal Communication Platforms
great-sage-futao | Published Tuesday, December 31, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, December 31, 2019This model aims to simulate Competition and Displacement of Online Interpersonal Communication Platforms process from a bottom-up angle. Individual interpersonal communication platform adoption and abandonment serve as the micro-foundation of the simulation model. The evolution mode of platform user online communication network determines how present platform users adjust their communication relationships as well as how new users join that network. This evolution mode together with innovations proposed by individual interpersonal communication platforms would also have impacts on the platform competition and displacement process and result by influencing individual platform adoption and abandonment behaviors. Three scenes were designed to simulate some common competition situations occurred in the past and current time, that two homogeneous interpersonal communication platforms competed with each other when this kind of platforms first came into the public eye, that a late entrant platform with a major innovation competed with the leading incumbent platform during the following days, as well as that both the leading incumbent and the late entrant continued to propose many small innovations to compete in recent days, respectively.
Initial parameters are as follows: n(Nmax in the paper), denotes the final node number of the online communication network node. mi (m in the paper), denotes the initial degree of those initial network nodes and new added nodes. pc(Pc in the paper), denotes the proportion of links to be removed and added in each epoch. pst(Pv in the paper), denotes the proportion of nodes with a viscosity to some platforms. comeintime(Ti in the paper), denotes the epoch when Platform 2 joins the market. pit(Pi in the paper), denotes the proportion of nodes adopting Platform 2 immediately at epoch comeintime(Ti). ct(Ct in the paper), denotes the Innovation Effective Period length. In Scene 2, There is only one major platform proposed by Platform 2, and ct describes that length. However, in Scene 3, Platform 2 and 1 will propose innovations alternately. And so, we set ct=10000 in simulation program, and every jtt epochs, we alter the innovation proposer from one platform to the other. Hence in this scene, jtt actually denotes the Innovation Effective Period length instead of ct.
A Pastoral Stoking Strategy Model with Fodder Import and Loan Scenarios
Yanbo Li | Published Tuesday, December 24, 2019This model was built to estimate the impacts of exogenous fodder input and credit loans services on livelihood, rangeland health and profits of pastoral production in a small holder pastoral household in the arid steppe rangeland of Inner Mongolia, China. The model simulated the long-term dynamic of herd size and structure, the forage demand and supply, the cash flow, and the situation of loan debt under three different stocking strategies: (1) No external fodder input, (2) fodders were only imported when natural disaster occurred, and (3) frequent import of external fodder, with different amount of available credit loans. Monte-Carlo method was used to address the influence of climate variability.
Managing ecological disturbances: Learning and the structure of social-ecological networks
Jacopo A. Baggio Vicken Hillis | Published Friday, March 03, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, August 02, 2018The aim of this model is to explore and understand the factors driving adoption of treatment strategies for ecological disturbances, considering payoff signals, learning strategies and social-ecological network structure
Vertical Communication in Organizations
vinz2711 Juliette Rouchier Victorien Barbet Noé Guiraud | Published Friday, December 20, 2019We propose an ABM replicating the evolution of action oriented groups (like NPO) due to disagreement among members on the practices to implement. Looking at the stability and representativeness (ability of groups to federate) we introduce vertical communication: the possibility for group to communicate around their practices to their members. We test for three levels (to whom it is addressed) and four types (how it influences agents) of communication.
Cliff Walking with Q-Learning NetLogo Extension
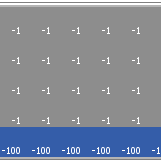
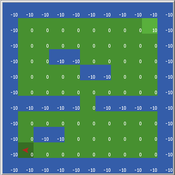
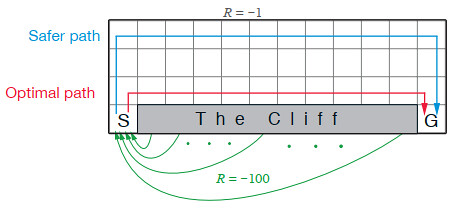
Kevin Kons Fernando Santos | Published Tuesday, December 10, 2019This model implements a classic scenario used in Reinforcement Learning problem, the “Cliff Walking Problem”. Consider the gridworld shown below (SUTTON; BARTO, 2018). This is a standard undiscounted, episodic task, with start and goal states, and the usual actions causing movement up, down, right, and left. Reward is -1 on all transitions except those into the region marked “The Cliff.” Stepping into this region incurs a reward of -100 and sends the agent instantly back to the start (SUTTON; BARTO, 2018).
The problem is solved in this model using the Q-Learning algorithm. The algorithm is implemented with the support of the NetLogo Q-Learning Extension
Maze with Q-Learning NetLogo extension
Kevin Kons Fernando Santos | Published Tuesday, December 10, 2019This is a re-implementation of a the NetLogo model Maze (ROOP, 2006).
This re-implementation makes use of the Q-Learning NetLogo Extension to implement the Q-Learning, which is done only with NetLogo native code in the original implementation.
A Model of the Gender Cliff in the Relative Contribution to the Household Income
André Grow Jan Van Bavel | Published Wednesday, December 18, 2019In Western countries, the distribution of relative incomes within marriages tends to be skewed in a remarkable way. Husbands usually do not only earn more than their female partners, but there also is a striking discontinuity in their relative contributions to the household income at the 50/50 point: many wives contribute just a bit less than or as much as their husbands, but few contribute more. Our model makes it possible to study a social mechanism that might create this ‘cliff’: women and men differ in their incomes (even outside marriage) and this may differentially affect their abilities to find similar- or higher-income partners. This may ultimately contribute to inequalities within the households that form. The model and associated files make it possible to assess the merit of this mechanism in 27 European countries.
Displaying 10 of 1252 results Sort by: Recently modified clear search