About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 141 results C clear search
The purpose of the study is to unpack and explore a potentially beneficial role of sharing metacognitive information within a group when making repeated decisions about common pool resource (CPR) use.
We explore the explanatory power of sharing metacognition by varying (a) the individual errors in judgement (myside-bias); (b) the ways of reaching a collective judgement (metacognition-dependent), (c) individual knowledge updating (metacognition- dependent) and d) the decision making context.
The model (AgentEx-Meta) represents an extension to an existing and validated model reflecting behavioural CPR laboratory experiments (Schill, Lindahl & Crépin, 2015; Lindahl, Crépin & Schill, 2016). AgentEx-Meta allows us to systematically vary the extent to which metacognitive information is available to agents, and to explore the boundary conditions of group benefits of metacognitive information.
Peer reviewed TRANSOPE: a multi-agent model to simulate outsourcing networks in road freight transport.
Aitor Salas-Peña Blanca Rosa Cases Gutiérrez | Published Friday, October 21, 2022A road freight transport (RFT) operation involves the participation of several types of companies in its execution. The TRANSOPE model simulates the subcontracting process between 3 types of companies: Freight Forwarders (FF), Transport Companies (TC) and self-employed carriers (CA). These companies (agents) form transport outsourcing chains (TOCs) by making decisions based on supplier selection criteria and transaction acceptance criteria. Through their participation in TOCs, companies are able to learn and exchange information, so that knowledge becomes another important factor in new collaborations. The model can replicate multiple subcontracting situations at a local and regional geographic level.
The succession of n operations over d days provides two types of results: 1) Social Complex Networks, and 2) Spatial knowledge accumulation environments. The combination of these results is used to identify the emergence of new logistics clusters. The types of actors involved as well as the variables and parameters used have their justification in a survey of transport experts and in the existing literature on the subject.
As a result of a preferential selection process, the distribution of activity among agents shows to be highly uneven. The cumulative network resulting from the self-organisation of the system suggests a structure similar to scale-free networks (Albert & Barabási, 2001). In this sense, new agents join the network according to the needs of the market. Similarly, the network of preferential relationships persists over time. Here, knowledge transfer plays a key role in the assignment of central connector roles, whose participation in the outsourcing network is even more decisive in situations of scarcity of transport contracts.
Addressing Barriers to Primary Care Access for Latinos in the U.S.: An Agent-Based Model
S.R. Aurora (a.k.a. Mai P. Trinh) Hyunsung Oh | Published Tuesday, August 16, 2022Disparities in access to primary health care have led to health disadvantages among Latinos and other non-White racial groups. To better identify and understand which policies are most likely to improve health care for Latinos, we examined differences in access to primary care between Latinos with proficient English language skills and Latinos with limited English proficiency (LEP) and estimated the extent of access to primary care providers (PCPs) among Latinos in the U.S.
Leviathan group model and its approximation
Thibaut Roubin Guillaume Deffuant | Published Tuesday, July 26, 2022The model is based on the influence function of the Leviathan model (Deffuant, Carletti, Huet 2013 and Huet and Deffuant 2017) with the addition of group idenetity. We aim at better explaining some patterns generated by this model, using a derived mathematical approximation of the evolution of the opinions averaged.
We consider agents having an opinion/esteem about each other and about themselves. During dyadic meetings, agents change their respective opinion about each other, and possibly about other agents they gossip about, with a noisy perception of the opinions of their interlocutor. Highly valued agents are more influential in such encounters. Moreover, each agent belongs to a single group and the opinions within the group are attracted to their average.
We show that a group hierarchy can emerges from this model, and that the inequality of reputations among groups have a negative effect on the opinions about the groups of low status. The mathematical analysis of the opinion dynamic shows that the lower the status of the group, the more detrimental the interactions with the agents of other groups are for the opinions about this group, especially when gossip is activated. However, the interactions between agents of the same group tend to have a positive effect on the opinions about this group.
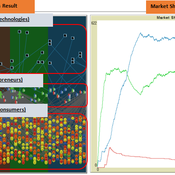
The simulation on the study of the optimal business strategy with the interaction between technologies and consumers.
sej-yoo | Published Monday, June 27, 2022 | Last modified Monday, July 04, 2022HOW IT WORKS
This model consists of three agents, and each agent type operates per business theories as below.
a. New technologies(Tech): It evolves per sustaining or disruptive technology trajectory with the constraint of project management triangle (Scope, Time, Quality, and Cost).
b. Entrepreneurs(Entre): It builds up the solution by combining Tech components per its own strategy (Exploration, Exploitation, or Ambidex).
c. Consumer(Consumer): It selects the solution per its own preference due to Diffusion of innovation theory (Innovators, Early Adopters, Early Majority, Late Majority, Laggards)
…
Peer reviewed The Viability of the Social-Ecological Agroecosystem (ViSA) Spatial Agent-based Model
Mostafa Shaaban | Published Friday, June 03, 2022ViSA simulates the decision behaviors of different stakeholders showing demands for ecosystem services (ESS) in agricultural landscape. The lack of sufficient supply of ESSs triggers stakeholders to apply different management options to increase their supply. However, while attempting to reduce the supply-demand gap, conflicts arise among stakeholders due to the tradeoff nature of some ESS. ViSA investigates conditions and scenarios that can minimize such supply-demand gap while reducing the risk of conflicts by suggesting different mixes of management options and decision rules.
ABM for Underwater optical wireless communication in a water tank
Mohamed ABID | Published Sunday, May 29, 2022This model simulates the propagation of photons in a water tank. A source of light emits an impulse of photons with equal energy represented by yellow dots. These photons are then scattered by water particles before possibly reaching the photo-detector represented by a gray line. Different types of water are considered. For each one of them we calculate the total received energy.
The water tank is represented by a blue rectangle with fixed dimensions. It’s exposed to the air interface and has totally absorbent barriers. Four types of water are supported. Each one is characterized by its absorption and scattering coefficients.
At the source, the photons are generated uniformly with a random direction within the beamwidth. Each photon travels a random distance drawn from a distribution depending on the water characteristics before encountering a water particle.
Based on the updated position of the photon, three situations may occur:
-The photon hits the barrier of the tank on its trajectory. In this case it’s considered as lost since the barriers are assumed totally absorbent.
…
ReMoTe-S. Residential Mobility of Tenants in Switzerland: an agent-based model
Claudia Binder Anna Pagani Francesco Ballestrazzi Emanuele Massaro | Published Friday, April 01, 2022ReMoTe-S is an agent-based model of the residential mobility of Swiss tenants. Its goal is to foster a holistic understanding of the reciprocal influence between households and dwellings and thereby inform a sustainable management of the housing stock. The model is based on assumptions derived from empirical research conducted with three housing providers in Switzerland and can be used mainly for two purposes: (i) the exploration of what if scenarios that target a reduction of the housing footprint while accounting for households’ preferences and needs; (ii) knowledge production in the field of residential mobility and more specifically on the role of housing functions as orchestrators of the relocation process.
The Levers of HIV Model
Arthur Hjorth Wouter Vermeer C. Hendricks Brown Uri Wilensky Can Gurkan | Published Tuesday, March 08, 2022 | Last modified Tuesday, October 31, 2023Chicago’s demographic, neighborhood, sex risk behaviors, sexual network data, and HIV prevention and treatment cascade information from 2015 were integrated as input to a new agent-based model (ABM) called the Levers-of-HIV-Model (LHM). This LHM, written in NetLogo, forms patterns of sexual relations among Men who have Sex with Men (MSM) based on static traits (race/ethnicity, and age) and dynamic states (sexual relations and practices) that are found in Chicago. LHM’s five modules simulate and count new infections at the two marker years of 2023 and 2030 for a wide range of distinct scenarios or levers, in which the levels of PrEP and ART linkage to care, retention, and adherence or viral load are increased over time from the 2015 baseline levels.
An Agent-Based Model of Insurance Customer Behaviour with Word of Mouth Network in C#
Rei England Iqbal Owadally Douglas Wright | Published Friday, March 04, 2022This is an agent-based model with two types of agents: customers and insurers. Insurers are price-takers who choose how much to spend on their service quality, and customers evaluate insurers based on premium, brand preference, and their perceived service quality. Customers are also connected in a small-world network and may share their opinions with their network.
The ABM contains two types of agents: insurers and customers. These act within the environment of a motor insurance market. At each simulation, the model undergoes the following steps:
- Network generation: At the start of the simulation, the model generates a small world network of social links between the customers, and randomly assigns each customer to an initial insurer ...
Displaying 10 of 141 results C clear search