About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 48 results for "Thomas Michael Schmitt" clear search
Pedestrian model
Gudrun Wallentin Dana Kaziyeva Martin Loidl Petra Stutz | Published Monday, August 07, 2023The model generates disaggregated traffic flows of pedestrians, simulating their daily mobility behaviour represented as probabilistic rules. Various parameters of physical infrastructure and travel behaviour can be altered and tested. This allows predicting potential shifts in traffic dynamics in a simulated setting. Moreover, assumptions in decision-making processes are general for mid-sized cities and can be applied to similar areas.
Together with the model files, there is the ODD protocol with the detailed description of model’s structure. Check the associated publication for results and evaluation of the model.
Installation
Download GAMA-platform (GAMA1.8.2 with JDK version) from https://gama-platform.github.io/. The platform requires a minimum of 4 GB of RAM.
…
Peer reviewed Evolutionary Economic Learning Simulation: A Genetic Algorithm for Dynamic 2x2 Strategic-Form Games in Python
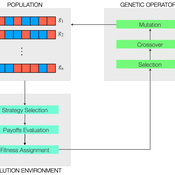
Vinicius Ferraz Thomas Pitz | Published Friday, April 08, 2022This project combines game theory and genetic algorithms in a simulation model for evolutionary learning and strategic behavior. It is often observed in the real world that strategic scenarios change over time, and deciding agents need to adapt to new information and environmental structures. Yet, game theory models often focus on static games, even for dynamic and temporal analyses. This simulation model introduces a heuristic procedure that enables these changes in strategic scenarios with Genetic Algorithms. Using normalized 2x2 strategic-form games as input, computational agents can interact and make decisions using three pre-defined decision rules: Nash Equilibrium, Hurwicz Rule, and Random. The games then are allowed to change over time as a function of the agent’s behavior through crossover and mutation. As a result, strategic behavior can be modeled in several simulated scenarios, and their impacts and outcomes can be analyzed, potentially transforming conflictual situations into harmony.
Confirmation Bias improves Performance in a Signal Detection Task and evolves in an Evolutionary Algorithm
Michael Vogrin | Published Monday, May 08, 2023Confirmation Bias is usually seen as a flaw of the human mind. However, in some tasks, it may also increase performance. Here, agents are confronted with a number of binary Signals (A, or B). They have a base detection rate, e.g. 50%, and after they detected one signal, they get biased towards this type of signal. This means, that they observe that kind of signal a bit better, and the other signal a bit worse. This is moderated by a variable called “bias_effect”, e.g. 10%. So an agent who detects A first, gets biased towards A and then improves its chance to detect A-signals by 10%. Thus, this agent detects A-Signals with the probability of 50%+10% = 60% and detects B-Signals with the probability of 50%-10% = 40%.
Given such a framework, agents that have the ability to be biased have better results in most of the scenarios.
Peer reviewed ABM to create populations with realistic Big Five Personality Trait Expressions
Michael Vogrin | Published Tuesday, May 30, 2023This model aims at creating agent populations that have “personalities”, as described by the Big Five Model of Personality. The expression of the Big Five in the agent population has the following properties, so that they resemble real life populations as closely as possible:
-The population mean of each trait is 0.5 on a scale from 0 to 1.
-The population-wide distribution of each trait approximates a normal distribution.
-The intercorrelations of the Big Five are close to those observed in the Literature.
The literature used to fit the model was a publication by Dimitri van der Linden, Jan te Nijenhuis, and Arnold B. Bakker:
…
Swidden farming by individual households
C Michael Barton | Published Sunday, April 27, 2008 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Swidden Farming is designed to explore the dynamics of agricultural land management strategies.
Patch choice model from Optimal Foraging Theory (Human Behavioral Ecology)
C Michael Barton | Published Saturday, November 22, 2008 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013NetLogo model of patch choice model from optimal foraging theory (human behavioral ecology).
Diet breadth model from Optimal Foraging Theory (Human Behavioral Ecology)
C Michael Barton | Published Wednesday, November 26, 2008 | Last modified Thursday, March 12, 2015Diet breadth is a classic optimal foraging theory (OFT) model from human behavioral ecology (HBE). Different resources, ranked according to their food value and processing costs, are distributed in th
Hominin ecodynamics v.2
C Michael Barton | Published Monday, September 19, 2011 | Last modified Friday, March 28, 2014Simulates biobehavioral interactions between 2 populations of hominins.
Peer reviewed Hominin ecodynamics v.1
C Michael Barton | Published Saturday, October 01, 2011 | Last modified Friday, March 28, 2014Biobehavioral interactions between two populations under different movement strategies.
Hominin Ecodynamics v.1.1 (update for perception and interaction)
C Michael Barton | Published Wednesday, August 15, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Models land-use, perception, and biocultural interactions between two forager populations.
Displaying 10 of 48 results for "Thomas Michael Schmitt" clear search