About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers at all levels engage in the establishment and adoption of community standards and good practices for developing and sharing computational models. Model authors can freely publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library alongside narrative documentation, open science metadata, and other emerging open science norms that facilitate software citation, reproducibility, interoperability, and reuse. Model authors can also request peer review of their computational models to receive a DOI.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with additional detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 37 results for "Michael Lewis" clear search
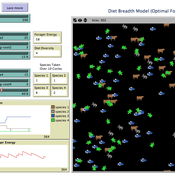
Diet breadth model from Optimal Foraging Theory (Human Behavioral Ecology)
C Michael Barton | Published Wednesday, November 26, 2008 | Last modified Thursday, March 12, 2015Diet breadth is a classic optimal foraging theory (OFT) model from human behavioral ecology (HBE). Different resources, ranked according to their food value and processing costs, are distributed in th
Hominin ecodynamics v.2
C Michael Barton | Published Monday, September 19, 2011 | Last modified Friday, March 28, 2014Simulates biobehavioral interactions between 2 populations of hominins.
Peer reviewed Hominin ecodynamics v.1
C Michael Barton | Published Saturday, October 01, 2011 | Last modified Friday, March 28, 2014Biobehavioral interactions between two populations under different movement strategies.
Hominin Ecodynamics v.1.1 (update for perception and interaction)
C Michael Barton | Published Wednesday, August 15, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Models land-use, perception, and biocultural interactions between two forager populations.
Peer reviewed Swidden Farming Version 2.0
C Michael Barton | Published Wednesday, June 12, 2013 | Last modified Wednesday, September 03, 2014Model of shifting cultivation. All parameters can be controlled by the user or the model can be run in adaptive mode, in which agents innovate and select parameters.
Scholars have written extensively about hierarchical international order, on the one hand, and war on the other, but surprisingly little work systematically explores the connection between the two. This disconnect is all the more striking given that empirical studies have found a strong relationship between the two. We provide a generative computational network model that explains hierarchy and war as two elements of a larger recursive process: The threat of war drives the formation of hierarchy, which in turn shapes states’ incentives for war. Grounded in canonical theories of hierarchy and war, the model explains an array of known regularities about hierarchical order and conflict. Surprisingly, we also find that many traditional results of the IR literature—including institutional persistence, balancing behavior, and systemic self-regulation—emerge from the interplay between hierarchy and war.
Formation of Lithic Assemblages v. 1
C Michael Barton Julien Riel-Salvatore | Published Thursday, September 04, 2014This model represents technological and ecological behaviors of mobile hunter-gatherers, in a variable environment, as they produce, use, and discard chipped stone artifacts. The results can be analyzed and compared with archaeological sites.
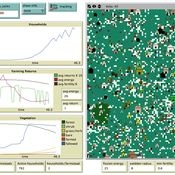
A simple model that aims to demonstrate the influence of agri-environmental payments on land-use patterns in a virtual landscape. The landscape consists of grassland (which can be managed extensively or intensively) and a river. Agri-environmental payments are provided for extensive management of grassland. Additionally, there are boni for (a) extensive grassland in proximity of the river; and (b) clusters (“agglomerations”) of extensive grassland. The farmers, who own randomly distributed grassland patches, make decisions either on the basis of simple income maximization or they maximize only up to an income threshold beyond which they seize making changes in management. The resulting landscape pattern is evaluated by means of three simple models for (a) agricultural yield, (b) habitat/biodiversity and (c) water quality. The latter two correspond to the two boni. The model has been developed within a small project called Aligning Agent-Based Modelling with Multi-Objective Land-Use Allocation (ALABAMA).
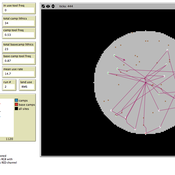
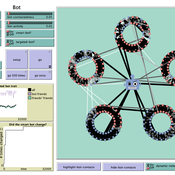
How do bots influence beliefs on social media? Why do beliefs propagated by social bots spread far and wide, yet does their direct influence appear to be limited?
This model extends Axelrod’s model for the dissemination of culture (1997), with a social bot agent–an agent who only sends information and cannot be influenced themselves. The basic network is a ring network with N agents connected to k nearest neighbors. The agents have a cultural profile with F features and Q traits per feature. When two agents interact, the sending agent sends the trait of a randomly chosen feature to the receiving agent, who adopts this trait with a probability equal to their similarity. To this network, we add a bot agents who is given a unique trait on the first feature and is connected to a proportion of the agents in the model equal to ‘bot-connectedness’. At each timestep, the bot is chosen to spread one of its traits to its neighbors with a probility equal to ‘bot-activity’.
The main finding in this model is that, generally, bot activity and bot connectedness are both negatively related to the success of the bot in spreading its unique message, in equilibrium. The mechanism is that very active and well connected bots quickly influence their direct contacts, who then grow too dissimilar from the bot’s indirect contacts to quickly, preventing indirect influence. A less active and less connected bot leaves more space for indirect influence to occur, and is therefore more successful in the long run.
Carington
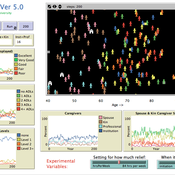
William Kennedy Emily S Ihara Catherine J Tompkins Michael E Wolf-Branigin | Published Thursday, July 13, 2017The Carington model is designed to provide insights into the factors affecting informal health care for older adults. It encompasses older adults, caregivers, and factors affecting informal health care. The Carington model includes no submodels.
Displaying 10 of 37 results for "Michael Lewis" clear search