About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 23 results for "Carlo Proietti" clear search
The role of argument strength and informational biases in polarization and bipolarization effects
Davide Chiarella Carlo Proietti | Published Thursday, March 30, 2023The model explores the informational causes of polarization and bi-polarization of opinions in groups. To this end it expands the model of the Argument Communication Theory of Bi-polarization. The latter is an argument-based multi-agent model of opinion dynamics inspired by Persuasive Argument Theory. The original model can account for polarization as an outcome of pure informational influence, and reproduces bi-polarization effects by postulating an additional mechanism of homophilous selection of communication partners. The expanded model adds two dimensions: argument strength and more sophisticated protocols of informational influence (argument communication and opinion update).
A Pastoral Stoking Strategy Model with Fodder Import and Loan Scenarios
Yanbo Li | Published Tuesday, December 24, 2019This model was built to estimate the impacts of exogenous fodder input and credit loans services on livelihood, rangeland health and profits of pastoral production in a small holder pastoral household in the arid steppe rangeland of Inner Mongolia, China. The model simulated the long-term dynamic of herd size and structure, the forage demand and supply, the cash flow, and the situation of loan debt under three different stocking strategies: (1) No external fodder input, (2) fodders were only imported when natural disaster occurred, and (3) frequent import of external fodder, with different amount of available credit loans. Monte-Carlo method was used to address the influence of climate variability.
Structural Violence and Neurobiological Adaptation: Modeling the Trajectory of Youth Outside of Care
masterpiece33330-prog | Published Thursday, November 27, 2025This study presents a System Dynamics (SD) model that explores the “trajectories of homelessness” among youth outside of the formal care system. Unlike traditional approaches that view runaway behavior as a discrete choice, this model reinterprets it as a neurobiological adaptation to chronic resource deprivation and systemic neglect.
The model incorporates key mechanisms such as ‘Allostatic Load’ accumulation, ‘PFC-Amygdala Switching’, and the ‘Iatrogenic Effects’ of shelter policies. It utilizes Monte Carlo simulations to demonstrate how structural factors create a “probabilistic vulnerability,” trapping youth in cycles of survival crime and isolation regardless of individual resilience.
The uploaded code includes a Python implementation of the model to ensure reproducibility of the stochastic analysis presented in the paper.
Emergency Warning Dissemination in a Multiplex Social Network
Charles Koll | Published Tuesday, January 31, 2023This is an interdisciplinary agent-based model with Monte Carlo simulations to assess the relative effects of broadcast and contagion processes in a multiplex social network. This multiplex approach models multiple channels of informal communication - phone, word-of-mouth, and social media - that vary in their attribute values. Each agent is an individual in a threatened community who, once warned, has a probability of warning others in their social network using one of these channels. The probability of an individual warning others is based on their warning source and the time remaining until disaster impact, among other variables. Default parameter values were chosen from empirical studies of disaster warnings along with the spatial aspects of Coos Bay, OR, USA and Seaside, OR, USA communities.
A Simple Agent Based Modeling Tool for Plastic and Debris Tracking in Oceans
Subu Kandaswamy Koushik Sura Bhaskar Sai Amulya Murukutla Sai Pranay Raju Chinthala Abhishek Bobbillapati | Published Monday, October 04, 2021Plastics and the pollution caused by their waste have always been a menace to both nature and humans. With the continual increase in plastic waste, the contamination due to plastic has stretched to the oceans. Many plastics are being drained into the oceans and rose to accumulate in the oceans. These plastics have seemed to form large patches of debris that keep floating in the oceans over the years. Identification of the plastic debris in the ocean is challenging and it is essential to clean plastic debris from the ocean. We propose a simple tool built using the agent-based modeling framework NetLogo. The tool uses ocean currents data and plastic data both being loaded using GIS (Geographic Information System) to simulate and visualize the movement of floatable plastic and debris in the oceans. The tool can be used to identify the plastic debris that has been piled up in the oceans. The tool can also be used as a teaching aid in classrooms to bring awareness about the impact of plastic pollution. This tool could additionally assist people to realize how a small plastic chunk discarded can end up as large debris drifting in the oceans. The same tool might help us narrow down the search area while looking out for missing cargo and wreckage parts of ships or flights. Though the tool does not pinpoint the location, it might help in reducing the search area and might be a rudimentary alternative for more computationally expensive models.
Forest Logging and Ecosystem Degradation
Carla Guerrero | Published Sunday, February 15, 2026This model simulates a forest ecosystem affected by human logging. We explore different kind of approaches and their possible consequences for the ecosystem. Loggers can either be responsible or irresponsible, they will either take care to cut trees or not. In turn their actions will have consequences on the quality of the soil, the atmosphere as well as their profit made from logging. In this model we see that even careful management cannot prevent the degradation of the forest ecosystem.
Alternative scenarios of green consumption in Italy: an empirically grounded model.
Giangiacomo Bravo Elena Vallino Alessandro K Cerutti Maria Beatrice Pairotti | Published Thursday, March 28, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013We provide a full description of the model following the ODD protocol (Grimm et al. 2010) in the attached document. The model is developed in NetLogo 5.0 (Wilenski 1999).
An agent-based model of scapegoating
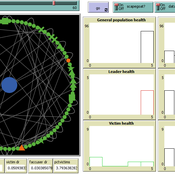
Carlos Paes | Published Thursday, August 28, 2025 | Last modified Thursday, August 28, 2025This agent-based model investigates scapegoating as a social mechanism of crisis management. Inspired by René Girard’s mimetic theory, it simulates how individual tension accumulates and spreads across a small-world network. When tension exceeds certain thresholds, leaders emerge and accuse marginalized agents, who may attempt to transfer blame to substitutes. If scapegoating occurs, collective tension decreases, but victims become isolated while leaders consolidate temporary authority. This simulation provides a conceptual and methodological framework for exploring how collective blame, crisis contagion, and leadership paradoxes emerge in complex networks. It can also be extended with empirical data, such as social media dynamics of online harassment and virtual lynching, offering potential applications for both theoretical research and practical crisis monitoring.
Sunshine or Shield?: Secret Voting Procedures and Legislative Accountability
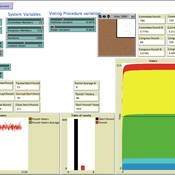
Matthew Taylor Michele Buttò Carlos Pereira | Published Tuesday, June 24, 2014 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019An agent-based model is used to simulate legislators’ behavior under secret voting rules, as influenced by the power of the accused politician, the composition of the voting body, and the publicity of the accusations.
Two agent-based models of cooperation in dynamic groups and fixed social networks
Carlos A. de Matos Fernandes | Published Thursday, January 20, 2022Both models simulate n-person prisoner dilemma in groups (left figure) where agents decide to C/D – using a stochastic threshold algorithm with reinforcement learning components. We model fixed (single group ABM) and dynamic groups (bad-barrels ABM). The purpose of the bad-barrels model is to assess the impact of information during meritocratic matching. In the bad-barrels model, we incorporated a multidimensional structure in which agents are also embedded in a social network (2-person PD). We modeled a random and homophilous network via a random spatial graph algorithm (right figure).
Displaying 10 of 23 results for "Carlo Proietti" clear search