About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 853 results for "Jes%C3%BAs M Zamarre%C3%B1o" clear search
Intra-Organizational Bandwagon
Davide Secchi | Published Sunday, October 18, 2015The model simulates the process of widespread diffusion of something due to popularity (i.e., bandwagon) within an organization.
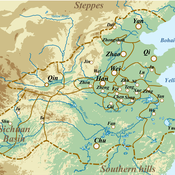
Evolutionary Dynamics of the Warring States Period: Initial Unification in Ancient China (475 BC to 221 BC)
zhuo zhang | Published Sunday, August 07, 2022If you have any questions about the model run, please send me an email and I will respond as soon as possible.
Under complex system perspectives, we build the multi-agent system to back-calculate this unification process of the Warring State period, from 32 states in 475 BC to 1 state (Qin) in 221 BC.
A modified model of breeding synchrony in colonial birds
James Millington | Published Tuesday, June 26, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This generic individual-based model of a bird colony shows how the influence neighbour’s stress levels synchronize the laying date of neighbours and also of large colonies. The model has been used to demonstrate how this form of simulation model can be recognised as being ‘event-driven’, retaining a history in the patterns produced via simulated events and interactions.
Structural Violence and Neurobiological Adaptation: Modeling the Trajectory of Youth Outside of Care
masterpiece33330-prog | Published Thursday, November 27, 2025This study presents a System Dynamics (SD) model that explores the “trajectories of homelessness” among youth outside of the formal care system. Unlike traditional approaches that view runaway behavior as a discrete choice, this model reinterprets it as a neurobiological adaptation to chronic resource deprivation and systemic neglect.
The model incorporates key mechanisms such as ‘Allostatic Load’ accumulation, ‘PFC-Amygdala Switching’, and the ‘Iatrogenic Effects’ of shelter policies. It utilizes Monte Carlo simulations to demonstrate how structural factors create a “probabilistic vulnerability,” trapping youth in cycles of survival crime and isolation regardless of individual resilience.
The uploaded code includes a Python implementation of the model to ensure reproducibility of the stochastic analysis presented in the paper.
Ant Colony Optimization for infrastructure routing
Igor Nikolic Emile Chappin P W Heijnen | Published Wednesday, March 05, 2014 | Last modified Saturday, March 24, 2018The mode implements a variant of Ant Colony Optimization to explore routing on infrastructures through a landscape with forbidden zones, connecting multiple sinks to one source.
Using Agent-Based Modelling and Reinforcement Learning to Study Hybrid Threats
kpadur | Published Friday, September 20, 2024Hybrid attacks coordinate the exploitation of vulnerabilities across domains to undermine trust in authorities and cause social unrest. Whilst such attacks have primarily been seen in active conflict zones, there is growing concern about the potential harm that can be caused by hybrid attacks more generally and a desire to discover how better to identify and react to them. In addressing such threats, it is important to be able to identify and understand an adversary’s behaviour. Game theory is the approach predominantly used in security and defence literature for this purpose. However, the underlying rationality assumption, the equilibrium concept of game theory, as well as the need to make simplifying assumptions can limit its use in the study of emerging threats. To study hybrid threats, we present a novel agent-based model in which, for the first time, agents use reinforcement learning to inform their decisions. This model allows us to investigate the behavioural strategies of threat agents with hybrid attack capabilities as well as their broader impact on the behaviours and opinions of other agents.
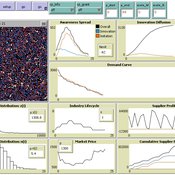
(Policy induced) Diffusion of Innovations - An integrated demand-supply Model based on Cournot Competition
Martin Rixin | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Objective is to simulate policy interventions in an integrated demand-supply model. The underlying demand function links both sides. Diffusion proceeds if interactions distribute awareness (Epidemic effect) and rivalry reduces the market price (Probit effect). Endogeneity is given due to the fact that consumer awareness as well as their willingness-to-pay drives supply-side rivalry. Firm´s entry and exit decisions as well as quantity and price settings are driven by Cournot competition.
Model of Context Switching with Segregation
Davide Nunes | Published Thursday, August 02, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013In the context switching model, a society of agents embedded in multiple social relations, engages in a simple abstract game: the consensus game. Each agent has to choose towards one of two possible choices which are basically arbitrary. The objective of the game is to reach a global consensus, but the particular choice that gets collectively selected is irrelevant.
Stoplight parrotfish population model
Tyler Pavlowich | Published Monday, April 02, 2018This agent-based model simulates a stoplight parrotfish population in a heavily-fished Caribbean coral reef. The model allows for the simulation of various fishing regulations and observation of population and catch outcomes. It was built using the structure and equations from several previously published models, including the work of Bozec et al. (2016) and Alonzo and Mangel (2004 and 2005). The initial model conditions are parameterized to population and fishing data collected in Buen Hombre, Dominican Republic by Tyler Pavlowich.
Gini Palma microsimulation
Edgar Oliveira | Published Wednesday, December 11, 2024The model is a microsimulation, where the agents don’t Interact with each other. It simulates income distribution, unemployment dynamics, education, and Family grant in Brazil, focusing on the impact on social inequality. It tracks the indicators Gini index, Lorenz curve, and Palma ratio. The objective is to explore how these factors influence wealth distribution and social inequality over time.
This work was developed in partnership with the Graduate Program in Computational Modeling, in the Universidade Federal do Rio Grande - FURG, in Brazil.
Displaying 10 of 853 results for "Jes%C3%BAs M Zamarre%C3%B1o" clear search